Nature’s Treasures – Complete Guide For Class 6 Science Chapter 11
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, Nature’s Treasures in Science for Class 6th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
Introduction: Exploring Nature’s Treasures
Nature is abundant with treasures that enrich our lives in countless ways. Let’s begin with the understanding of the chapter Nature’s Treasures with the example of Bhoomi and Surya.
Bhoomi and Surya, during their vacation at their grandmother Ajji’s village in the Western Ghats, discover these treasures firsthand—the pure air, the fertile soil, and the abundance of sunlight that sustains both plants and animals. This chapter takes us on a journey to explore some of the key elements of nature that are essential for life on Earth.
Air: The Breath of Life
Further in the chapter NAture’s Treasures, we’ll understand the concept of air. One morning, Bhoomi and Surya observe Ajji doing breathing exercises. She explains that breathing helps to bring fresh air into our lungs, which keeps us healthy. Air is essential for all living beings as it provides oxygen, which our bodies need to survive.
Activity: Experiencing the Importance of Breathing
- Instructions:
- Take a deep breath and exhale slowly.
- Hold your breath for as long as you can and then exhale.
This simple exercise shows how vital oxygen is for survival. Without it, we would struggle to perform even basic functions.
Composition of Air
Air is a mixture of gases, with 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% consisting of other gases like carbon dioxide and argon. This balance is crucial for sustaining life on Earth and having this balance is what makes it one of the most significant nature’s treasures.
| Gas | Percentage |
| Nitrogen | 78% |
| Oxygen | 21% |
| Other gases | 1% |
Moving air is called wind. Wind can blow gently, as a breeze, or forcefully, as in storms. Wind power is harnessed using windmills to run flour mills, to pull up water from a well, or to generate electricity. In India, there are many windmill farms. A windmill farm is an area that has a large number of windmills that use the energy of the wind to generate electricity.
Water: A Precious Resource
Water is essential for survival and it is one of the most important nature’s treasures. Bhoomi and Surya help Ajji water plants and fill troughs for cows. Ajji teaches them how to water plants efficiently to avoid waste.
Activity: Understanding the Uses of Water
- Uses of Water: Drinking, cooking, bathing, watering plants, cleaning, and industrial uses.
Water covers about two-thirds of Earth’s surface, but most of it is salty seawater, unsuitable for drinking or farming. Only a small portion is available as freshwater, found in rivers, lakes, and underground sources. Freshwater is precious, and Ajji teaches Bhoomi and Surya to use it wisely.
Water Conservation
Further in the chapter Nature’s Treasures, we’ll understand the concept of water conservation. Ajji emphasizes the importance of conserving water. People in some parts of India walk long distances to fetch water, and pollution further limits our supply of freshwater. Water pollution occurs when waste materials like plastic bags, wrappers, and industrial waste are dumped into rivers, streams, and lakes. This makes water unfit for consumption by living beings.
Freshwater sources are limited, leading to water shortages in many parts of India, where people often have to walk long distances to fetch drinking water. To reduce water pollution and conserve water, it is essential to avoid polluting water bodies, use water wisely, and promote sustainable practices. Conserving water ensures that it remains accessible and fit for use by all living beings.
Activity How Water is Wasted Suggestions to Reduce Wastage Hand Washing Leaving the tap on Turn off the tap when not needed Washing Clothes Overuse of water Use efficient washing techniques Gardening Watering unnecessarily Water plants early in the morning
Rainwater Harvesting
Further in the chapter Nature’s Treasures, Ajji explains the process of rainwater harvesting, where rainwater is collected and stored for later use. It is practiced in many homes, schools, and residential societies. An age-old practice in India, traditional systems like stepwells (called Bawadi in Rajasthan and Vav in Gujarat) were built for water harvesting in water-scarce regions. These stepwells not only store rainwater but also collect water seeping from nearby lakes, ponds, and rivers. They have stone-lined trenches that allow water to seep in and be stored. Exploring traditional water harvesting practices in local areas can provide further insights into sustainable water conservation methods.

Energy from the Sun: A Source of Life
The Sun is the primary source of energy for life on Earth making it one of the most important nation’s treasures. Bhoomi and Surya learn from Ajji that sunlight helps plants make food through photosynthesis. The Sun’s energy is also used for drying clothes, making solar power, and even cooking in solar cookers.
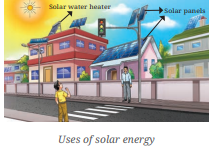
Uses of Solar Energy
- Solar panels on rooftops and streetlights capture sunlight to generate electricity.
- Solar water heaters and solar cookers use sunlight for heating and cooking.
The energy from the Sun is essential for sustaining life, from plants to animals, and we rely on it in countless ways.
Forests: The Green Treasure
While further discussing nature’s treasures, Ajji takes Bhoomi and Surya on a walk through the forest, where they see various plants, animals, and birds. Forests are vital ecosystems that provide shelter, food, and oxygen for living beings. They help maintain the balance of nature and play a crucial role in preventing soil erosion.
