Getting to Know Plants – Complete Guide For Class 3 EVS Chapter 4
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for Chapter 4, “Getting to Know Plants,” in Class 3 EVS are thoughtfully crafted to provide students with a deep and thorough grasp of plant life. The materials include interactive activities, hands-on learning, and clear explanations of plant structures such as roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. With detailed examples and observation-based tasks, students explore the role of plants in the ecosystem. From basic plant types to their functions, these resources ensure a solid understanding of the chapter’s core concepts.
The concept of “Getting to Know Plants” in Class 3 EVS explores the fundamental principles of life by examining essential plant characteristics. It focuses on different types of plants such as trees, shrubs, herbs, and creepers, highlighting their unique structures and functions. The chapter “Getting To Know Plants” delves into how plants grow, the role of their parts like roots and stems, and their importance in the ecosystem. This exploration fosters an understanding of nature’s diversity and the interconnection between plants and their environment.
So Many Kinds of Plants

In the chapter “Getting to Know Plants” Class 3 EVS, uncovers the story of Gopu, Simmi, and Raj, who observe different plants on their way to school. They notice the diversity in plant shapes, sizes, and leaf textures. Trees, such as the Jamun tree, stand out with their thick trunks and expansive branches. Examples of trees include:
Trees Examples Large Trees Mango, Coconut Other Trees Khejri, Jackfruit, Peepal, Chinar
Shrubs
As mentioned in the chapter “Getting To Know Plants” Shrubs are medium-sized plants with several stems, usually found close to the ground. They don’t grow as tall as trees and have multiple woody stems. Examples include:
Shrubs Examples Flowering Shrubs Hibiscus, Rose Other Shrubs Holy Basil (Tulsi), Curry Leaf
Herbs and Grasses

Herbs are small plants with soft, green stems, and they don’t become woody. Grasses also have soft, green stems and thin leaves. Both herbs and grasses are found abundantly in nature. Some common examples are:
Herbs Examples Herbs with Soft Stems Mint, Tomato, Coriander Grasses Examples Wild Grasses Sugarcane, Bamboo
Climbers and Creepers
Climbers are plants with thin, flexible stems that climb up trees or structures for support, while creepers spread along the ground.

| Type | Examples |
| Climbers | Money Plant, Jasmine, Bottle Gourd |
| Creepers | Watermelon, Pumpkin |
Making Friends with a Plant
Students are encouraged to make friends with a plant, observe its growth, and record their observations about its leaves, flowers, and fruits. Tracking these changes helps to build an understanding of plant growth patterns. Here is a sample observation table:
Plant Parts Many/Few/None Colour Shape Observations Leaves Many Green Oval New leaves visible Flowers Few Yellow Round Buds forming Fruits None N/A N/A Not seen yet
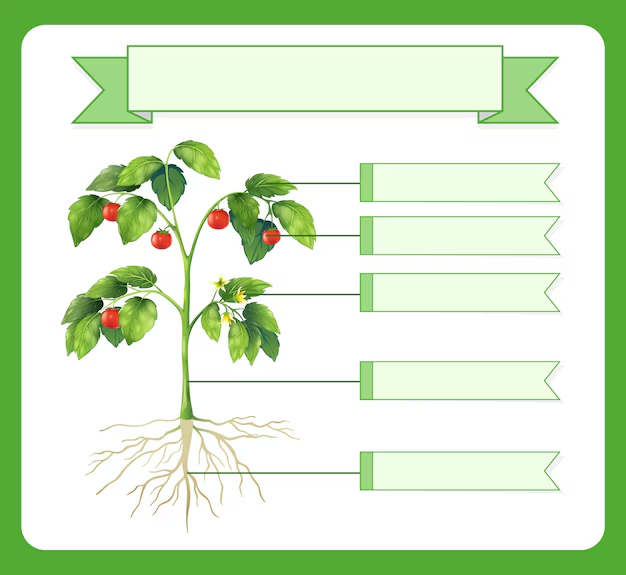
Parts of a Plant
Every plant consists of parts like roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds. Understanding the role of each part is crucial for understanding plant biology.
- Roots: Anchor the plant and absorb nutrients.
- Stem: Supports the plant and transports nutrients.
- Leaves: Carry out photosynthesis.
- Flowers: Aid in reproduction.
- Fruits: Contain seeds for new plants.
Leaves and Their Characteristics
Leaves come in various shapes, sizes, textures, and smells. Activities in this section encourage children to explore and describe the leaves around them by observing their unique characteristics. Some examples of leaves are:
Plant Type Special Characteristic Peepal Tree Heart-shaped leaves Lotus Aquatic Round, large leaves Mango Tree Long and leathery leaves
The Importance of Plants
In a discussion-based activity, students reflect on the importance of plants in maintaining life on Earth. They explore how roots help plants grow, how stems provide support, and the significance of leaves in food production.
Fun with Plants: Rangoli Activity
A creative activity where students collect fallen leaves and flowers to create beautiful patterns in the form of rangoli. This encourages creativity while nurturing respect for nature.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Chapter 4: “Getting to Know Plants” in Class 3 EVS serves as a crucial foundation for young learners to understand the world of plants. Through this chapter, students are introduced to different types of plants—trees, shrubs, herbs, climbers, and creepers—and their unique features. By learning about plant parts, such as roots, stems, and leaves, students develop a strong appreciation for how plants grow and contribute to ecosystems.
Chapter 4: “Getting to Know Plants” in Class 3 EVS also encourages observation-based learning, helping students form a deeper connection with the environment. By observing plants in their surroundings, students become more aware of the diversity of plant life and its significance in everyday life. The activities in this chapter, such as making friends with a plant or creating plant-based rangoli patterns, offer hands-on learning that makes the concepts engaging and memorable.
Overall, Chapter 4: “Getting to Know Plants” in Class 3 EVS not only covers the scientific aspects of plant life but also promotes environmental stewardship, fostering a lifelong appreciation for nature.
Practice questions on Chapter 4 - Getting To Know Plants
Get your free Chapter 4 - Getting To Know Plants practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








