Natural Vegetation and Wildlife- Complete Guide For Class 9 Geography Chapter 5
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife” in Geography for Class 9th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best-integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
The chapter “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife” explores the rich biodiversity of India, focusing on the various types of vegetation and wildlife found across different regions. It delves into the factors that influence the distribution of these natural resources and highlights the significance of conserving them. The chapter categorizes the natural vegetation of India into five distinct types and provides an overview of the unique wildlife associated with each type of vegetation.
India is home to a diverse range of natural vegetation and wildlife, thanks to its varied climate, topography, and soil types. The chapter “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife” offers an in-depth look at the different types of vegetation found in the country, from lush tropical forests to thorny shrubs. Understanding these ecosystems is crucial for appreciating the natural beauty of India and recognizing the importance of conserving its flora and fauna.
Objectives Of Learning The Chapter
Now that we know the importance of studying this chapter, let’s understand the objectives behind studying “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife”
- Understand the different types of natural vegetation found in India.
- Recognize the factors influencing the distribution of vegetation and wildlife.
- Learn about the various forest types and their characteristics.
- Identify the regions where specific types of vegetation are found.
- Explore the relationship between natural vegetation and wildlife.
Lets now delve into the various sections of the chapter in detail.
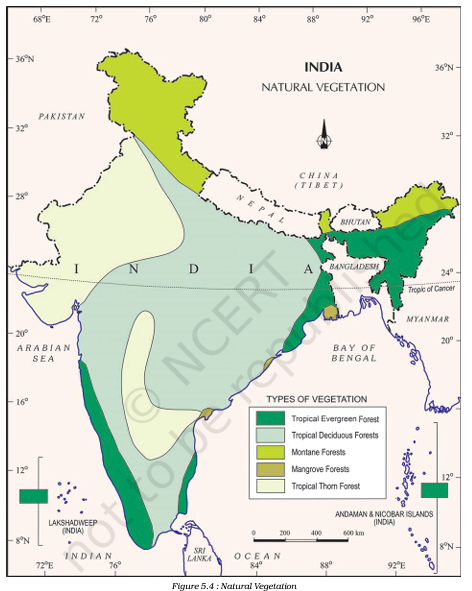
First of all, to understand the unique characteristics of dense, year-round greenery, let’s delve into the section “Tropical Evergreen Forests” of the chapter “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife.”
Tropical Evergreen Forests
- Flora:
- These forests are characterized by dense, multi-layered vegetation with a variety of trees, shrubs, and creepers.
- Common tree species include rosewood, ebony, and mahogany.
- The dense canopy allows little sunlight to reach the forest floor, promoting the growth of shade-tolerant plants.
- Fauna:
- The rich and diverse habitat supports a wide range of wildlife.
- Common animals include elephants, monkeys, deer, and a variety of birds.
- The thick vegetation also provides shelter for reptiles, insects, and smaller mammals.
Now, to understand the seasonal changes in vegetation, let’s explore the section “Tropical Deciduous Forests” of the chapter “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife.”
Tropical Deciduous Forests
- Flora:
- Also known as monsoon forests, these forests shed their leaves during the dry season to conserve water.
- Common tree species include teak, sal, and bamboo.
- The undergrowth is less dense compared to evergreen forests, allowing more sunlight to reach the forest floor.
- Fauna:
- These forests are home to a variety of herbivores like deer and elephants, which thrive on the seasonal abundance of leaves and fruits.
- Predators such as tigers and leopards are also found here, relying on the herbivores for food.
- The diverse habitat supports numerous bird species, reptiles, and insects.

Now, to understand how vegetation adapts to arid conditions, let’s delve into the section “Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs” of the chapter “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife.”
Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs
- Flora:
- These forests are characterized by thorny trees and shrubs, adapted to survive in regions with low rainfall.
- Common plant species include acacia, cactus, and various types of grasses.
- The vegetation is sparse, with plants having deep roots to access water from underground.
- Fauna:
- The arid environment supports animals adapted to dry conditions, such as camels, blackbucks, and various lizards.
- Birds like vultures, eagles, and other raptors are commonly found in these regions.
- Smaller mammals and reptiles have also adapted to the harsh climate.
Now, to understand the impact of altitude on vegetation, let’s explore the section “Montane Forests” of the chapter “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife.”
Montane Forests
- Flora:
- Montane forests are found in mountainous regions, where vegetation changes with altitude.
- Lower altitudes are covered with deciduous forests, while higher altitudes feature coniferous forests with trees like pine, fir, and deodar.
- Alpine vegetation, including shrubs and meadows, is found at the highest altitudes.
- Fauna:
- The diverse vegetation supports a variety of wildlife, including the snow leopard, musk deer, and several species of bears.
- Birds like the monal, which is the state bird of Uttarakhand, are commonly found in these forests.
- The region is also home to numerous smaller mammals, reptiles, and insects adapted to the cooler climate.
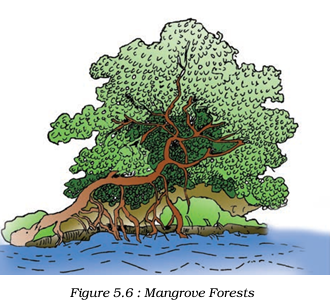
Now, to understand the unique ecosystems along coastlines, let’s delve into the section “Mangrove Forests” of the chapter “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife.”
Mangrove Forests
- Flora:
- Mangrove forests are found in coastal regions, particularly where rivers meet the sea.
- The vegetation is characterized by salt-tolerant trees with stilt-like roots, which help them survive in saline waters.
- Common species include the Sundari tree, from which the Sundarbans derive their name.
- Fauna:
- These forests provide a habitat for a variety of aquatic and terrestrial animals, including fish, crabs, and shrimp.
- The Sunderbans are famous for the Bengal tiger, which is adapted to living in this unique environment.
- Other wildlife includes various bird species, reptiles, and smaller mammals that thrive in the swampy terrain.
Now that we have gained complete knowledge about the chapter “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife” let us know the overall learning value of the lesson.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter
In conclusion, the chapter “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife” not only introduces us to the diverse ecosystems of India but also emphasizes the importance of preserving these natural resources. Each type of vegetation and its associated wildlife forms a vital part of the ecological balance, contributing to the country’s rich biodiversity.
In conclusion, the chapter “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife” serves as a gateway to understanding the rich and diverse ecosystems that shape India’s natural landscape. By exploring various types of vegetation—ranging from Tropical Evergreen Forests to Mangrove Forests—and their associated wildlife, you gain a comprehensive view of how these elements interact to form complex ecosystems. The insights into how factors like climate, soil, and altitude influence the distribution of flora and fauna highlight the importance of preserving these vital resources.
The chapter “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife” not only enhances your knowledge about different forest types and wildlife but also reinforces the critical role conservation plays in maintaining ecological balance. As you delve deeper into each section, from the lush greenery of Tropical Evergreen Forests to the unique Mangrove Forests, you’ll appreciate the intricate relationships that sustain India’s biodiversity.
Ultimately, the chapter “Natural Vegetation and Wildlife” underscores the need for continued efforts in environmental conservation. Understanding these ecosystems enriches your awareness and equips you with the knowledge to advocate for and contribute to preserving India’s natural heritage.
Practice questions on Chapter 5 - Natural Vegetation And Wildlife
Get your free Chapter 5 - Natural Vegetation And Wildlife practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








