Introduction to Remote Sensing – Complete Guide For Class 11 Geography Practical Chapter 6

Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter “Introduction to Remote Sensing” in Geography for Class 11th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
The chapter “Introduction to Remote Sensing” from Geography Class 11 provides an in-depth understanding of how remote sensing technology works, including the stages involved in capturing and analyzing data about the Earth from space. This chapter explores the use of satellites, the various types of sensors, and how the data gathered through remote sensing is converted into valuable information used in mapping, environmental studies, and more.
Remote sensing is a revolutionary technique that allows the collection of information about the Earth’s surface without being in direct contact with it. In Chapter 6, “Introduction to Remote Sensing,” students are introduced to the fundamentals of this technology, its stages, and how data is captured, processed, and interpreted. The chapter discusses the energy transmission process, types of sensors, satellite resolutions, and the interpretation of satellite imagery. Understanding remote sensing is crucial for students as it plays a key role in fields such as geography, environmental monitoring, and natural resource management.
Objectives of the Chapter
Now that we have explored the importance of the chapter, let’s outline the objectives of studying it.
- To understand the concept and stages of remote sensing.
- To explore the different types of sensors and their applications.
- To learn about the resolving powers of satellites and sensor resolutions.
- To understand the methods of interpreting satellite imagery.
- To grasp the practical applications of remote sensing in geographical studies.
Now let’s explore the various sections of the chapter.
Firstly, in order to understand the basics of remote sensing, let’s delve into the Introductory section of the chapter ‘Introduction to Remote Sensing’.
Remote Sensing
- Remote sensing is the science of obtaining information about objects or areas from a distance, typically using satellites.
- It plays a critical role in observing, analyzing, and mapping the Earth’s surface without physical contact.
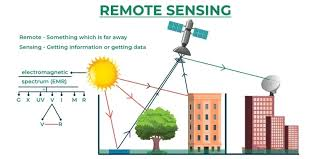
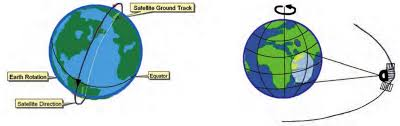
Now, to explore how remote sensing works, let’s undertake the section Stages in Remote Sensing of the chapter ‘Introduction to Remote Sensing’.
Stages in Remote Sensing
- Source of Energy:
The sun is the primary source of energy for remote sensing. It emits electromagnetic radiation that interacts with the Earth’s surface.
- Transmission of Energy from the Source to the Surface of the Earth:
Electromagnetic radiation travels through space and reaches the Earth’s surface.
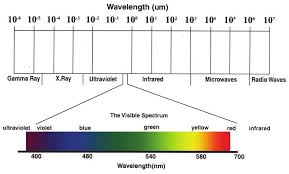
- Interaction of Energy with the Earth’s Surface:
Different objects on the Earth’s surface reflect or absorb energy differently based on their properties.
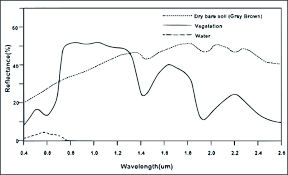
- Propagation of Reflected/ Emitted Energy through Atmosphere:
The reflected or emitted energy passes through the Earth’s atmosphere, which can affect its intensity and spectral composition.
- Detection of Reflected/Emitted Energy by the Sensor:
Sensors on satellites or aircraft capture the reflected or emitted energy.
- Conversion of Energy Received into Photographic/ Digital Form of Data:
The captured energy is converted into a digital or photographic format.
- Extraction of Information Contents from Data Products:
The data is analyzed to extract information about the Earth’s surface.
- Conversion of Information into Map/Tabular Forms:
The extracted information is presented in the form of maps, tables, or other visual representations.
Now, in order to understand the technology behind remote sensing, let’s delve into the section Sensors of the chapter ‘Introduction to Remote Sensing’.
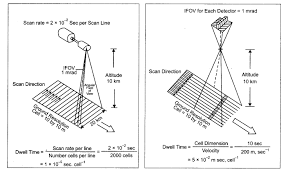
Sensors
Multispectral Scanners: These sensors capture data in multiple wavelengths of light.
There are two types:
- Whiskbroom Scanners: Use a rotating mirror to scan the Earth’s surface.
- Pushbroom Scanners: Use a linear array of detectors to capture a swath of the Earth’s surface.
Now, to understand the details captured by satellites, let’s discuss the section Resolving Powers of the Satellites of the chapter ‘Introduction to Remote Sensing’.
Resolving Powers of the Satellites
- Satellites vary in their ability to resolve or distinguish small details of the Earth’s surface.
- This power is determined by the satellite’s design and its sensors.

Now, in order to explore sensor capabilities, let’s delve into the section Sensor Resolutions of the chapter ‘Introduction to Remote Sensing’.
Sensor Resolutions
- Spatial Resolution: Refers to the smallest object that can be detected by a sensor.
- Spectral Resolution: Refers to the sensor’s ability to distinguish between different wavelengths of light.
- Radiometric Resolution: Refers to the sensor’s ability to detect slight differences in energy levels.
Now, to understand the types of data generated, let’s explore the section Data Products of the chapter ‘Introduction to Remote Sensing’.
Data Products
- Photographic Images: Analog images captured by satellites, useful in visual interpretation.
- Digital Images: Digital representations of the Earth’s surface, easily processed by computers.
Now, to learn how to analyze remote sensing data, let’s undertake the section Interpretation of Satellite Imageries of the chapter ‘Introduction to Remote Sensing’.
Interpretation of Satellite Imageries
- Interpreting satellite imagery involves understanding visual clues from images, such as color, texture, and shape.
Elements of Visual Interpretation
- Tone or Colour: Helps identify different materials or land cover types.
- Texture: Refers to the smoothness or roughness of the image.
- Size: Larger objects are easier to identify.
- Shape: Specific shapes can indicate particular features, such as buildings or roads.
- Shadow: Shadows help reveal the height and orientation of objects.
- Pattern: Repeating features can indicate human-made structures.
- Association: Identifying one feature in relation to others for context.

Finally, as we have gained comprehensive knowledge about the chapter ‘Introduction to Remote Sensing’, let’s reflect on the overall learning value of this important lesson.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter
The chapter “Introduction to Remote Sensing” offers students a valuable understanding of how satellites gather and transmit data to study the Earth’s surface. By learning about the stages of remote sensing, the types of sensors used, and how data is interpreted, students gain insights into how modern technology enhances geographical studies. The chapter equips learners with the knowledge to understand the role of remote sensing in mapping, environmental monitoring, and various real-world applications. Understanding these principles is essential for advancing in the fields of geography, environmental science, and resource management.
Let’s Conclude
In conclusion, the chapter “Introduction to Remote Sensing” in Geography for Class 11th provides an essential foundation for understanding the transformative role of remote sensing technology. As we explored throughout this chapter, remote sensing helps in capturing and analyzing data about the Earth’s surface without direct contact. Through the study of various stages, sensors, and resolutions, students gain critical insights into how data is collected, processed, and interpreted for real-world applications, including mapping and environmental monitoring.
The knowledge gained in this chapter enhances your understanding of how remote sensing contributes to geographical studies and equips you for future learning in this exciting field. We hope that with the resources available on the iPrep Learning Super App, including animated videos, notes, and practice questions, you are well-equipped to master the concepts of the chapter “Introduction to Remote Sensing” and apply them in your academic journey. Keep exploring, and continue learning with iPrep!
Practice questions on Chapter 6 - Introduction to Remote Sensing
Get your free Chapter 6 - Introduction to Remote Sensing practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now