Food Security in India – Complete Guide For Class 9 Economics Chapter 4

Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, “Food Security in India” in Economics for Class 9th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
The chapter “Food Security in India” delves into the critical issue of ensuring that all citizens have access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food. It explores the concept of food security, its importance, and the various measures taken by the Indian government to address food insecurity. The chapter also discusses the Public Distribution System (PDS), buffer stock, and the role of cooperatives in enhancing food security across the nation.
“Food Security in India” is a vital chapter that addresses one of the most pressing concerns in the country: ensuring that everyone has access to adequate food. The chapter provides an in-depth understanding of what food security means, and why it is essential and uses real-life examples like the story of Ramu.
It also highlights the measures taken by the government, such as the creation of buffer stocks, the implementation of the Public Distribution System (PDS), and the introduction of schemes like the Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY). Furthermore, the chapter emphasizes the role of cooperatives in securing food for all, particularly in rural areas. By understanding the key aspects of food security, we can appreciate the challenges and efforts involved in ensuring that no one goes hungry in India.
Objectives of the Chapter
Now that we have analyzed the significance of the chapter, let us know the objectives of studying ‘Food Security in India’
- To understand the concept and importance of food security.
- To identify the factors that lead to food insecurity in India.
- To learn about the measures taken by the government, such as buffer stock and the Public Distribution System (PDS).
- To explore the role of cooperatives in enhancing food security.
- To recognize the current status and challenges of the Public Distribution System (PDS) in India.
Now let’s discuss the various sections of the chapter in detail.
In the first place, in order to understand the concept and importance of food security, let’s delve into the “What is Food Security?” section of the chapter “Food Security in India.”
What is Food Security?
- Food security refers to the availability, accessibility, and affordability of food to all people at all times.
- It ensures that all individuals have access to the food they need for an active and healthy life.
- Food security encompasses the entire food system, from production and distribution to consumption, and aims to prevent hunger and malnutrition.

Now, to understand the reasons behind the need for reliable access to food, let’s examine the “Why Food Security?” section of the chapter “Food Security in India.”
Why Food Security?
- Food security is essential because it ensures the well-being of individuals and the overall stability of a nation.
- Without food security, people face hunger, malnutrition, and related health issues.
- In addition, food insecurity can lead to social unrest, and economic instability, and hinder the development of a country.
- Therefore, ensuring food security is a top priority for any government.
Now, to understand who faces challenges in accessing adequate food, let’s delve into the “Who are Food-Insecure?” section of the chapter “Food Security in India.”
Who Are Food-Insecure?
- Food insecurity affects millions of people in India, particularly those living below the poverty line, landless laborers, and marginalized communities.
- These individuals often do not have the means to secure enough food for themselves and their families.
- The story of Ramu, a poor landless laborer, illustrates the harsh realities faced by food-insecure individuals.
- Ramu’s struggles highlight the importance of food security measures to ensure that even the most vulnerable have access to food.
Now, in order to understand how India ensures food availability for its population, let’s delve into the “Food Security in India” section of the chapter “Food Security in India.”
Food Security in India
- Food security in India is a major concern due to the large population and the socio-economic disparities across the country.
- The government has implemented several measures to address food insecurity, including the establishment of buffer stocks and the Public Distribution System (PDS).
- These initiatives aim to ensure that food is available to everyone, especially during times of crisis, such as droughts or economic downturns.
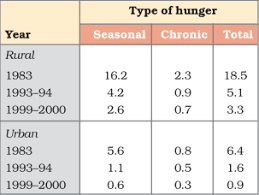
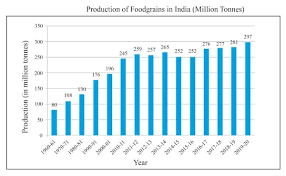
Now, to understand the role of food reserves in ensuring food security, let’s delve into the “What is Buffer Stock?” section of the chapter “Food Security in India.”
What is Buffer Stock?
- Buffer stock refers to the reserve of food grains, such as wheat and rice, maintained by the government to ensure food security during emergencies.
- The Food Corporation of India (FCI) is responsible for procuring and storing these grains.
- The buffer stock helps stabilize prices, prevent food shortages, and provide food to the needy during crises.
Now, in order to understand the functioning and significance of food distribution in India, let’s delve into the “What is the Public Distribution System?” section of the chapter “Food Security in India.”
What is the Public Distribution System?
- The Public Distribution System (PDS) is a government program that distributes food grains to the poor at subsidized prices.
- The PDS is operated through a network of fair-price shops, which provide essential commodities like rice, wheat, sugar, and kerosene to eligible families.
- The PDS plays a crucial role in ensuring food security for the poor and vulnerable sections of society.
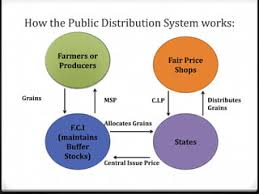
Now, to understand the effectiveness and challenges of food distribution in India, let’s delve into the “Current Status of the Public Distribution System” section of the chapter “Food Security in India.”
Current Status of the Public Distribution System
- The Public Distribution System (PDS) in India has faced several challenges, including leakages, inefficiencies, and corruption.
- However, reforms such as the introduction of the Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY) have improved the system’s reach and effectiveness.
- The AAY targets the poorest of the poor, providing them with highly subsidized food grains.
- Despite these improvements, the PDS still requires further reforms to ensure that it reaches all those in need.
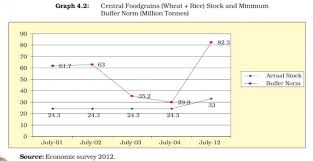
Now, to understand the role of cooperatives in food security, let’s delve into the “Role of Cooperatives in Food Security” section of the chapter “Food Security in India.”
Role of Cooperatives in Food Security
- Cooperatives play a significant role in enhancing food security in India, particularly in rural areas.
- These organizations help in the procurement, storage, and distribution of food grains, ensuring that even the most remote communities have access to essential commodities.
- Cooperatives also provide farmers with better access to markets, fair prices for their produce, and support in times of crisis.
Finally, as we have gained comprehensive knowledge about the chapter “Food Security in India”, let’s reflect on the overall learning value of this important lesson.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter
In conclusion, the chapter “Food Security in India” highlights the importance of ensuring that all citizens have access to adequate food. Through various measures like buffer stocks, the Public Distribution System (PDS), and the role of cooperatives, the Indian government aims to tackle food insecurity and provide for the most vulnerable sections of society. While significant progress has been made, challenges remain, and continuous efforts are needed to improve food security for all. The chapter emphasizes that food security is not just about providing food but ensuring a sustainable, equitable, and efficient system that benefits everyone.
Let’s Conclude
In summary, the chapter “Food Security in India” in CBSE Class 9th Economics offers students a deep understanding of the essential steps and strategies needed to ensure food accessibility and affordability for every citizen. By exploring topics like buffer stock, the Public Distribution System (PDS), and the contributions of cooperatives, “Food Security in India” provides a comprehensive look at the Indian government’s efforts to reduce hunger and malnutrition.
This chapter not only informs students about the challenges of food security but also highlights the progress made toward equitable food distribution across the nation. As we conclude our study on “Food Security in India,” it is evident that achieving food security for all is critical for a stable and healthy society. This chapter serves as an important lesson in understanding how interconnected systems, policies, and community efforts contribute to a robust framework for addressing food insecurity in India.
Practice questions on Chapter 4 - Food Security in India
Get your free Chapter 4 - Food Security in India practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








