Natural Hazards and Disasters – Complete Guide for Class 11 Geography Unit 2 Chapter 6
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, “Natural Hazards and Disasters” in Geography for Class 11th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
Understanding natural hazards is not just an academic exercise; it is essential for the safety and resilience of communities. By exploring the causes and impacts of these disasters, students will develop a critical awareness of the vulnerabilities that exist within their environments. This knowledge empowers learners to contribute to disaster preparedness and response efforts, making them more informed and proactive citizens.
Objectives Of Learning The Chapter – Natural Hazards and Disasters
This chapter “Natural Hazards and Disasters” explores the various natural hazards and disasters that affect India, including earthquakes, tsunamis, floods, droughts, and landslides. It examines the causes, consequences, and mitigation strategies for these disasters, highlighting their significant impact on India’s society and economy.
India is prone to a variety of natural hazards, ranging from earthquakes and tsunamis to floods and droughts. These disasters can have devastating consequences for communities, infrastructure, and the environment. This chapter provides a comprehensive overview of the different types of natural hazards in India, their causes, impacts, and mitigation measures.
Now that we have explored the importance of the chapter, let’s outline the objectives of studying it.
- To understand the different types of natural hazards that affect India.
- To explore the causes and consequences of these hazards.
- To analyze the vulnerability of different regions in India to natural disasters.
- To examine the strategies for disaster management and mitigation.
Now let’s explore the various sections of the chapter.
Firstly, in order to understand the key concepts, let’s delve into the ‘Introductory Section’ of the chapter ‘Natural Hazards and Disasters’.
Introduction:
- Natural disasters, caused by both natural forces and human activities, have increased in frequency and severity.
- While efforts are being made to mitigate the impact of natural disasters, the increasing vulnerability of human settlements and the changing climate pose significant challenges.
- International cooperation is essential to address the global consequences of natural disasters.
Now, in order to understand the different types of natural disasters, let’s delve into the classification of natural disasters in this chapter “Natural Hazards and Disasters”.
Classification of Natural Disasters
Natural disasters can be classified based on their origin and characteristics.
- Geophysical Disasters: These include earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and landslides.
- Hydrological Disasters: Floods and tsunamis fall under this category.
- Meteorological Disasters: Events such as tropical cyclones and droughts are classified here.
- Biological Disasters: Epidemics and pandemics are examples of biological disasters.
Now, to understand the impact of these disasters in India, let’s explore the section on natural disasters and hazards in the chapter “Natural Hazards and Disasters”.
Natural Hazards and Disasters in India
- India’s geographical diversity makes it susceptible to a range of natural disasters, including earthquakes, tsunamis, tropical cyclones, floods, droughts, and landslides.
- This vulnerability is exacerbated by factors such as high population density, poverty, and inadequate infrastructure. The country’s long coastline, mountainous regions, and diverse climatic zones all contribute to its exposure to these natural hazards.
Now, in order to understand earthquakes and their impact, let’s delve into the section on earthquakes in the chapter.
Earthquakes
Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of energy stored in the Earth’s crust.
The key topics covered under this section are discussed below:
- Socio-Environmental Consequences of Earthquakes
Earthquakes can have devastating consequences, including loss of life, property damage, and infrastructure disruption.
- Effects of Earthquakes
The effects of earthquakes can vary depending on factors such as magnitude, location, and the vulnerability of the affected area.
- Earthquake Hazard Mitigation
Measures can be taken to mitigate the impact of earthquakes, such as building codes, early warning systems, and emergency preparedness plans.

Now, to understand tsunamis, let’s explore the section on tsunamis in the chapter “Natural Hazards and Disasters”.
Tsunami
Tsunamis are large-scale ocean waves caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions.
Causes of Tsunami:
- Undersea earthquakes.
- Volcanic eruptions.
- Landslides into the ocean.
Consequences of Tsunami:
- Widespread flooding.
- Destruction of coastal communities.
- Loss of life and ecosystems.

