Map Scale – Complete Guide For Class 11 Geography Practical Chapter 2

Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter “Map Scale” in Geography for Class 11th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions, and notes offer the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
This chapter focuses on the concept of map scale and its significance in geography. Understanding map scale is vital for accurately interpreting and analyzing maps.
Map scale plays a crucial role in cartography, providing a visual representation of the relationship between distances on a map and actual distances on the Earth’s surface. This chapter delves into various methods of representing scale on maps and the conversion techniques between different scale formats.
Objectives of Learning the Chapter –
Now that we have explored the importance of the chapter, let’s outline the objectives of studying it.
- To grasp the fundamental concept of map scale.
- To comprehend the significance of map scale in geography.
- To explore different methods of representing scale on maps.
- To learn the conversion techniques between different scale formats.
Now let’s explore the various sections of the chapter.
Firstly, to understand the scale of the map, let’s explore the section ‘What is a scale’ of the chapter Map Scale.
What is a Map Scale?
A map scale provides the relationship between the map and the whole or a part of the earth’s surface shown on it.
Now, to understand different ways to express map scale, let’s explore the section ‘METHODS OF SCALE’ of the chapter Map Scale.
METHODS OF SCALE
Now, let’s explore the different methods used for representing scale on maps:
- Statement of Scale
- A statement of scale expresses the relationship between map distance and ground distance in words. For example, “1 cm on the map represents 10 km on the ground.”
- Graphical or Bar Scale
- A graphical scale is a visual representation of a scale using a bar or line. It shows the equivalent distances on the map and the ground.
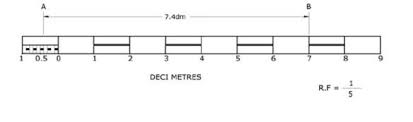
- Representative Fraction
- A representative fraction expresses the scale as a ratio. For example, 1:50,000 indicates that 1 unit on the map represents 50,000 units on the ground.
Now, in order to understand how to convert between different types of map scales, let’s explore the section ‘CONVERSION OF SCALE’ of the chapter Map Scale.
Conversion Of Scale
This section elaborates on the conversion techniques between various scale formats:
- Statement of Scale into R. F
- To convert a statement of scale into a representative fraction, ensure both distances are in the same units and then write the ratio. For example, “1 cm on the map represents 10 km on the ground” becomes 1:1,000,000.
- R. F. into Statement of Scale
- To convert a representative fraction into a statement of scale, choose a convenient unit (e.g., cm, km) and multiply it by the denominator of the fraction. For example, 1:25,000 becomes “1 cm on the map represents 25,000 cm (or 0.25 km) on the ground.”
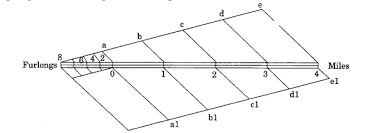
- Construction of the Graphical/Bar Scale
To construct a graphical scale, follow these steps:
- Choose a suitable length for the scale bar.
- Divide the bar into equal parts based on the desired scale.
- Label the divisions with corresponding ground distances.
Finally, as we have gained comprehensive knowledge about the chapter “Map Scale”, let’s reflect on the overall learning value of this important lesson.
Overall Learning Value
By understanding map scale, you can accurately measure distances on maps, interpret the information presented, and make informed decisions based on spatial data. This knowledge is invaluable for various fields, including geography, cartography, and navigation.
Let’s Conclude
In conclusion, mastering the chapter “Map Scale – Complete Guide for Class 11 Geography Practical Chapter 2” provides you with essential skills for interpreting and utilizing maps accurately. This foundational knowledge about map scale empowers students in Class 11 Geography to analyze distances, spatial relationships, and map representations with confidence. Through this complete guide, you’ve explored various methods of map scale representation, including statements of scale, graphical scales, and representative fractions, along with conversion techniques to bridge different formats.
Whether for academic or practical use, the insights from “Map Scale – Complete Guide for Class 11 Geography Practical Chapter 2” will serve you well in your journey to understanding the Earth’s geography and mapping intricacies. Keep revisiting these concepts for a solid grasp, and let iPrep be your constant companion in this learning endeavor!
Practice questions on Chapter 2 - Map Scale
Get your free Chapter 2 - Map Scale practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now