Acids Bases and Salts – Complete Guide For Class 10 Science Chapter 2
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, Acids Bases and Salts in Science for Class 10th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
Acids bases and salts play a crucial role not just in chemistry, but in our daily lives as well. From the sourness of lemons to the cleaning power of soaps, these compounds are all around us, affecting everything from the food we eat to the products we use. In Acids Bases and Salts – Complete Guide For CBSE Class 10th Science Chapter 2, we will break down these essential concepts in a way that’s easy to understand, providing you with the knowledge and confidence to tackle this topic.
Through relatable examples, interactive learning, and in-depth explanations, you’ll master this chapter and be well-prepared for your exams. Let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of acids, bases, and salts!
What is an Acid?
According to the chapter Acids Bases and Salts, An acid is a substance with the following characteristics:
- Contains Replaceable Hydrogen Atom: An acid is defined as a compound that contains at least one replaceable hydrogen atom in its molecule.
- Produces Hydronium Ions: In an aqueous solution, an acid produces hydronium ions.
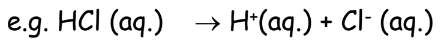
Arrhenius’s Theory of Acids
As stated in the chapter acids bases and salts, according to Arrhenius’s theory:
- Acid: A substance that furnishes H+\text{H}^+H+ ions in its aqueous solution.
- Hydronium Ion Formation:
Classification of Acids
Based on Strength
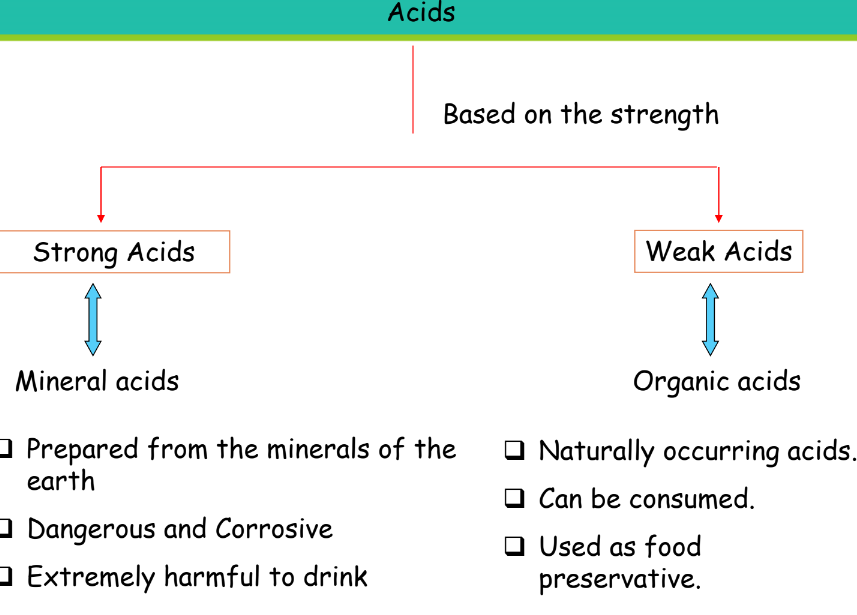
| Type of Acid | Description |
| Strong Acids | Mineral acids that are corrosive and harmful if ingested. |
| Weak Acids | Organic acids that are naturally occurring and safe to consume. |
Based on Concentration

| Type of Acid | Description |
| Concentrated Acids | Contains the minimum possible amount of water. |
| Dilute Acids | Contains a large amount of water. |
Basicity of Acids
According to the chapter Acids bases and salts, basicity refers to the number of hydronium ions furnished by one molecule of an acid:
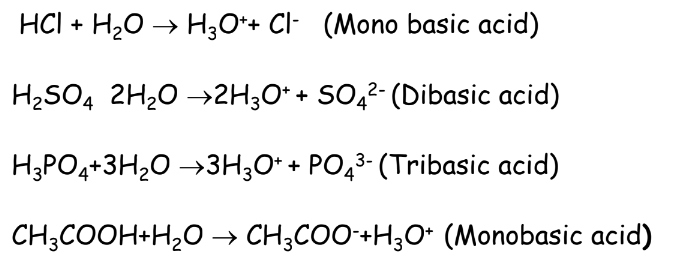
Chemical Properties of Acids
The chapter Acids Bases and Salts distinctively discusses the chemical properties of acids. These include:
Action on Indicators
| Indicator | Effect |
| Blue Litmus | Turns red |
| Methyl Orange | Turns red |
| Phenolphthalein | Remains colorless |
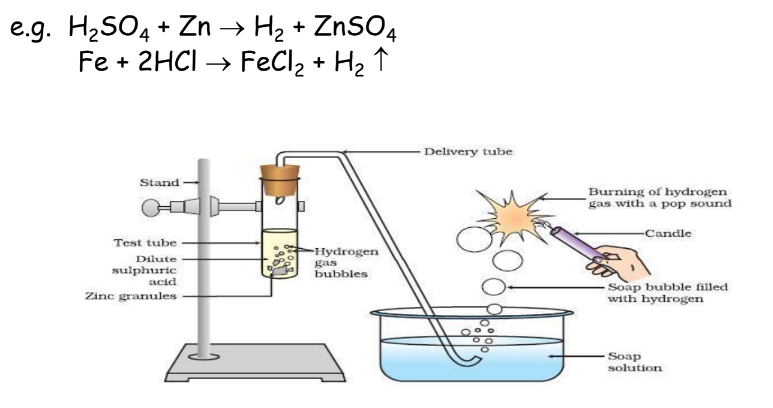
Action on Active Metals
Active metals like K, Na, Ca, Mg, Al, Zn, and Fe react with dilute acids to liberate hydrogen gas:
Action on Carbonates and Bicarbonates
As stated in the chapter Acids Bases and Salts, Acids react with metal carbonates or bicarbonates to produce salt, water, and carbon dioxide gas.
