Climate – Complete Guide For Class 11 Geography Unit 2 Chapter 4
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, “Climate” in Geography for Class 11th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
With iPrep’s comprehensive resources for CBSE Class 11th Geography Chapter “Climate,” students can dive into the intriguing dynamics of weather and climate across India. The chapter “Climate” is designed to deepen your understanding of complex concepts, from monsoon patterns to seasonal variations, in an engaging and accessible way. With our tools, Class 11th students can build a strong foundation in Geography, making learning both enjoyable and effective.
Objectives Of Learning The Chapter – Climate
This chapter explores the diverse climate of India, focusing on the factors that influence its weather patterns and the impact of the monsoon on the country’s geography, economy, and society.
India’s climate is characterized by its unique monsoon system, which brings significant rainfall to the country during the summer months. This chapter delves into the factors that determine India’s climate, the nature of the monsoon, and the impact of climate change on the country’s weather patterns.
Now that we have explored the importance of the chapter, let’s outline the objectives of studying it.
- To understand the factors that influence India’s climate.
- To explore the nature and characteristics of the Indian monsoon.
- To analyze the seasonal variations in India’s weather patterns.
- To assess the impact of climate change on India’s climate.
Now let’s explore the various sections of the chapter.
Firstly, in order to understand the unity and diversity in India’s monsoon climate, let’s explore this introductory section of the chapter “Climate”.
Unity and Diversity in the Monsoon Climate
- Despite its vast geographical extent, India experiences a relatively unified climate due to the influence of the monsoon.
- However, there is also significant regional variation in climate, depending on factors such as latitude, altitude, and proximity to the sea.
Now, to grasp the factors influencing India’s climate, let’s explore the Factors Determining the Climate of India section of the chapter “Climate.”
Factors Determining the Climate of India
Several factors contribute to India’s unique climate.
- Latitude:
India’s location between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn influences its tropical climate.
- The Himalayan Mountains:
The Himalayas act as a barrier, preventing cold air from entering India from the north.
- Distribution of Land and Water:
The distribution of land and water in India affects its climate, with coastal areas experiencing a more moderate climate than inland regions.
- Distance from the Sea:
Proximity to the sea influences temperature and rainfall patterns.
- Altitude:
Higher altitudes experience cooler temperatures and lower precipitation levels.
- Relief:
The topography of India, including its mountain ranges and plains, affects wind patterns and rainfall distribution.
- InterTropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ):
The ITCZ is a belt of low pressure that migrates north and south throughout the year, influencing India’s monsoon.
Now, in order to understand the nature of the Indian monsoon, let’s explore this section in the chapter “Climate”.
The Nature of the Indian Monsoon
The Indian monsoon is a unique meteorological phenomenon that brings significant rainfall to India during the summer months.
- (i) The onset of the monsoon: The monsoon typically begins in early June and progresses northward.
- (ii) Break in the monsoon: There are often periods of dry weather during the monsoon season, known as “breaks.”

Now, in order to understand India’s seasonal climate, let’s delve into the Rhythm of Seasons section of the chapter “Climate”.
The Rhythm of Seasons
India experiences four distinct seasons: the cold weather season, the hot weather season, the southwest monsoon season, and the retreating monsoon season.
- The cold weather season:
This season is characterized by cool temperatures, clear skies, and gentle winds. It occurs from November to February in most parts of India.
- The hot weather season:
This season is marked by high temperatures, dry conditions, and occasional heatwaves. It occurs from March to May in most parts of India.
- The southwest monsoon season:
This is the rainy season in India, brought about by the southwest monsoon winds. It occurs from June to September, with the heaviest rainfall occurring in central and northern India.
- The retreating monsoon season:
This season marks the gradual withdrawal of the monsoon winds, leading to a decrease in rainfall and a rise in temperatures. It occurs from October to November.
EI-Nino and the Indian Monsoon
The El Niño phenomenon can influence the strength and timing of the Indian monsoon.
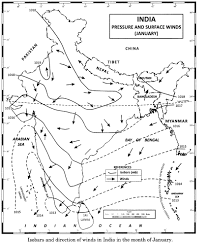
Now, in order to understand India’s traditional seasons, let’s explore the Traditional Indian Seasons section of the chapter “Climate”.
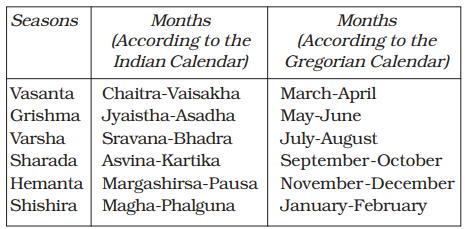
Traditional Indian Seasons
In the Indian tradition, a year is divided into six two-monthly seasons.
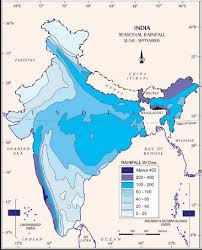
Now, in order to understand how rainfall is distributed across India, let’s explore the Distribution of Rainfall section of the chapter “Climate”.
Distribution of Rainfall
- Overall, India experiences a wide range of rainfall patterns, with the highest rainfall occurring in the Western Ghats and northeastern regions, while the lowest rainfall is found in the western and southern parts of the country.
Now, in order to understand the impact of monsoons on economic life in India, let’s delve into this section of the chapter “Climate”.
Monsoons and the Economic Life in India
- The monsoon is crucial for India’s agriculture, as it provides essential water for crops.
- However, variations in monsoon rainfall can lead to droughts, floods, and other challenges for agriculture.
Now, in order to understand the effects of global warming on India’s climate, let’s explore this section in the chapter “Climate”.
Global Warming
- Global warming is caused by human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere.
- This warming is leading to rising sea levels, changes in agricultural patterns, and increased risk of natural disasters.
Finally, as we have gained comprehensive knowledge about the chapter “Climate“, let’s reflect on the overall learning value of this important lesson.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter:
India’s climate is characterized by its unique monsoon system and diverse regional variations. Understanding the factors that influence India’s climate is essential for effective planning and adaptation to climate change. The monsoon plays a crucial role in India’s economy and society, and its variability can have significant implications for agriculture, water resources, and human well-being.
Let’s Conclude
In conclusion, the chapter “Climate” in CBSE Class 11th Geography has offered us an in-depth understanding of India’s unique climate and the numerous factors that shape it. From exploring the diversity in monsoon patterns to understanding the implications of global warming, this chapter equips Class 11th students with essential knowledge on how climate impacts both the geography and economy of India. The “Climate” chapter not only explains the distinct seasonal cycles but also highlights how regional variations influence rainfall distribution and agricultural productivity. By mastering these concepts in Class 11th Geography, students are better prepared to appreciate the vital role of climate in shaping India’s natural and economic landscape.
Practice questions on Chapter 4 - Climate
Get your free Chapter 4 - Climate practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








