Conservation of Plants and Animals – Complete Guide For Class 8 Science Chapter 5
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App! Our learning resources for the chapter, Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8th chapter 5 are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
The chapter on Conservation of Plants and Animals in Class 8 Science highlights the importance of preserving biodiversity and natural habitats. It discusses deforestation and its adverse effects, such as climate change and loss of species. Conservation methods like wildlife sanctuaries, national parks, and biosphere reserves are crucial for protecting flora and fauna. The topic emphasizes reforestation and the protection of endemic and endangered species. It also covers the significance of recycling and resource conservation to maintain ecological balance.
Conservation of Plants and Animals


Conservation of plants and animals is essential to maintain biodiversity and ecological balance. It helps preserve natural habitats, ensuring the survival of various species that are crucial for ecosystem functions. Moreover, conserving plants and animals supports human livelihoods by sustaining natural resources and ecosystem services vital for agriculture, medicine, and clean air and water.
Understanding Forests
Have you ever wondered about the role of forests in our ecosystem? Forests are vibrant places filled with a wide variety of plants and animals. They provide essential food and shelter to wildlife and play a crucial role in maintaining the atmosphere. However, human activities have led to the destruction of forests, known as deforestation, which is why the conservation of plants and animals is vital. This is achieved through initiatives like wildlife sanctuaries and national parks.
What is Deforestation?
Conservation efforts are crucial in combating deforestation, which involves the permanent destruction of indigenous forests and woodlands. It is primarily done to utilize the land and resources for various purposes.
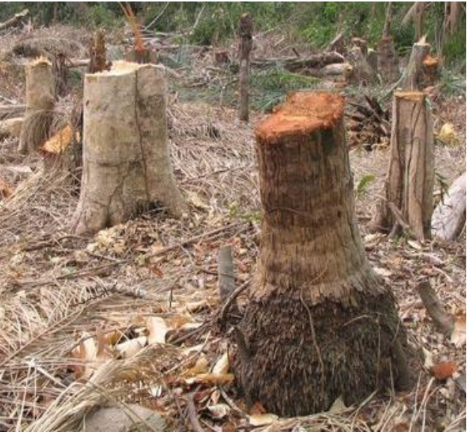

Reasons for Deforestation: Conservation is important to mitigate activities that lead to the destruction of forests. By conserving natural resources, we aim to protect biodiversity and promote sustainable land use. For that we need to explore the following reasons for deforestation –
- Procuring Land for Cultivation: Land is cleared to make way for agricultural activities.
- Building Houses and Factories: Urbanization leads to the conversion of forested areas into residential and industrial zones.
- Making Furniture: Trees are cut down to supply wood for furniture manufacturing.
- Using Wood as Fuel: In many areas, wood remains a primary source of fuel for cooking and heating.
- Natural Causes: Forest fires and severe droughts can also contribute to deforestation.
Consequences of Deforestation
Deforestation affects the environment by disrupting ecosystems and reducing biodiversity, which in turn harms both plant and animal life. Conservation efforts help reduce the impacts of deforestation by protecting natural habitats and promoting sustainable land use. Let us explore the consequences of deforestation given as under-.
- Increased CO2 Levels: Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. When forests are cleared, this carbon is released back into the atmosphere, leading to increased CO2 levels.
- Lowered Groundwater Levels: Trees draw groundwater through their roots and release it into the atmosphere through transpiration. Removing trees can lead to a drier climate and reduced groundwater levels.
- Decrease in Rainfall and Soil Fertility: Continuous deforestation can result in decreased rainfall and soil fertility, increasing the risk of natural disasters like floods and droughts.
- Desertification: Fertile land can turn into deserts, a process known as desertification.

Conservation Efforts
Conservation of forests and wildlife is essential to maintaining the biosphere and biodiversity. The government has implemented rules, policies, and methods to preserve these biologically important areas.

Protected Areas: To conserve wildlife, plant, and animal resources following areas are being considered protected –
- Wildlife Sanctuaries: Designated areas reserved for the protection of animals where human activities like hunting and poaching are prohibited.

