Fair Share – Complete Guide For Class 3 Math Chapter 8
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, Fair Share in Mathematics for Class 3rd are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
Students will study the ideas of division and sharing in this chapter in an interesting and simple manner. This chapter uses a realistic story and useful pictures to demonstrate key ideas such as halves, quarters, and wholes. These ideas serve as the basis for understanding fractions, a crucial topic in mathematics. Below is a summary of the subjects discussed in this chapter. Let’s Start with the meaning of Fair Share.
Meaning Of Fair Share
The term “Fair Share” refers to dividing something equally among all participants, ensuring that everyone gets an equal portion. In CBSE Class 3rd Math, Chapter 8 – Fair Share, students learn this concept through division, where items are split into halves or quarters to make sure each person receives a fair and equal amount. This idea forms the foundation for understanding fractions in mathematics.
A Story About Two Girls Sharing
The chapter “Fair Share” begins with a story of two girls, Shabnam and Mukta, who decide to share a chocolate bar. The idea of sharing helps students understand the basic concept of division and fairness.
Story Example:
Their mother gives Shabnam and Mukta one chocolate bar. They want an equal division of it. How much will each girl get if they each take half? To ensure that each girl receives an equal portion, the chocolate bar is cut into two equal portions.
- Shabnam gets half the chocolate,
- Mukta gets half the chocolate.

This simple story illustrates the concept of fairness and equality in division, setting the stage for the introduction of halves and quarters.
Concept of Half and Double
Once students understand sharing, the concept of half and double is introduced in the chapter Fair Share. “Half” means dividing something into two equal parts, while “double” means multiplying or adding the quantity to make it twice as much.
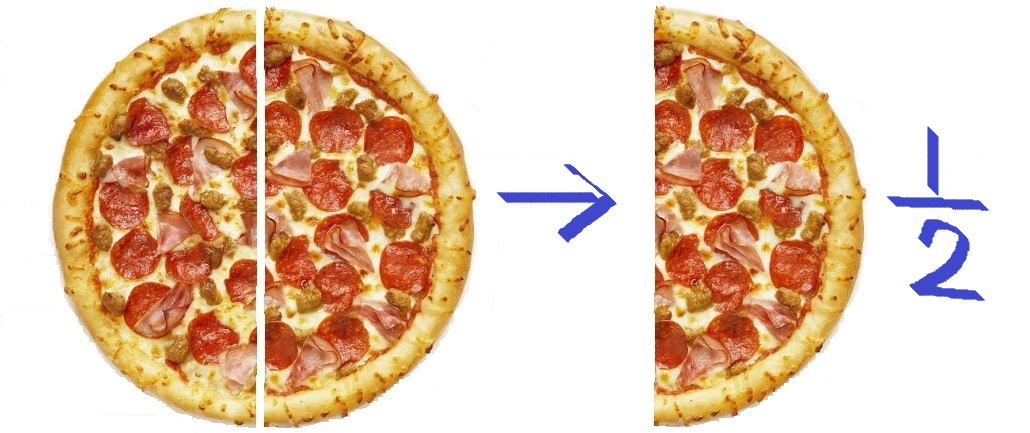
- Half of an object or number is one of the two equal parts.
Example: If you cut an apple into 2 equal pieces, each piece is half. So, half of 1 apple is ½ apple. - Double is the opposite of half, meaning two times as much.
Example: If Shabnam had 1 chocolate bar and Mukta had 1 chocolate bar, together they would have double the amount, which is 2 chocolate bars.
These concepts are explored with more examples to show how numbers and objects can be halved or doubled.
Key Practice:
- Half of 8 is 4 (8 ÷ 2 = 4),
- The double of 5 is 10 (5 × 2 = 10).
Half and Quarter
Next, students learn about quarters. The idea of quarters builds on their understanding of halves and doubles. A quarter is one part when something is divided into four equal parts.
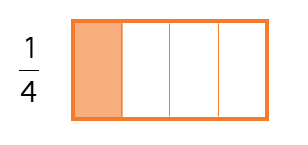
Example:
If Shabnam and Mukta invite two more friends, they now have 1 chocolate bar to share among 4 people. If they divide the chocolate bar equally, each person will get a quarter of the chocolate. A quarter is represented as ¼.
- Half is one of two equal parts (½).
- The quarter is one of four equal parts (¼).
Students are encouraged to practice dividing different objects into halves and quarters, using examples such as cutting a pizza, dividing a cake, or sharing a basket of fruits.
Key Practice:
- Half of 1 chocolate bar is ½,
- A quarter of 1 chocolate bar is ¼.
Quarters and Wholes with Examples
In this section of the chapter Fair Share, students learn how quarters combine to form wholes. Four quarters make a whole, just as two halves make a whole.

Example:
If Shabnam and her friends each receive ¼ of the chocolate bar, then:
- ¼ + ¼ + ¼ + ¼ = 1 whole chocolate bar.
This concept helps students understand that fractions can be used to divide and recombine objects into wholes.
Similarly, if you have two halves of a pizza:
- ½ + ½ = 1 whole pizza.
Real-Life Example:
- If a cake is cut into 4 equal pieces, and you eat 2 pieces, you have eaten half of the cake (2/4 = ½).
- If you eat 1 piece of the cake, you have eaten one-quarter of the cake (¼).
- If all 4 pieces are put back together, you will have the whole cake again.
This part of the chapter emphasizes that fractions like halves and quarters are parts of a whole, helping students grasp the idea that fractions represent division and parts of a whole object.
Conclusion
Through the chapter “Fair Share,” students learn fundamental concepts of division and fractions. They will understand how to:
- Divide objects and numbers into halves and quarters.
- Recognize the relationship between wholes, halves, and quarters.
- Apply these ideas in real-life situations like sharing food, dividing objects, and counting.
Students will have a solid understanding of fractions and how to use them in everyday situations by the end of this chapter. As children go through more difficult division and fractional concepts in mathematics, these ideas will get them ready.
In conclusion, CBSE Class 3rd Math, Chapter 8 – Fair Share provides students with a foundational understanding of division, halves, and quarters through engaging examples and relatable stories. The chapter introduces concepts such as sharing, halving, doubling, and dividing into quarters, which are essential for grasping more advanced topics like fractions. Through real-life scenarios and simple practices, students learn to apply these ideas in everyday tasks like sharing food or dividing objects equally. By the end of CBSE Class 3rd Math, Chapter 8 – Fair Share, students will be well-prepared to use these concepts to solve problems involving division and fractions. The knowledge gained from Fair Share will serve as a stepping stone for understanding more complex mathematical topics in the future.
Practice questions on Chapter 8 - Fair Share
Get your free Chapter 8 - Fair Share practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now