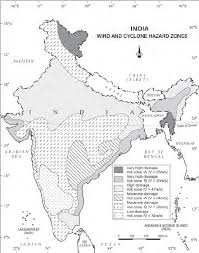
Now, to understand tropical cyclones, let’s delve into the section on tropical cyclones in the chapter “Natural Hazards and Disasters”.
Tropical Cyclone
- Tropical cyclones are intense low-pressure systems that form over warm ocean waters.
- They require specific conditions, including warm, moist air, strong Coriolis force, unstable atmospheric conditions, and the absence of strong vertical winds, to develop and intensify.
The key topics covered under this section are:
Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Tropical Cyclones in India:
- Most occur in the Bay of Bengal.
- Cyclones are common during pre-monsoon (May-June) and post-monsoon (October-November) periods.
Consequences of Tropical Cyclones:
- Strong winds causing structural damage.
- Heavy rainfall leading to floods.
- Storm surges causing coastal erosion.

Now, to grasp the effects of floods and their implications, let’s explore the section on floods in the chapter “Natural Hazards and Disasters”.
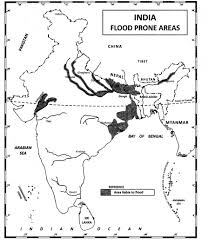
Floods
Floods occur when excessive rainfall or other factors lead to overflowing rivers or lakes.
Causes of Floods:
- Excessive rainfall.
- River overflow.
- Dam failure.
Consequence and Control of Floods:
- Damage to property and infrastructure.
- Spread of water-borne diseases.
- Flood control measures include dams, levees, and proper drainage systems.
Now, to understand droughts and their effects, let’s explore the section on droughts in the chapter “Natural Hazards and Disasters”.
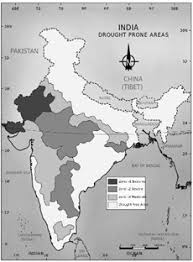
Droughts
Droughts occur when there is a prolonged period of below-average rainfall.
The key topics that are included in this section are:
Types of Droughts
- Meteorological drought (low precipitation).
- Agricultural drought (soil moisture deficiency).
- Hydrological drought (reduced water supply).
Drought Prone Areas in India:
- Rajasthan, Gujarat, and parts of Maharashtra.
Consequences of Drought:
- Crop failure and food shortages.
- Water scarcity.
- Migration and social unrest.
Now, to understand landslides and their impact, let’s delve into the section on landslides in the chapter ‘Natural Hazards and Disasters’.
Landslides
Landslides occur when soil or rock masses move downslope. The important topics under this section are:
Landslide Vulnerability Zones:
- Himalayan region.
- Western Ghats.
- Northeastern India.
Consequences of Landslides:
- Loss of life and property.
- Disruption of transportation networks.
- Environmental degradation.
Mitigation:
- Afforestation and slope stabilization.
- Construction of retaining walls.
- Early warning systems.

Now, in order to understand how to manage natural disasters, let’s explore the section on disaster management in the chapter “Natural Hazards and Disasters”.
Disaster Management
- Effective disaster management involves preparedness, response, recovery, and mitigation.
- This includes the development of early warning systems, public education, and the establishment of disaster response teams.
Finally, as we have gained comprehensive knowledge about the chapter “Natural Hazards and Disasters“, let’s reflect on the overall learning value of this important lesson.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter:
India is vulnerable to a variety of natural hazards, which can have significant consequences for its population and economy. Understanding the causes, impacts, and mitigation strategies for these hazards is essential for building resilience and protecting communities.
Let’s Conclude
In conclusion, the chapter “Natural Hazards and Disasters” in Class 11 Geography provides an in-depth exploration of the various natural hazards that affect India. By studying this chapter, students gain valuable insights into the causes and consequences of disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, floods, droughts, and landslides. The chapter emphasizes the need for effective disaster management and mitigation strategies to minimize the impact of these hazards on society and the economy.
Through the comprehensive resources available on iPrep, including engaging animated videos and practice questions, learners can solidify their understanding of these crucial concepts. As we navigate the complexities of natural hazards and their ramifications, it’s imperative to foster awareness and preparedness. By doing so, we not only enhance our knowledge but also contribute to building resilient communities capable of withstanding the challenges posed by natural disasters.
Remember, the lessons learned in this chapter “Natural Hazards and Disasters” are vital not only for academic success in Class 11 Geography but also for fostering a deeper understanding of the world around us. Embrace the learning journey, and let’s ensure that the knowledge gained equips us for the future!
Practice questions on Chapter 6 - Natural Hazards and Disasters
Get your free Chapter 6 - Natural Hazards and Disasters practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