- National Parks: Regions reserved for wildlife, allowing them to utilize habitats and natural resources freely.
- Biosphere Reserves: Large protected areas that conserve wildlife, plant and animal resources, and the traditional lifestyles of tribal communities.
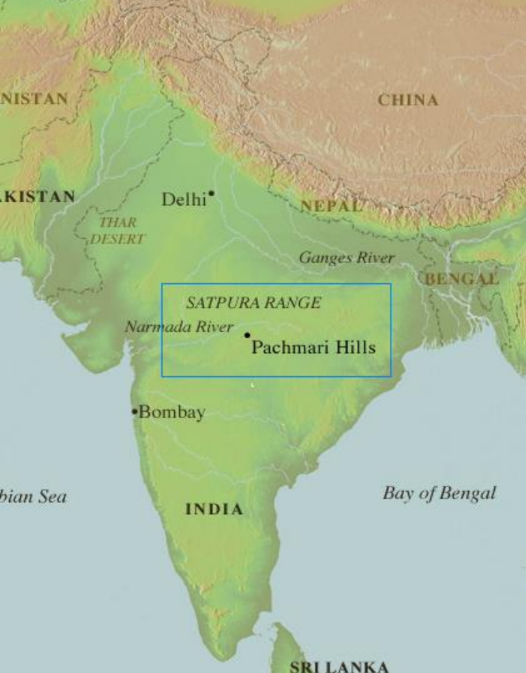
Examples of Biosphere Reserves in India: The following reserves play a crucial role in conservation by providing protected areas for diverse wildlife and plant species.
- Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve in Madhya Pradesh includes Satpura National Park and two wildlife sanctuaries, Bori and Panchmarhi.
- Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve is an International Biosphere Reserve in the Western Ghats, South India.
- Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve in Uttarakhand is part of the Garhwal Himalayas.
- Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve in West Bengal is part of the world’s largest delta formed by the rivers Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna.
Flora and Fauna: Conservation efforts aim to protect both flora and fauna by preserving their natural habitats and ensuring biodiversity.

- Flora: Refers to the plants and plant life found in a particular area. For example, in Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve, the flora includes Sal, Mango, and Teak trees.
- Fauna: Refers to the animals and animal life found in a particular area. In the Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve, tigers, cheetahs, and crocodiles are considered fauna.
Endemic Species


Conservation efforts are crucial for protecting endemic species, as these are plants and animals that are found only in a specific location or area. For example:
- Nilgiri Flycatcher and Nilgiri Pipit are endemic to the Nilgiri Hills range in South India.
- Sal and Wild Mango trees are found in the Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve.
Reforestation
As stated in the chapter Conservation of Plants and Animals, Reforestation supports conservation by restoring deforested areas, which helps reestablish ecosystems and biodiversity. Reforestation involves planting or seeding trees in areas that previously contained forests. It can occur naturally or through artificial means.
- Natural Reforestation: Occurs when an area is left undisturbed for a long time, allowing nature to restore the forest.
- Artificial Reforestation: Involves human efforts to plant or seed areas where forest vegetation has been removed.
Importance of Recycling Paper

Recycling paper plays a crucial role in conservation by reducing the need for raw materials from trees, which helps prevent deforestation and preserves natural habitats. Approximately 17 fully grown trees are required to produce one tonne of paper. Saving just one sheet of paper a day can help save numerous trees annually.
Wildlife Sanctuaries in India
Wildlife sanctuaries in India help in conservation by providing protected habitats for animals, preventing human interference and poaching, and supporting biodiversity. India is home to many wildlife sanctuaries that provide natural habitats for wild animals. Some renowned wildlife sanctuaries include:
- Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary: Located in Rajasthan, it is one of the finest bird parks in the world, home to over 300 species of birds.
- Periyar Wildlife Sanctuary: Situated in Kerala, it offers habitats for elephants, wild pigs, sambar, and occasionally, tigers.

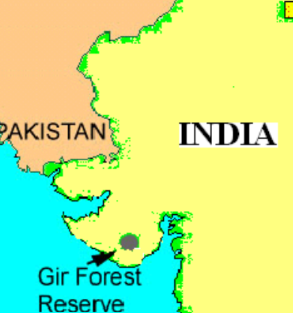
- Gir Wildlife Sanctuary: Located in Gujarat, it is one of the most important protected areas in Asia, known for its Asiatic lion population.
National Parks in India
National parks are crucial for wildlife conservation, allowing animals to use their habitats and resources freely. Some notable national parks include:
- Satpura National Park: India’s first reserve forest, known for its teak forests and rock shelters.
- Project Tiger: Launched in 1972 to protect Bengal tigers, aiming to maintain viable tiger populations in their natural environments.

- Tiger Reserves: Initially, nine tiger reserves were established in India, now expanded to 28, including Corbett, Kanha, Bandipur, Ranthambhore, and Sunderbans.
Red Data Book
The Red Data Book is published for the conservation of nature and natural resources. It records endangered animals and plants, with separate books for different species.
Migration
Many birds migrate to warmer regions during winter and return when the season ends. Some travel up to 15,000 km to escape harsh climates, returning to the same places annually.
This comprehensive guide on the conservation of plants and animals delves into the critical need for preserving our natural world. It underscores the significance of safeguarding biodiversity, which is essential for maintaining ecological balance and ensuring the sustainability of ecosystems. By focusing on various strategies such as protected areas, reforestation, and wildlife sanctuaries, the guide illustrates how these measures contribute to the health of our environment.
Practice questions on Chapter 5 - Conservation of Plants And Animals
Get your free Chapter 5 - Conservation of Plants And Animals practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








