Physical Features of India- Complete Guide For Class 9th Geography Chapter 2
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Geography helps us understand the world we live in, and in Class 9, one of the most essential chapters is ‘Physical Features of India.’ This chapter provides insights into the unique and diverse landforms that shape our country. From the snow-capped Himalayas to the vast coastal plains, India’s geography is filled with wonders waiting to be explored. In this blog, we will dive deep into the key aspects of the chapter, ‘Physical Features of India,’ making it easier for you to grasp and retain essential concepts for your studies.
Our learning resources for the chapter, “Physical Features of India” in Geography for Class 9th, are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions, and notes offer you the best-integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
Physical Features of India
This chapter explores the diverse physical landscapes of India, from the towering Himalayas to the vast coastal plains. It delves into the major physiographic divisions of the country, explaining their formation, characteristics, and significance.
India is a land of remarkable geographical contrasts, characterized by a diverse range of physical features. These features have significantly influenced the country’s climate, natural resources, and human settlement patterns. To gain a comprehensive understanding of India, it is essential to explore its physical geography.
Objectives of the Chapter
Now that we know the importance of studying this chapter, let’s understand the objectives behind studying “Physical Features of India”.
- Identify the major physiographic divisions of India
- Understand the geological processes that shaped India’s landforms
- Analyze the impact of physical features on India’s climate, resources, and population distribution.
Let’s now learn about the various sections of the chapter in detail.
Now to understand the building blocks of India’s diverse terrain, let’s discuss the section ‘Major Physiographic Divisions’ of the chapter ‘Physical Features of India’.
Major Physiographic Divisions
The Himalayan Mountains
The Himalayas, often referred to as the ‘Roof of the World’, form the majestic northern frontier of India.
- Formation: These young fold mountains arose due to the collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates.
- Divisions: The Himalayas can be divided into the Greater Himalayas, the Middle Himalayas, and the Outer Himalayas (Siwaliks).
- Significance: The Himalayas are a vital water tower, providing perennial rivers, and acting as a natural barrier.
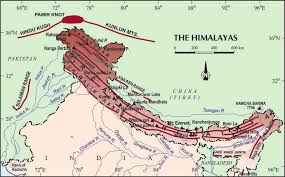
Let’s move south to explore the vast expanse known as the Northern Plains in the chapter ‘Physical Features of India’.
The Northern Plains
- Formation: These plains are primarily alluvial, formed by the deposition of sediments by the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra rivers.
- Divisions: The plains can be further classified into the Punjab Plains, the Ganga Plains, and the Brahmaputra Plains.
- Significance: The Northern Plains are India’s breadbasket, supporting a dense population and intensive agriculture.

Now, let’s turn our attention to the Deccan Plateau, the heart of India, as part of the ‘Physical Features of India’ chapter.
The Peninsular Plateau
- Formation: This plateau is a part of the ancient Gondwana landmass and is characterized by its triangular shape.
- Divisions: The plateau can be divided into the Central Highlands, the Deccan Traps, and the Eastern and Western Ghats.
- Significance: The Peninsular Plateau is rich in mineral resources and supports a variety of crops, including cotton and millet.

Continuing our exploration of India’s physical diversity, let’s focus on the arid region known as the Thar Desert within the chapter ‘Physical Features of India’.
The Indian Desert
- Formation: The desert’s formation is primarily due to the arid climate and sparse vegetation.
- Characteristics: The Thar Desert is characterized by sand dunes, saline soils, and scanty rainfall.
- Significance: Despite its challenging conditions, the desert supports unique flora and fauna and has gained importance for renewable energy projects.

Now, let’s shift our focus to the coastal regions of India as we continue our exploration of the chapter ‘Physical Features of India’.
The Coastal Plains
- Formation: The coastal plains have been formed by the deposition of sediments brought down by rivers.
- Divisions: India has two major coastlines – the Arabian Sea coast and the Bay of Bengal coast.
- Significance: The coastal plains are crucial for fisheries, ports, and tourism.
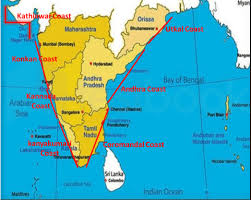
Finally, let’s conclude our exploration of India’s physical features by examining the island territories in the chapter ‘Physical Features of India’.
The Islands
- Major Island Groups: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Arabian Sea.
- Significance: These islands are known for their pristine beaches, coral reefs, and rich biodiversity.

Now that we have gained complete knowledge about the chapter ‘Physical Features of India’ lets know the overall learning value of the lesson.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter
The chapter ‘Physical Features of India’ offers a comprehensive understanding of the nation’s geographical diversity, highlighting the formation and significance of its major landforms such as the Himalayas, Northern Plains, Peninsular Plateau, Thar Desert, Coastal Plains, and Islands. It elucidates how these physical features influence India’s climate, natural resource distribution, and human settlement patterns. By exploring the geological processes behind these landscapes, the chapter enhances appreciation for India’s natural history and emphasizes the importance of preserving its ecosystems. This knowledge is essential for understanding India’s environmental and socio-economic fabric, and fostering informed and responsible citizenship.
In conclusion, CBSE Class 9th Geography Chapter ‘Physical Features of India’ takes us on a journey across the diverse landscapes of our country, from the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the arid expanses of the Thar Desert. Understanding the formation and significance of these physical features helps us appreciate the unique geographical makeup of India. As we studied the Himalayas, Northern Plains, Peninsular Plateau, Coastal Plains, and Islands, it became evident how these landforms shape our climate, resources, and settlement patterns. With the help of iPrep’s resources, mastering the chapter ‘Physical Features of India’ becomes an engaging and enriching experience, ensuring that you’re well-prepared for your academic success.
Practice questions on Chapter 2 - Physical Features of India
Get your free Chapter 2 - Physical Features of India practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