Van Mahotsav: Celebrating Forests
As mentioned in the chapter Nature’s Treasures, saaan Mahotsav, celebrated in July, is a week-long festival in India dedicated to planting trees and raising awareness about forest conservation.
The Importance of Forests
The chapter Nature’s Treasures significantly shares the importance of forests. It involves-
- Forests provide wood, fruits, medicinal plants, and many other resources.
- The roots of trees hold the soil together, preventing erosion.
- The decaying leaves enrich the soil with nutrients, supporting new growth.
The Chipko movement, where women hugged trees to protect them from being cut down, highlights the importance of conserving forests.
Soil, Rocks, and Minerals
The chapter Nature’s Treasures further discusses soil, rocks, and minerals.

Bhoomi and Surya help Ajji prepare the garden soil for planting vegetables by loosening lumps and digging the soil. While working, they observe earthworms, which naturally aid in turning and loosening soil. Through an activity, they collect soil samples from different places, observe their color and texture, and compare their observations using a magnifying lens. Soil contains various materials, including sand, insects, and organic matter from decomposed plants and animals.
Soil is formed over thousands of years from the disintegration of rocks due to natural forces. Different types of soil are suitable for different purposes, such as growing plants or making bricks. Rocks like granite, sandstone, and marble are essential in construction, while minerals extracted from rocks are used in tools, electronics, and other products.
Rocks are made of minerals, which provide important metals like gold, copper, and iron. These minerals are vital for manufacturing goods like vehicles and electronics. Since rocks and minerals take millions of years to form, it is crucial to use and conserve them responsibly. Additionally, most transportation relies on fossil fuels, connecting the use of minerals to energy consumption.
Activity: Investigating Soil
- Instructions:
- Collect soil samples from different areas.
- Observe the color, texture, and contents of each sample.
- Use a magnifying lens to look closely at the soil.
| Location | Guess | Observation with Naked Eye | Observation with Magnifying Lens |
| Garden | Dark soil | Moist with organic matter | Tiny particles and organisms |
| Roadside | Dry and sandy | Coarse and rocky | No visible organisms |
Soil is formed over thousands of years through the weathering of rocks, and it supports biodiversity.
Fossil Fuels: The Buried Treasure
Petrol, diesel, and kerosene, the most commonly used fuels for vehicles, are derived from petroleum. Along with natural gas and coal, these are called fossil fuels, formed from the remains of ancient microorganisms and plants buried deep within the earth over millions of years. Natural gas is used for cooking, electricity generation, and as Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for vehicles, offering a cleaner alternative to petrol and diesel. Coal is mainly used for electricity production.
Fossil fuels are finite, and their overuse leads to air pollution through the release of smoke and carbon dioxide. As supplies diminish, there is a growing need to explore alternative energy sources.
Activity: Survey of Vehicles and Fuels
- Instructions:
- Conduct a survey in your neighborhood to identify the types of vehicles and fuels used.
| Vehicle Type | Fuel Used |
| Car | Petrol or Diesel |
| Bike | Petrol |
| Bus | Diesel |
As fossil fuels are limited, there is a growing need to explore alternative energy sources like solar and wind power.
Renewable and Non-renewable Resources
Natural resources are classified into two categories:
- Renewable Resources: Air, water, and forests, which can be replenished by nature over time.
- Non-renewable Resources: Fossil fuels and minerals, which are limited in quantity and cannot be replenished quickly.
Ajji teaches Bhoomi and Surya that we must use resources responsibly, ensuring they are available for future generations.
Resources we use
Bhoomi and Surya notice the polluted air in the city compared to the fresh air at their grandmother Ajji’s home, where fewer vehicles are present. Their mother explains that vehicles using fossil fuels release smoke, contributing to air pollution, but alternatives like electric vehicles reduce pollution. The text prompts a discussion on ways to reduce air pollution and conserve natural resources.
Our daily activities include the usage of natural resources, such as water for washing clothes and wood for fire. The lesson emphasizes the importance of using resources like air, water, and soil responsibly to protect the environment for future generations. The quote by M. K. Gandhi highlights the need to avoid greed and conserve resources.
Conclusion: Conserving Nature’s Treasures
Nature provides us with everything we need—air, water, sunlight, forests, and fossil fuels. It is our responsibility to use these treasures wisely, conserve them, and prevent pollution. By practicing rainwater harvesting, using renewable energy, and protecting our forests, we can ensure a sustainable future for all living beings.
In conclusion, CBSE Class 6th Science Chapter 11 – Nature’s Treasures helps us understand the importance of the natural resources around us. From air and water to forests and sunlight, we rely on these elements for our survival. As highlighted in the chapter Nature’s Treasures, it’s crucial to use these resources responsibly and work towards their conservation. By making sustainable choices, such as practicing rainwater harvesting and protecting forests, we can ensure that the treasures of nature continue to benefit future generations. With the help of the iPrep Learning Super App, you can master Nature’s Treasures through engaging learning resources that bring these concepts to life!
Practice questions on Chapter 11 - Nature's Treasures
Get your free Chapter 11 - Nature's Treasures practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








