Tissues – Complete Guide For Class 9 Science Chapter 6
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, Tissues Class 9th chapter 5 are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
The concept of “Tissues” in Class 9 explores the basic building blocks of all living organisms, delving into how cells group together to form complex structures with specialized functions. This chapter elucidates how tissues are not just isolated entities but integral components that collaborate to sustain life. By examining the diverse types of tissues in plants and animals-ranging from the protective epithelial layers and supportive connective tissues in animals to the water-transporting xylem and nutrient-conducting phloem in plants, students gain a deeper appreciation of how these building blocks contribute to the organism’s overall functionality.
Understanding tissues is pivotal for grasping how different parts of an organism work in harmony, which is essential for studying everything from cellular processes to ecological interactions. This foundational knowledge lays the groundwork for more advanced studies in biology, highlighting the intricate organization and interdependence of life at the tissue level.
What Are Tissues?
In biological terms, tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform a specific function. Each tissue type has a unique structure and role within an organism, contributing to the overall health and functionality of the living being.
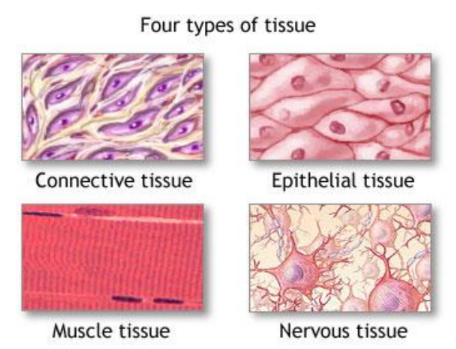
Types of Tissues in Animals
Animal tissues are classified into four main types:
- Epithelial Tissue: This tissue covers the body surfaces and lines cavities and organs. It acts as a protective barrier and is involved in absorption, secretion, and sensation.
- Connective Tissue: Connective tissues support, bind together, and protect tissues and organs. Examples include bone, blood, and adipose (fat) tissue.
- Muscle Tissue: Muscle tissue is responsible for movement. It is divided into three types:
- Skeletal Muscle: Voluntary muscles attached to bones.
- Cardiac Muscle: Involuntary muscle found in the heart.
- Smooth Muscle: Involuntary muscle found in internal organs.
- Nervous Tissue: Nervous tissue is involved in receiving stimuli and transmitting electrical impulses. It consists of neurons and supporting cells.
