Poverty as a Challenge – Complete Guide For Class 9 Economics Chapter 3

Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, “Poverty as a Challenge” in Economics for Class 9th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
This chapter explores the multifaceted issue of poverty, examining its various dimensions, causes, and potential solutions. It examines different perspectives on poverty, including social exclusion and vulnerability, and delves into the challenges faced by individuals and communities living in poverty.
Poverty is a complex and pervasive issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It is not merely a lack of material resources but also a condition characterized by social exclusion, vulnerability, and limited opportunities. The chapter ‘Poverty as a Challenge’ will delve into the various dimensions of poverty, explore its causes, and examine the efforts being made to address this pressing global challenge.
Objectives Of Learning The Chapter – Poverty as a Challenge
Now that we have analyzed the significance of the chapter, let’s now understand the objectives of studying ‘Poverty as a Challenge’
- Understand the different dimensions of poverty
- Analyze the causes of poverty
- Explore the challenges faced by people living in poverty
- Examine the efforts being made to address poverty
- Appreciate the complexities and interlinked nature of poverty
Now let’s discuss the various sections of the chapter in detail.
First of all, in order to understand the real-life implications of poverty, let’s delve into the section “Two Typical Cases of Poverty” of the chapter “Poverty as a Challenge.”
Two Typical Cases of Poverty
Now, to understand the reality of poverty, let’s examine two typical cases.
Case 1: Lakha Singh
Lakha Singh is a farmer from a rural village, struggling to make ends meet due to low crop yields and rising costs.- Despite his hard work, the lack of adequate irrigation, high costs of seeds and fertilizers, and fluctuating market prices have left him in a cycle of debt.
- His family often goes without necessities, highlighting the harsh realities faced by many rural poor.

Case 2: Ram Saran
Ram Saran is an urban slum dweller facing challenges related to the lack of access to basic amenities and employment opportunities.- Living in overcrowded conditions, with limited access to clean water, sanitation, and healthcare, he struggles to find stable work.
- The lack of job security and low wages in the informal sector makes it difficult for him to support his family, illustrating the struggles of the urban poor.

These cases illustrate the diverse experiences of people living in poverty and the various factors that contribute to their situation.
Now, to understand the different perspectives on poverty, let’s delve into the section “Poverty as Seen by Social Scientists” of the chapter “Poverty as a Challenge.”
Poverty as Seen by Social Scientists
Social scientists have identified several key dimensions of poverty:
- Social exclusion:
Poverty can lead to social isolation and marginalization, limiting access to opportunities and resources.
- Vulnerability:
People living in poverty are often more vulnerable to shocks, such as illness, natural disasters, or economic downturns.
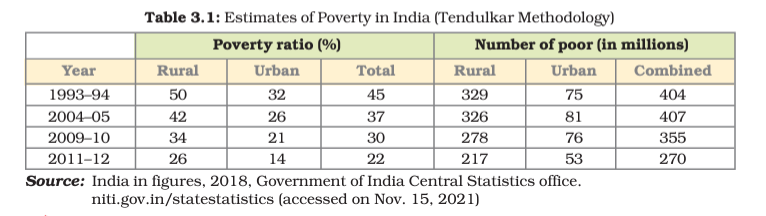
In order to understand how poverty is measured and quantified, let’s delve into the section “Poverty Line” of the chapter “Poverty as a Challenge.”
Poverty Line
To measure poverty, governments and organizations use poverty lines.
- Poverty Estimates:
Poverty lines vary across countries and regions, reflecting differences in living standards.
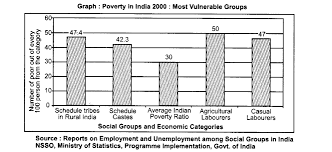
- Vulnerable Groups:
Certain groups, such as children, women, and minorities, are particularly vulnerable to poverty.
- Story of Sivaraman:
Sivaraman’s case highlights the challenges faced by those living below the poverty line.

