Federalism – Complete Guide For Class 11 Political Science Chapter 7
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, “Federalism” in Political Science for Class 11th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
Federalism is more than just a system of governance; it’s the backbone of how large and diverse countries maintain both unity and regional autonomy. In Class 11th Political Science Chapter 7 – Federalism, you’ll explore how power is shared between different levels of government and why this balance is crucial for the smooth functioning of a democratic nation. From understanding the different types of federations to analyzing the unique features of Indian federalism, this chapter offers valuable insights into one of the most important political structures in the world. Let’s dive into the dynamics of Federalism and uncover the reasons behind its significance.
Federalism

This chapter delves into the concept of federalism, examining its key features, the types of federations, and how federalism operates within the Indian context. It discusses the distribution of powers between the Union and State governments, the challenges faced by federal systems, and the unique features of federalism in India. The chapter also touches upon federalism in other countries like West Indies and Nigeria and discusses the specific provisions for states like Jammu and Kashmir.
Federalism is a system of governance in which power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units, typically states or provinces. This chapter explores the essence of federalism, its necessity, and how it is implemented in different countries, particularly focusing on the Indian model of federalism. The chapter also highlights the challenges of maintaining a federal structure in a diverse country like India and the measures taken to address these challenges.
Objectives of the Chapter
Now that we have explored the importance of the chapter, let’s outline the objectives of studying it.
- Understand the concept and features of federalism.
- Explore the various types of federations and their significance.
- Analyze the distribution of powers between different levels of government.
- Examine the unique aspects of Indian federalism.
- Understand the challenges and conflicts in India’s federal structure.
- Study the special provisions in the Indian federal system.
Now let’s explore the various sections of the chapter.
Now, to understand the basic concept of federalism, let’s delve into the section “Introduction to Federalism” of the chapter “Federalism.”
Introduction to Federalism
- Federalism is a system of government where power is divided between a central government and constituent units.
- It is a mechanism for balancing the need for national unity with the desire for regional autonomy.
- Federalism is often associated with large, diverse countries, as it allows for the recognition of regional differences and the effective governance of vast territories.
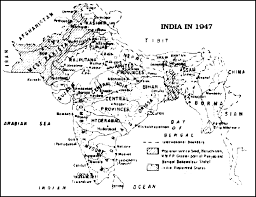
To grasp the definition and significance of federalism, let’s explore the section titled “What is Federalism?” in the chapter “Federalism.”
What is Federalism?
- Federalism is a system of government where power is divided between a central government and constituent units.
- It is a mechanism for balancing the need for national unity with the desire for regional autonomy.
- Federalism is often associated with large, diverse countries, as it allows for the recognition of regional differences and the effective governance of vast territories.
Key Features of Federalism
- Two or More Levels of Government: A federal system has two or more levels of government, such as a central government and state governments.
- Distribution of Powers: The powers of government are divided between the central and state governments.
- Supremacy of the Constitution: The Constitution is the supreme law of the land, and it outlines the powers and responsibilities of the central and state governments.
- Independent Judiciary: An independent judiciary is essential for interpreting the Constitution and resolving disputes between the central and state governments.
- Bicameralism: Many federal systems have a bicameral legislature, consisting of two houses that represent different levels of government.
Federalism in Other Countries
- Federalism in West Indies: The West Indies Federation was a short-lived federation of British colonies in the Caribbean. It was established in 1958 but dissolved in 1962 due to internal divisions and economic difficulties.
- Federalism in Nigeria: Nigeria is a federal republic with a central government and 36 states. The federal government has significant powers, but the states also have autonomy in certain areas.
Now, to comprehend the distinct characteristics of Indian federalism, let’s explore the section titled “Federalism in the Indian Context” in the chapter “Federalism.”
Federalism in the Indian Context
- India is a federal republic with a central government of 28 states and 8 union territories.
- The Indian Constitution establishes a federal system, but it also grants significant powers to the central government.
Division of Powers
The Indian Constitution divides powers between the central government and the state governments through a system of lists:
- Union List: This list contains subjects that are exclusively within the purview of the central government, such as defense, foreign affairs, and communications.
- State List: This list contains subjects that are exclusively within the purview of the state governments, such as agriculture, public health, and local government.
- Concurrent List: This list contains subjects that can be legislated upon by both the central and state governments.
Federalism with a Strong Central Government
- While India is a federal system, the central government has significant powers.
- This is due to various factors, including the need for national unity, the diversity of the country, and the historical context of Indian independence.
Now, to gain insight into the conflicts within India’s federal structure, let’s examine the section titled “Conflicts in India’s Federal System” in the chapter “Federalism.”
Conflicts in India’s Federal System
- Centre-State Relations
The relationship between the central government and the states has been marked by periods of cooperation and conflict. The central government has often asserted its dominance, while the states have demanded greater autonomy.
- Demands for Autonomy
Several states, particularly in the northeast and south, have demanded greater autonomy or even secession. These demands have been fueled by factors such as regional disparities, cultural differences, and historical grievances.
- Role of Governors and President’s Rule
Governors, appointed by the central government, play a crucial role in the federal system. They can impose President’s Rule in a state if the state government fails to function according to the Constitution. This has often led to conflicts between the central government and the state governments.
- Demands for New States
Several states have demanded the creation of new states based on linguistic or regional grounds. This has led to political agitations and, in some cases, the formation of new states.
- Interstate Conflicts
Conflicts can also arise between different states, particularly over issues such as water sharing, border disputes, and the allocation of resources.
Now, to understand the special provisions in India’s federal structure, let’s delve into the section “Special Provisions” of the chapter “Federalism.”
Special Provisions
Certain states in India have been granted special provisions under the Constitution. These provisions are aimed at addressing the unique needs and challenges of these states.
Jammu and Kashmir
- Jammu and Kashmir is a special category state under the Constitution.
- It has a special status that grants it certain autonomy and safeguards its cultural identity.
- However, the state’s status has been a subject of controversy and has led to conflicts between India and Pakistan.
Finally, as we have gained comprehensive knowledge about the chapter ‘Federalism’, let’s reflect on the overall learning value of this important lesson.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter
The chapter “Federalism” provides a comprehensive understanding of the federal system, particularly in the Indian context. It highlights the balance of power between different levels of government and the importance of federalism in managing a diverse and populous country like India. The chapter also addresses the challenges faced in a federal system and the unique features that make Indian federalism distinct. Through this chapter, students will gain insight into how federalism contributes to the functioning of a democratic nation and the complexities involved in maintaining such a system.
A compelling introduction which will be added after the first paragraph
Practice questions on Chapter 7 - Federalism
Get your free Chapter 7 - Federalism practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now