Introduction to Maps – Complete Guide For Class 11 Geography Practical Chapter 1

Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter “Introduction to Maps” in Geography practicals for Class 11th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions, and notes offer the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
This chapter explores the essential elements of mapmaking, including scale, projection, generalization, and design. It also delves into the history of mapmaking, the different types of maps, and the various uses of maps in geography and other fields.
Maps are visual representations of the Earth’s surface, providing valuable information about locations, distances, and features. This chapter introduces the fundamental concepts of mapmaking and explores the different types of maps and their uses.
Objectives Of Learning The Chapter – Introduction to Maps
Now that we have explored the importance of the chapter, let’s outline the objectives of studying it.
- To understand the basic elements of mapmaking.
- To explore the history of mapmaking.
- To identify the different types of maps based on scale and function.
- To learn the uses of maps in various fields.
Now let’s explore the various sections of the chapter.
Firstly, in order to understand the process of map-making, let’s delve into the Essentials of Map-Making section of the chapter Introduction to Maps.
Essentials of Map Making
Effective mapmaking involves several key elements, including scale, projection, generalization, and design.
Scale
- Definition: The ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground.
- Purpose: Essential for determining the level of detail a map represents.
Map Projection
- Definition: The method of transferring the Earth’s spherical surface onto a flat map.
- Types: Includes cylindrical, conical, and azimuthal projections.
Map Generalisation
- Definition: The process of simplifying the information on a map by omitting unnecessary details.
- Purpose: Helps to make the map more readable without overwhelming the user.
Map Design
- Definition: The aesthetic and functional arrangement of elements on a map, including symbols, colors, and typography.
- Purpose: Ensures that the map effectively communicates the intended information.
Map Construction and Production
- Definition: The technical process of creating and producing maps.
- Tools: Includes both traditional methods and modern GIS (Geographic Information Systems) technologies.
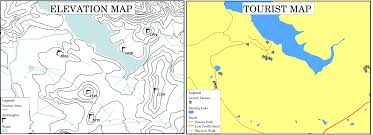
Now, in order to understand the historical background of map-making, let’s delve into the History of Map-Making section of the chapter Introduction to Maps.
History of Map Making
Early Maps
- Ancient civilizations like the Babylonians, Greeks, and Romans were pioneers in map-making.
- Maps evolved from simple sketches of territories to more detailed representations of regions.
- The roots of map-making in India can be traced back to the Vedic period when astronomical insights and cosmological revelations were first expressed.
Modern Cartography
- With technological advancements, map-making has transformed into a science, incorporating satellite imagery and digital mapping techniques.
Now, in order to understand the classification of maps, let’s explore the Types of Maps Based on Scale section of the chapter Introduction to Maps.
Types of Maps Based on Scale
Maps can be classified based on their scale, which determines the level of detail they show.
Large-scale Maps
- Cadastral Maps: Used for detailed representation of small areas, typically used in property management.
- Topographical Maps: Display both natural and man-made features of a region.
Small-scale Maps
- Wall Maps: Provide a broad overview of a large area and are typically used for educational purposes.
- Atlas Maps: Found in atlases, showing large regions or the entire world on a smaller scale.
Now, in order to understand the different purposes of maps, let’s delve into the Types of Maps Based on Function section of the chapter Introduction to Maps.
Types of Maps Based on Function
Maps can also be classified based on their function, which determines the type of information they convey.
Physical Maps
- Relief Maps: Show the elevation of the terrain using colors and contour lines.
- Geological Maps: Represent the distribution of geological features such as rock types and faults.
- Climatic Maps: Show weather patterns and climate zones.
- Soil Maps: Provide information on the distribution of different soil types.
Cultural Maps
- Political Maps: Display boundaries between countries, states, and cities.
- Population Maps: Represent the population distribution across different regions.
- Economic Maps: Show the distribution of resources, industries, and economic activities.
- Transportation Maps: Highlight the network of roads, railways, and other transportation routes.
Now, in order to understand the practical applications of maps, let’s explore the Uses of Maps section of the chapter Introduction to Maps.
Uses of Maps
Maps are used in a variety of fields, including navigation, planning, and research.
- Measurement of Distance
- Maps can be used to measure distances between different locations.
- Measurement of Direction
- Maps can be used to determine the direction of travel.
- Measurement of Area
- Maps can be used to calculate the area of different regions.
Finally, as we have gained comprehensive knowledge about the chapter “Introduction to Maps“, let’s reflect on the overall learning value of this important lesson.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter
This chapter provides a comprehensive understanding of the art and science of map-making. By learning about the essentials of map construction, the different types of maps, and their practical uses, students gain valuable insights into how maps are designed and used in various fields. The chapter emphasizes the importance of maps in geographical studies and highlights the evolution of cartography over time.
Let’s Conclude
In conclusion, the chapter “Introduction to Maps – Complete Guide For Class 11 Geography Practical Chapter 1” serves as a foundational step in understanding the critical aspects of map-making and its applications. Through this chapter, students of Class 11 gain insights into the essentials of map-making, from scale and projection to the classification of different types of maps. Additionally, “Introduction to Maps” emphasizes how maps are not only tools for navigation but also instruments of research, planning, and analysis across various fields.
By studying “Introduction to Maps,” students develop a thorough understanding of the intricate details involved in creating maps that are both functional and visually informative. This knowledge provides Class 11 Geography students with an appreciation of cartography’s role in capturing and representing the physical and cultural landscapes of the world.
Practice questions on Chapter 1 - Introduction to Maps
Get your free Chapter 1 - Introduction to Maps practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now