Drainage- Complete Guide For Class 9th Geography Chapter 3
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, “Drainage” in Geography for Class 9th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best-integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
Understanding the intricate network of rivers and lakes in India is more than just a geographic exercise—it’s a window into the life and vitality of the country. The chapter “Drainage” in Class 9 Geography does precisely that. It takes students on a journey through the diverse drainage systems that crisscross the Indian subcontinent, illustrating how these water bodies have shaped our physical geography and influenced human settlements. By exploring the Himalayan and Peninsular rivers, as well as the critical role of lakes, this chapter reveals how our environment is intertwined with economic activities, cultural practices, and daily life. Dive into “Drainage” to uncover how rivers carve landscapes, sustain economies, and highlight the urgent need for environmental stewardship.
Drainage
The chapter “Drainage” in Class 9 Geography discusses the various drainage systems in India, focusing on the Himalayan and Peninsular rivers, as well as the importance of lakes, the role of rivers in the economy, and the growing concern of river pollution. This chapter provides a comprehensive understanding of how rivers shape the landscape, influence human activity, and face challenges due to pollution.
The chapter “Drainage” is a crucial part of Class 9 Geography, providing students with an in-depth understanding of India’s vast and intricate drainage systems. It explains how rivers, lakes, and water bodies not only shape the physical geography of the country but also play a significant role in the economy and daily lives of people. In this chapter, we explore the major river systems in India, the importance of lakes, the economic impact of rivers, and the pressing issue of river pollution.
Objectives of the Chapter
Now that we know the importance of studying this chapter, let’s understand the objectives behind studying “Drainage”.
- Understand the significance of drainage systems in shaping India’s geography.
- Learn about the major river systems in India, including the Himalayan and Peninsular rivers.
- Explore the importance of lakes and their role in India’s water resources.
- Analyze the impact of rivers on India’s economy and their importance for agriculture and industry.
- Identify the causes and consequences of river pollution in India and explore potential solutions.
Lets now learn about the various sections of the chapter in detail.
First of all, to understand the drainage systems in India, let’s discuss the section “Drainage Systems in India” in the chapter “Drainage.”
Drainage Systems in India
The drainage systems in India are divided into two major categories: the Himalayan Rivers and the Peninsular Rivers.
The Himalayan Rivers
The Himalayan rivers are snow-fed and perennial, meaning they flow throughout the year. They have large basins and flow through deep gorges. In this section of the chapter “Drainage,” we explore the three major river systems in the Himalayan region:
- The Indus River System:
Originating in Tibet near Lake Mansarovar, the Indus River flows through India and Pakistan. It is one of the longest rivers in the world and supports millions of people along its banks.
- The Ganga River System:
The Ganga is perhaps the most significant river in India, revered in Indian culture and religion. It originates in the Gangotri Glacier and flows through several states, providing water to a large population.

- The Brahmaputra River System:
Originating in Tibet as the Yarlung Tsangpo River, the Brahmaputra flows through China, India, and Bangladesh. It is known for its massive volume and the fertile plains it creates.
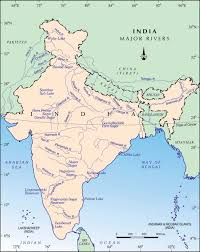
The Peninsular Rivers
The Peninsular rivers are mostly rain-fed and have shorter courses compared to the Himalayan rivers. In this part of the chapter “Drainage,” we look at the major river basins of the Peninsular region:
- The Narmada Basin:
Flowing westward between the Vindhya and Satpura ranges, the Narmada River is one of the few rivers in India that flows westward into the Arabian Sea.
- The Tapi Basin:
Similar to the Narmada, the Tapi River also flows westward into the Arabian Sea and drains a smaller basin compared to the Narmada.
- The Godavari Basin:
Known as the ‘Dakshin Ganga’ or ‘Ganga of the South,’ the Godavari is the longest river in Peninsular India, flowing eastward into the Bay of Bengal.
- The Mahanadi Basin:
Originating in Chhattisgarh, the Mahanadi flows through Odisha and into the Bay of Bengal, providing water for extensive agricultural activities.
- The Krishna Basin:
The Krishna River flows from the Western Ghats towards the Bay of Bengal, supporting agriculture in Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
- The Kaveri Basin:
The Kaveri River, known for its scenic beauty, flows through Karnataka and Tamil Nadu before emptying into the Bay of Bengal.
Now, to understand the importance of lakes, let’s discuss the section “Lakes” of the chapter “Drainage.”
Lakes
Lakes play a vital role in the ecology and economy of India. They act as natural reservoirs, support biodiversity, and are used for irrigation, drinking water, and recreation. Some of the most prominent lakes in India include:
- Wular Lake:
One of the largest freshwater lakes in Asia, located in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Chilika Lake:
Asia’s largest brackish water lagoon is located in Odisha.
- Sambhar Lake:
India’s largest inland salt lake is located in Rajasthan.


To grasp the significance of rivers, let’s delve into the section “Role of Rivers in the Economy” in the chapter “Drainage.”
Role of Rivers in the Economy
Rivers are the lifeblood of India’s economy. They provide water for irrigation, support agriculture, and are a source of drinking water for millions. Rivers also play a crucial role in transportation, hydropower generation, and as a source of livelihood for fishing communities. The chapter “Drainage” emphasizes the economic importance of rivers in sustaining life and driving the economy.
To fully understand the challenges facing our rivers, let’s discuss the section “River Pollution” in the chapter “Drainage.”
River Pollution
River pollution has become a major concern in recent decades. Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and domestic sewage are polluting India’s rivers, threatening both human health and the environment. The chapter “Drainage” highlights the need for immediate action to protect our rivers from further degradation and to ensure they remain a vital resource for future generations.

Now that we have gained complete knowledge about the chapter “Drainage” let us know the overall learning value of the lesson.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter
In conclusion, the chapter “Drainage” offers a comprehensive look at India’s drainage systems, emphasizing the importance of rivers and lakes in shaping the country’s geography and supporting its economy. Understanding the role of these water bodies is essential for appreciating their impact on human life and the environment. As we learn more about the challenges of river pollution, it becomes clear that protecting our water resources is crucial for a sustainable future.
In conclusion, CBSE Class 9th Geography Chapter – Drainage provides an in-depth exploration of India’s complex drainage systems, focusing on the vital role that rivers and lakes play in shaping the landscape, supporting human activities, and contributing to the economy. From the majestic Himalayan rivers to the essential Peninsular rivers, this chapter highlights their importance and the pressing issue of river pollution. By studying Drainage, students gain a deeper understanding of the environmental challenges and the need to preserve these invaluable natural resources. Mastering the concepts in Chapter – Drainage will equip students with the knowledge to appreciate and contribute to sustainable water management practices in the future.
Practice questions on Chapter 3 - Drainage
Get your free Chapter 3 - Drainage practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