Now, to understand the regional differences in poverty, let’s delve into the section “Inter-State Disparities” of the chapter “Poverty as a Challenge.”
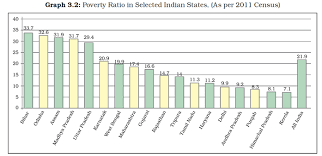
Inter-State Disparities
Poverty is not evenly distributed within countries.
- Regional Differences:
Some regions have higher poverty rates than others.
- Urban-Rural Divide:
Poverty is often more prevalent in rural areas compared to urban centers.
Now, to understand poverty on a global scale, let’s delve into the section “Global Poverty Scenario” of the chapter “Poverty as a Challenge.”
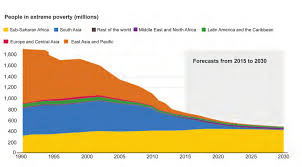
Global Poverty Scenario
Poverty is a global challenge, with significant disparities between countries.
- Developing Countries:
Developing countries generally have higher poverty rates than developed countries.
- Inequality:
Poverty is often accompanied by significant income inequality.
Now, to understand the underlying reasons for poverty, let’s delve into the section “Causes of Poverty” of the chapter “Poverty as a Challenge.”
Causes of Poverty
Poverty is a complex issue with multiple causes, including:
- Economic Factors:
Lack of economic opportunities, unemployment, and low wages.
- Social Factors:
Discrimination, social exclusion, and lack of access to education and healthcare.
- Political Factors:
Corruption, governance failures, and conflict.
- Environmental Factors:
Natural disasters, climate change, and resource scarcity.
Now, to understand the strategies to combat poverty, let’s delve into the section “Anti-Poverty Measures” of the chapter “Poverty as a Challenge.”
Anti-Poverty Measures
Governments and organizations have implemented various anti-poverty measures:
- Social Safety Nets:
Programs like food stamps, welfare, and housing assistance.
- Education and Training:
Investing in education and skills development.
- Healthcare Access:
Ensuring access to affordable healthcare.
- Infrastructure Development:
Improving infrastructure in poverty-stricken areas.
- Sustainable Development:
Promoting sustainable economic growth and environmental protection.
Now, in order to understand the future obstacles in addressing poverty, let’s delve into the section “The Challenges Ahead” of the chapter “Poverty as a Challenge.”
The Challenges Ahead
Addressing poverty requires a comprehensive and multi-faceted approach.
- Global Cooperation: International cooperation is essential to tackle global poverty.
- Sustainable Development Goals: The Sustainable Development Goals provide a framework for addressing poverty and other global challenges.
- Inclusive Growth: Ensuring that economic growth benefits everyone, not just the wealthy.
Finally, as we have gained comprehensive knowledge about the chapter “Poverty as a Challenge”, let’s reflect on the overall learning value of this important lesson.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter
The chapter “Poverty as a Challenge” provides a comprehensive understanding of poverty as a multifaceted issue affecting millions globally. By exploring real-life cases, examining poverty from a social scientist’s perspective, and analyzing data through the poverty line, students gain insight into the depth and complexity of this social issue. The chapter highlights regional and global disparities, delves into the root causes of poverty, and discusses both past and current measures taken to alleviate it. It also outlines the ongoing challenges in combating poverty, emphasizing the need for continued efforts and innovative solutions. Overall, this chapter equips students with the knowledge to understand poverty’s impact on society and the importance of addressing it for sustainable development.
Let’s Conclude
In conclusion, CBSE Class 9th Economics Chapter “Poverty as a Challenge” provides students with a deep understanding of poverty as a critical social issue. By examining case studies, understanding various dimensions like social exclusion and vulnerability, and exploring different causes, students learn about the realities faced by millions worldwide. The chapter “Poverty as a Challenge” offers insights into poverty at both national and global levels, emphasizing the disparities and root causes that contribute to this complex issue.
With strategies like anti-poverty measures and sustainable development initiatives, students gain a broader perspective on how society can work towards alleviating poverty. Through the lens of CBSE Class 9th Economics Chapter “Poverty as a Challenge,” learners are encouraged to reflect on the importance of inclusive growth and global cooperation to create a future where everyone has equal opportunities to thrive.
Practice questions on Chapter 3 - Poverty as a Challenge
Get your free Chapter 3 - Poverty as a Challenge practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








