Topographical Maps – Complete Guide For Class 11 Geography Practical Chapter 5

Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter “Topographical Maps” in Geography for Class 11th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions, and notes offer the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
The chapter “Topographical Maps” in Geography Class 11 provides a comprehensive understanding of topographical maps, their importance, and how to interpret them. The chapter covers various aspects such as the international map series, methods of relief representation, reading topographical maps, and the identification of physical and cultural features. It also delves into the interpretation of maps, which is essential for geographical studies.
Topographical maps are one of the most crucial tools in geography for representing the Earth’s surface in detail. Chapter 5 of Geography Class 11, titled “Topographical Maps,” introduces students to the basics of topographical maps, how they are created, and how to read and interpret them effectively. The chapter offers insights into different methods of representing relief features and understanding contour lines. It also emphasizes the importance of being able to identify various natural and cultural features on maps, which helps in understanding geographical landscapes better.
Objectives of Learning The Chapter – Topographical Maps
Now that we have explored the importance of the chapter, let’s outline the objectives of studying it.
- To understand the significance of topographical maps.
- To learn how to read and interpret topographical maps.
- To explore various methods of relief representation, such as contour lines.
- To identify physical and cultural features from topographical sheets.
- To grasp the basic principles of map interpretation.
Now let’s explore the various sections of the chapter.
Firstly, to understand the fundamentals of topographical maps, let’s delve into the Introductory section of the chapter ‘Topographical Maps’.
What Are Topographical Maps?
Topographical maps are detailed, large-scale maps that represent the Earth’s surface features, including natural landscapes (such as mountains, rivers, and valleys) and human-made elements (like roads, buildings, and railways). They use contour lines to show elevation and relief, helping users interpret the shape, height, and depth of terrain.
Key Points:
- Topographical maps represent the Earth’s surface features in detail, including natural landscapes, relief, and cultural features.
- They are essential for understanding geography, planning, and navigation.
Now, to understand the global standard for mapping, let’s explore the section International Map Series of the World in the chapter ‘Topographical Maps’.
International Map Series of the World
- The International Map Series of the World (IMSW) is a standardized set of maps that provides consistent coverage and scale across the globe.
- It is widely used for various purposes, including scientific research, planning, and navigation.
Now, to learn how to read maps, let’s discuss the section Reading of Topographical Maps of the chapter ‘Topographical Maps’.
Reading of Topographical Maps
- Reading topographical maps involves understanding symbols, scales, and the layout of natural and man-made features.
- Essential for navigation, geographical analysis, and interpretation of landscapes.
Now, to understand the different ways relief is shown on maps, let’s undertake the section Methods of Relief Representation of the chapter ‘Topographical Maps’.
Methods of Relief Representation
- Relief representation methods include hachures, shading, and contours.
- These methods help depict the elevation and slope of the terrain.
Now, to explore how contours are used to depict terrain, let’s delve into the section Contours of the chapter ‘Topographical Maps’.
Contours
- Contour lines represent elevation on topographical maps.
- They connect points of equal altitude and help visualize the land’s shape and slope.
Some Basic Features of Contour Lines Are:
- Spacing: Close contours indicate steep slopes, while wide-spaced contours indicate gentle slopes.
- Crossing Rivers: Contour lines form a V-shape when crossing rivers, pointing upstream.
Now, to understand how to represent landforms through contour lines, let’s explore the section Drawing of Contours and Their Cross Sections of the chapter ‘Topographical Maps’.
Drawing of Contours and Their Cross Sections
- Drawing cross sections from contour maps gives a side view of the terrain.
- This method helps in visualizing the gradient of slopes and landforms.
Now, in order to understand the types of the slope, let’s delve into the section Types of Slope of the chapter ‘Topographical Maps’.
Types of Slope
- Gentle Slope: Wide-spaced contour lines.
- Steep Slope: Close contour lines.
- Concave Slope: Contours are closely spaced at the top, and wider at the bottom.
