Crop Production and Management – Complete Guide For Class 8 Science Chapter 1
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, Crop Production and Management in Science Class 8th chapter 1 are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
The concept of Crop Production and Management in Class 8 Science introduces students to a comprehensive understanding of how crops are cultivated, maintained, and managed to ensure a stable food supply. This topic is crucial as it addresses the fundamental need for food security and highlights the importance of agriculture in sustaining human life.
Crop Production and Management
Food is essential for all living organisms. It provides the necessary energy for survival and growth. While animals, including humans, cannot produce their own food, plants have the unique ability to produce food through photosynthesis. This makes crop production and management crucial for our sustenance.
What is a Crop?
A crop refers to any plant cultivated on a large scale. For example, if a field is entirely planted with wheat, it is termed a wheat crop. Effective crop production and management practices are vital to growing healthy crops, meeting the food demands of the population, and maintaining agricultural productivity.

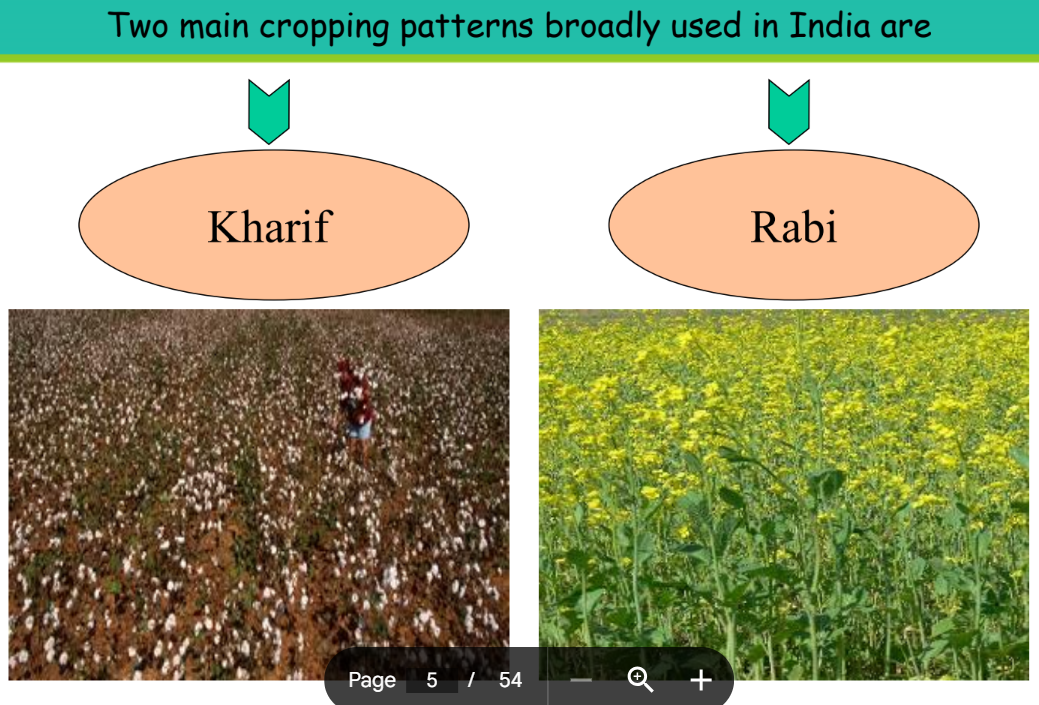
Cropping Patterns in India
In India, crop production and management are closely linked to the country’s cropping patterns, which are largely influenced by seasonal variations in climate and water availability. India primarily follows two main cropping patterns:
- Kharif Crops: Grown during the rainy season (June to September). Examples include maize, soybean, and cotton.
- Rabi Crops: Cultivated in the winter season (October to March). Examples are wheat, peas, and mustard.
Agricultural Practices
Crop production and management involve a series of agricultural practices designed to ensure the optimal growth and yield of crops. These practices are similar to the care and maintenance of ornamental plants at home but on a larger scale. Farmers engage in a range of activities to cultivate crops effectively, aiming to ensure healthy plants and maximize yields.
Basic Practices of Crop Production
In crop production and management, following basic practices are essential to ensure optimal growth and high yields.
Soil Preparation: In crop production and management, soil preparation is a foundational step that significantly impacts the success of subsequent agricultural practices. It involves several key activities aimed at creating an optimal environment for seed germination and plant growth:
- Purpose: Turning and loosening the soil to bring nutrient-rich soil to the top and allow root penetration. Loosened soil also aids in the growth of earthworms and microbes.
- Loosening is done in two steps :
- Ploughing: Loosening and turning of soil using plows made of wood or iron.
- Leveling: Breaking big pieces of soil lumps using a leveler.
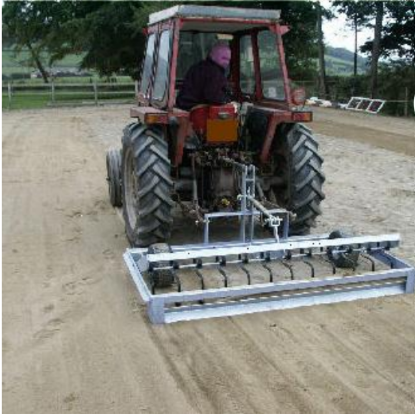

