The French Revolution-Complete Guide For Class 9th History Chapter 1

Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, “The French Revolution” in History for Class 9th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best-integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
The French Revolution
The French Revolution, a pivotal chapter in world history, was a period of profound transformation that shook the foundations of French society. It unfolded between 1789 and the late 1790s, culminating in overthrowing the absolute monarchy and the establishment of a republic. This chapter explores the complex factors that led to the revolution, the key events that shaped its course, and the far-reaching consequences that extended beyond France’s borders. By examining French society before the revolution, the key stages of the revolution, and its impact on different segments of society, this chapter offers a comprehensive understanding of this momentous event.
The French Revolution was more than just a political upheaval; it was a social, economic, and cultural transformation. It marked a decisive break from the past, challenging the established order and ushering in new ideas about liberty, equality, and popular sovereignty. This chapter delves into the heart of The French Revolution, examining its causes, course, and consequences.
Objectives Of Learning the French Revolution
Now that we know the importance of studying this chapter, let’s understand the objectives behind studying the chapter, “The French Revolution”.
- To understand the social and economic conditions in France before the revolution.
- To analyze the key events and phases of The French Revolution.
- To evaluate the impact of The French Revolution on different sections of society.
Let’s now discuss the sections of the chapter in detail.
First of all, to understand the social and economic conditions that fueled the revolutionary fervor, let’s discuss the section ‘French Society During the Late Eighteenth Century’ of the chapter ‘The French Revolution’.
French Society During the Late Eighteenth Century
The seeds of The French Revolution were sown in the deep-rooted inequalities and contradictions of French society.
- The Struggle to Survive: The majority of the French population, comprising peasants and artisans, lived in dire conditions. They bore the brunt of taxation and faced subsistence crises.
- A Growing Middle Class Envisages an End to Privileges: The bourgeoisie, a burgeoning middle class, accumulated wealth and education but was denied political power. They yearned for equality and an end to aristocratic privileges.
Now to understand the critical events that triggered the French Revolution and the transition from monarchy to a constitutional government, let’s discuss the section ‘The Outbreak of the Revolution’ of the chapter ‘The French Revolution’.
The Outbreak of The French Revolution
A confluence of factors ignited the spark of revolution in France.
- Introduction: Economic hardship, social inequality, and political discontent created a volatile atmosphere.
- France Becomes a Constitutional Monarchy: The Estates-General convened to address the financial crisis, and evolved into the National Assembly, marking the first step towards limited monarchy. The storming of the Bastille symbolized the people’s determination to overthrow the old order.
Now to understand the radical shifts in governance that led to the establishment of a republic and the end of the monarchy, let’s discuss the section ‘France Abolishes Monarchy and Becomes a Republic’ of the chapter ‘The French Revolution’.
France Abolishes Monarchy and Becomes a Republic
The revolution intensified, leading to the abolition of monarchy and the establishment of a republic.
- The Reign of Terror: A period of radical change and violence, characterized by the dominance of the Jacobins and the execution of those deemed enemies of the revolution.
- A Directory Rules France: After the fall of Robespierre, the Directory assumed power, but it faced challenges in stabilizing the nation.
Now to understand the role and impact of women during the French Revolution, let’s discuss the section ‘Did Women Have a Revolution?’ of the chapter ‘The French Revolution’.
Did Women Have a Revolution?
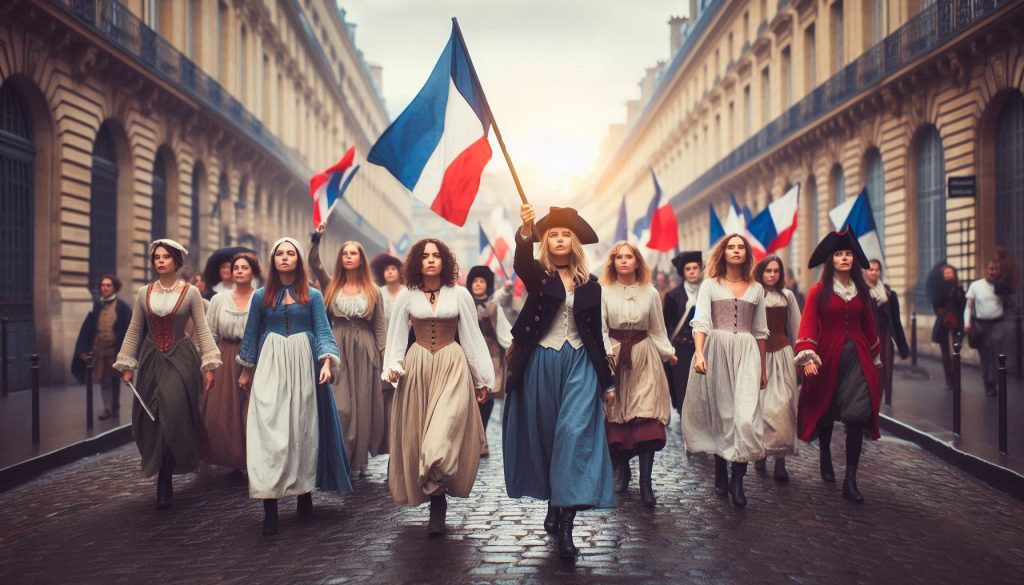

The French Revolution raised hopes for women’s emancipation, but the reality fell short of expectations.
- Women’s Role in The French Revolution: Women actively participated in revolutionary activities, demanding rights and equality.
- The Declaration of Rights of Woman and the Female Citizen: Olympe de Gouges authored this declaration, advocating for women’s rights.
- Limitations and Setbacks: Despite their contributions, women’s rights were not fully realized during The French Revolution.
Now to understand the daily experiences and societal changes brought about by the French Revolution, let’s discuss the section ‘The Revolution and Everyday Life’ of the chapter ‘The French Revolution’.
The Revolution and Everyday Life
The French Revolution had a profound impact on the lives of ordinary people.
- Changes in Society and Culture: The revolution challenged traditional social norms and introduced new ideas about citizenship and governance.
- Economic Transformations: Efforts were made to reform the economy, but the revolution’s impact on the lives of the common people was complex and varied.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter
The overall learning value of the chapter “The French Revolution” lies in understanding the profound social, political, and economic transformations that reshaped France and influenced global history. It provides insight into the causes and effects of revolutionary change, the struggles for equality and rights, and the enduring legacy of these events in shaping modern democratic and social institutions.
Practice questions on Chapter 1 - French Revolution
Get your free Chapter 1 - French Revolution practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now