Democratic Rights – Complete Guide For Class 9 Political Science Chapter 5

Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, “Democratic Rights” in Political Science for Class 9th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
This chapter, Democratic Rights, explores the concept of democratic rights, their significance in a democracy, and their implementation in India. It delves into various aspects of rights, including their classification, the challenges in their realization, and the ongoing efforts to expand their scope.
In a democracy, Democratic Rights are the cornerstone of any democratic society. They guarantee fundamental freedoms and protections to citizens, ensuring equality, fairness, and justice. This chapter, Democratic Rights, will delve into the world of democratic rights, examining their importance, their embodiment in the Indian Constitution, and the challenges and strides made in their realization.
Objectives Of Learning The Chapter Democratic Rights
Now that we have analyzed the significance of the chapter, let’s know the objectives of studying “Democratic Rights”.
- Understand the concept of Democratic Rights.
- Analyze the importance of rights in a democracy.
- Explore the fundamental rights enshrined in the Indian Constitution as part of Democratic Rights.
- Examine the challenges faced in realizing these Democratic Rights.
- Appreciate the ongoing efforts to expand the scope of Democratic Rights.
Now let’s explore the various sections of the chapter.
Firstly, in order to understand the true value of Democratic Rights, let’s delve into the Life Without Rights section of the chapter Democratic Rights.
Life Without Rights

Prison in Guantanamo Bay:
This notorious detention camp symbolizes the extreme violation of human rights, highlighting the absence of Democratic Rights.
Citizens’ Rights in Saudi Arabia:
Despite being a wealthy nation, Saudi Arabia has a long history of suppressing basic freedoms, demonstrating what life without Democratic Rights looks like.
Ethnic Massacre in Kosovo:
This tragic event highlights the consequences of denying rights to specific groups, emphasizing the importance of Democratic Rights.
These examples underscore the significance of Democratic Rights in protecting individuals and societies from oppression and violence.
Now, to grasp the necessity of rights in a democratic society, let’s delve into the Rights in a Democracy section of the chapter Democratic Rights.
Rights in a Democracy
What are Rights?
- Democratic Rights are fundamental freedoms and entitlements enjoyed by citizens in a democratic state.
- They are essential for an individual’s dignity, development, and participation in society.
Why Do We Need Rights in a Democracy?
- Democratic Rights protect individuals from the arbitrary power of the state.
- They ensure equality and fairness for all citizens.
- Democratic Rights promote diversity and dissent, vital for a healthy democracy.
- They empower citizens to participate meaningfully in decision-making.
Now, to explore how Democratic Rights are enshrined in the Indian legal framework, let’s delve into the Rights in the Indian Constitution section of the chapter Democratic Rights.
Rights in the Indian Constitution
- The Indian Constitution guarantees a wide range of fundamental rights to its citizens as part of Democratic Rights.
- These Democratic Rights are enshrined in Part III of the Constitution and are enforceable by courts.
Now, to understand the specific Democratic Rights protected by the Indian Constitution, let’s delve into The Fundamental Rights in the Indian Constitution section of the chapter Democratic Rights.
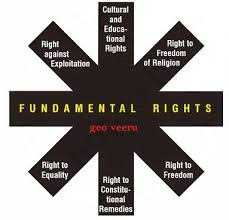
The Fundamental Rights in the Indian Constitution

Right to Equality
- Prohibits discrimination based on religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth.
- Guarantees equality of opportunity in public employment.
- Abolishes untouchability.
Right to Freedom
- Ensures freedom of speech, expression, assembly, association, and movement.
- Protects the right to form associations and unions.
- Safeguards the right to life and personal liberty.
Right against Exploitation
- Prohibits forced labor, child labor, and human trafficking.
- Ensures fair working conditions and wages.
Right to Freedom of Religion
- Guarantees freedom of conscience, religion, and worship.
- Protects the right to propagate and practice religion.
- Prohibits religious discrimination.
Cultural and Educational Rights
- Protects the rights of cultural and linguistic minorities.
- Ensures access to education.
Right to Constitutional Remedies
- Provides legal remedies for the enforcement of Democratic Rights.
- Enables citizens to approach courts for redressal of grievances.
Now, in order to understand the evolving nature of Democratic Rights, let’s delve into the Expanding Scope of Rights section of the chapter Democratic Rights.
Expanding Scope of Rights
New challenges:
Globalization, technology, and social changes pose new challenges to the protection of Democratic Rights.
Expanding horizons:
Rights like the right to information, right to privacy, and right to food have gained recognition as part of Democratic Rights.
Continuous struggle:
Ensuring the effective implementation and protection of Democratic Rights remains an ongoing endeavor.
Finally, as we have gained comprehensive knowledge about the chapter Democratic Rights, let’s reflect on the overall learning value of this important lesson.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter
Understanding Democratic Rights is crucial for a just and equitable society. These rights empower individuals, protect minorities, and promote a vibrant democracy. The Indian Constitution guarantees a wide range of Democratic Rights, but their realization is an ongoing process. By understanding the importance of Democratic Rights and actively participating in their protection, we can contribute to building a stronger and more inclusive democracy.
This chapter, Democratic Rights, has provided a comprehensive overview of these essential rights, their significance, and their implementation in India. It is crucial to continue learning and engaging with this topic to ensure the ongoing protection and expansion of these fundamental freedoms.
Let’s Conclude
As we conclude our exploration of the CBSE Class 9th Political Science chapter “Democratic Rights,” it becomes clear that democratic rights are not just theoretical concepts but vital elements that shape a just and fair society. This chapter on “Democratic Rights” has underscored the importance of rights in safeguarding individual freedom, equality, and justice in a democracy. By understanding how “Democratic Rights” are enshrined in the Indian Constitution, students gain insight into the protections and freedoms that uphold the democratic fabric of our nation.
The chapter on “Democratic Rights” equips students with knowledge that extends beyond academic exams, inspiring a deeper appreciation of our constitutional framework. By continuing to learn about, respect, and protect these rights, each student can contribute to a more equitable and democratic society.
Practice questions on Chapter 5 - Democratic Rights
Get your free Chapter 5 - Democratic Rights practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now