Sowing: In crop production and management, sowing is a crucial step that directly influences crop growth and yield. This phase involves-
- Seed Selection: Choosing healthy and good quality seeds for high yield.
- Traditional Tools: Using a funnel-shaped tool for sowing.
- Modern Methods: Seed drills ensure seeds are sown in well-spaced rows and are covered with soil, protecting them from birds.
Adding Manures and Fertilizers: In crop production and management, adding manures and fertilizers plays a critical role in ensuring that crops receive the essential nutrients needed for healthy growth and optimal yields.
- Manures: Natural substances from decomposed plant and animal waste. They improve soil texture and water retention.
- Fertilizers: Compounds that promote plant growth, rich in nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Irrigation: In crop production and management, irrigation is essential for providing the necessary water supply to crops, especially in areas where rainfall is insufficient or irregular. Effective irrigation practices ensure that crops receive adequate moisture throughout their growth stages, leading to healthier plants and improved yields.
- Sources: Wells, tube wells, ponds, rivers, dams, and canals.
- Traditional Methods: Moat, chain pump, dhekli, and rahat.
- Modern Methods: Sprinkler and drip systems.


Weeding: In crop production and management, weeding is a critical practice aimed at removing undesirable plants, or weeds, that compete with crops for resources such as nutrients, water, and sunlight.
- Methods: Manual removal and use of weedicides.
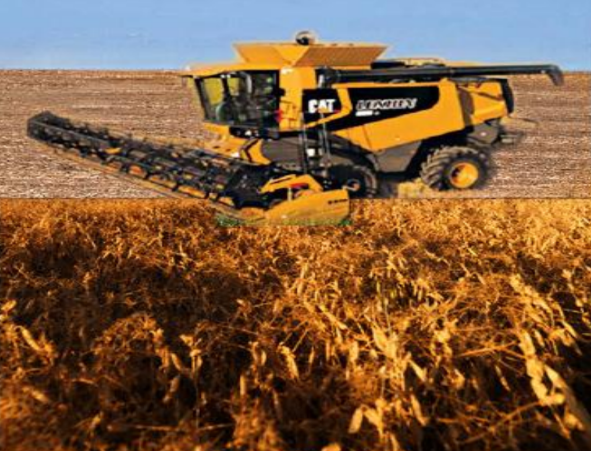
Harvesting: In crop production and management, harvesting is a crucial final step that involves gathering mature crops from the fields. Proper harvesting techniques are essential to ensure the quality and quantity of the produce, which directly impacts overall crop yield and profitability.
- Threshing: Separating grain seeds from the harvested crop.
- Winnowing: Separating the chaff from the grain.

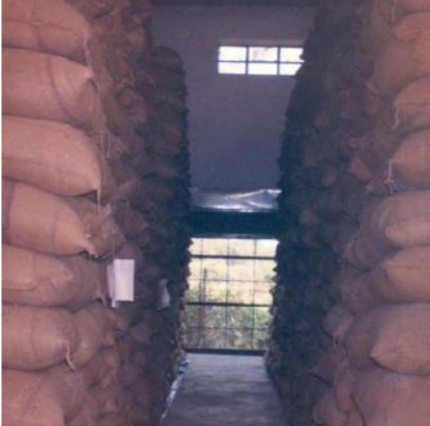
Storage: In crop production and management, storage is a vital process that involves preserving harvested crops for future use.
- Safety Measures: Protecting grains from moisture, insects, and rats using proper drying techniques and natural repellents like Neem leaves.

Food from Animals
In crop production and management, the concept of food from animals plays a complementary role, as animal husbandry and crop cultivation are interlinked in agricultural systems. Effective management of both crops and livestock contributes to overall farm productivity and sustainability.
Animals also provide various food products:
- Fish Products: A staple in coastal diets, available in forms like raw fish, grilled fish, and fish curry.
- Meat Products: Includes fried chicken, chicken burgers, sausage, and salami.
- Milk and Milk Products: Considered an ‘ideal food’ due to its balanced diet components.

Animal Husbandry
In crop production and management, animal husbandry plays a critical role by complementing crop cultivation and contributing to the overall efficiency of agricultural systems. Animal husbandry involves the care and breeding of domestic animals on a large scale, providing them with proper food and shelter to meet human needs. The types of animal husbandry are as follows:
Types of Animal Husbandry
- Dairy Farming: Raising cattle, buffalo, goats, and sheep for milk production.
- Poultry Farming: Rearing chickens, ducks, turkeys, and other birds for eggs and meat.
- Sheep and Goat Farming: Raising sheep and goats for wool, meat, and milk.
- Aquaculture: Cultivating fish, shellfish, and other aquatic organisms in controlled environments for food.
This comprehensive guide offers an in-depth exploration of the essence of crop production and management, highlighting the various processes and techniques involved in agriculture. It also highlights the significant role of animal husbandry in food production.
Practice questions on Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management
Get your free Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