Types of Tissues in Plants
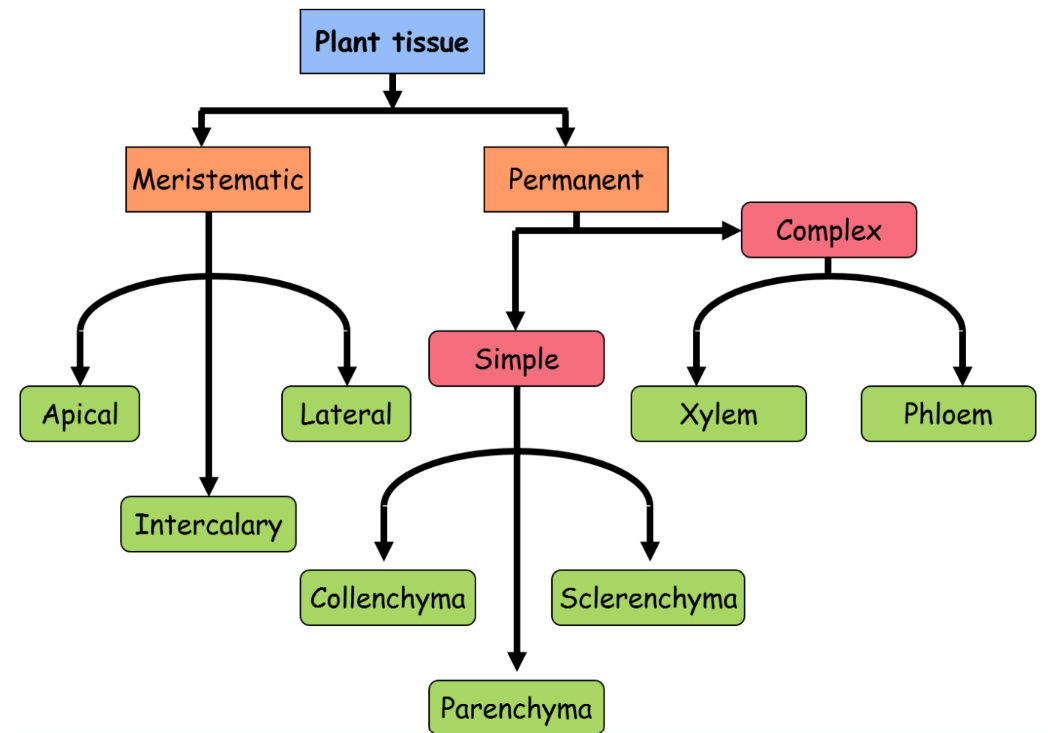
Plant tissues are categorized into two main types:
- Simple Tissue: Composed of a single type of cell, simple tissues include:
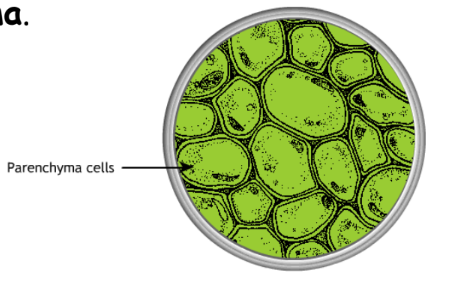
- Parenchyma: Involved in photosynthesis and storage.
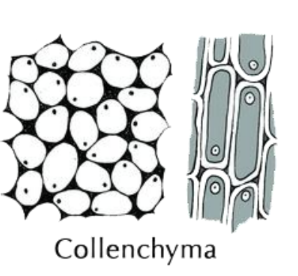
- Collenchyma: Provides structural support.
- Sclerenchyma: Offers rigidity and strength.
- Complex Tissue: Made up of more than one type of cell, complex tissues include:
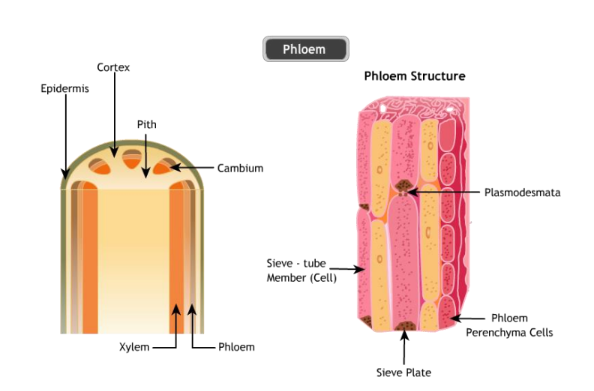
- Xylem: Responsible for water and mineral transport.
- Phloem: Transports nutrients and food throughout the plant.
The Role of Tissues in Organisms
Tissues are essential for the proper functioning of both plant and animal organisms. They work together to maintain homeostasis, perform specialized functions, and ensure survival. Understanding tissues helps us appreciate the complexity of life and the intricacies of how living organisms are structured and function.
In summary, our exploration of “Tissues” in Class 9 Science Chapter 6 has provided a comprehensive overview of the fundamental building blocks of life. The study of tissues—whether it be the epithelial layers, connective tissues, muscle tissues, nervous tissues in animals, or the xylem and phloem in plants—reveals the intricate and essential roles these structures play in sustaining life. Understanding how tissues function and collaborate within organisms enhances our grasp of biological processes and the complex interplay between different tissue types.
This chapter serves as a critical foundation for further studies in biology, offering insights into how cells form specialized structures that perform vital functions. By mastering the concepts in “Tissues,” students can better appreciate the dynamic nature of living organisms and their various systems. Whether you are preparing for exams or seeking to deepen your knowledge, our resources are designed to support and enhance your learning journey. Dive into Class 9 Science Chapter 6 – Tissues with confidence and curiosity, knowing that each type of tissue is a crucial piece of the larger puzzle of life.
Practice questions on Chapter 6 - Tissues
Get your free Chapter 6 - Tissues practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