- Convex Slope: Contours are widely spaced at the top, closer at the bottom.
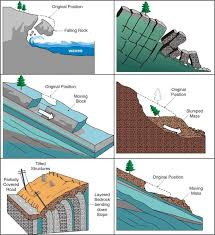
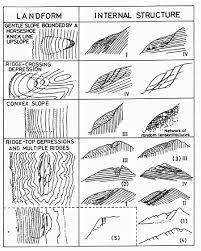
Now, to explore various landforms represented on maps, let’s discuss the section Types of Landforms of the chapter ‘Topographical Maps’.
Types of Landforms
- Conical Hill: Represented by concentric contour lines that form circles.
- Plateau: Flat-topped landforms with steep sides.
- Valley:
- V-shaped Valley: Indicated by V-shaped contour lines.
- U-shaped Valley: Wider and more open than V-shaped valleys.
- Gorge: Steep-sided valleys, often represented by close contours.
- Spur: A ridge projecting out from the side of a mountain.
Now, to understand how to create terrain profiles, let’s undertake the section Steps for Drawing a Cross-section of the chapter ‘Topographical Maps’.
Steps for Drawing a Cross-section
- Identify the points of interest on the map.
- Mark the contour intervals.
- Plot the elevation points and connect them to create a side profile of the landform.
Now, to understand how to identify human-made features on maps, let’s explore the section Identification of Cultural Features from Topographical Sheets of the chapter ‘Topographical Maps’.
Identification of Cultural Features from Topographical Sheets
- Distribution of Settlements: Identifying urban or rural areas.
- Transport and Communication Pattern: Roads, railways, and communication lines are depicted using specific symbols.
Now, to understand how to interpret topographical maps, let’s delve into the section Interpretation of Topographical Maps of the chapter ‘Topographical Maps’.
Interpretation of Topographical Maps
(a) Marginal Information:
- Provides essential details like scale, grid reference, and map symbols.
(b) Relief and Drainage:
- Relief features like mountains, valleys, and drainage patterns like rivers and lakes.
(c) Land Use:
- Different land uses such as agriculture, forests, and settlements are identified.
(d) Means of Transport and Communication:
- Identification of roads, railways, and communication lines.
(e) Human Settlement:
- Differentiates between types of settlements, such as villages and cities.
Now, to explore the process of interpreting maps, let’s undertake the section Map Interpretation Procedure of the chapter ‘Topographical Maps’.
Map Interpretation Procedure
- Start by understanding the map’s scale and orientation.
- Identify major landforms and relief features.
- Analyze cultural and natural features to get a comprehensive understanding.
Finally, as we have gained comprehensive knowledge about the chapter “Topographical Maps”, let’s reflect on the overall learning value of this important lesson.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter
The chapter “Topographical Maps” provides students with the foundational skills to interpret and understand topographical maps. From recognizing contour lines and landforms to interpreting cultural and physical features, the chapter equips learners with valuable tools for geographical analysis. By mastering these skills, students can apply this knowledge to various real-world scenarios, such as navigation, planning, and environmental studies. Understanding topographical maps is crucial for anyone studying geography or related fields.
Let’s Conclude
In conclusion, CBSE Class 11th Geography Chapter “Topographical Maps” offers students a robust foundation in reading and interpreting topographical maps, an essential skill in geographical studies. Throughout this chapter, “Topographical Maps,” learners explore various techniques for identifying natural and cultural features, understand the importance of contour lines, and gain insights into different types of slopes and landforms.
By mastering these elements, students can enhance their spatial awareness and apply these skills to real-life scenarios, from environmental assessments to urban planning. We hope that through the iPrep Learning Super App, Class 11th Geography learners find this chapter, “Topographical Maps,” not only informative but also engaging and practical. Embark on your journey of learning and let Chapter “Topographical Maps” in Geography for Class 11th open new horizons in understanding our world’s landscapes!
Practice questions on Chapter 5 - Topographical Maps
Get your free Chapter 5 - Topographical Maps practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now