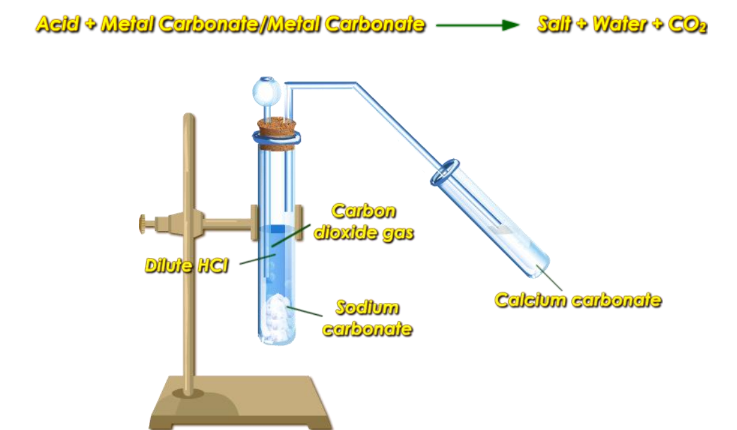
Action on Bases (Neutralization Reaction)
Acids react with bases to form salt and water:
Action on Metal Oxides
Acids react with metal oxides to form salt and water:
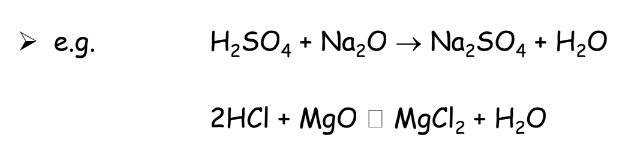
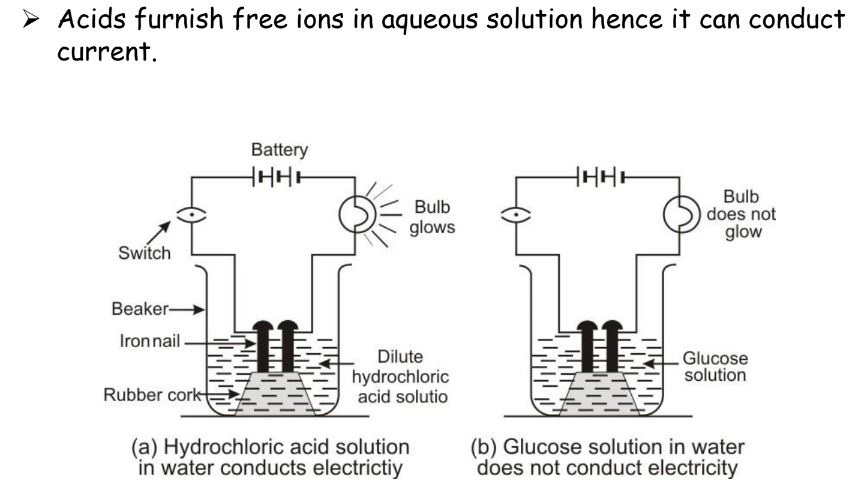
Acid as an Electrolyte
Acids furnish free ions in an aqueous solution, enabling them to conduct electricity.
What is a Base?
Bases are substances that furnish hydroxide ions (OH−\text{OH}^-OH−) in their aqueous solution:
- Example:
Acidity of Bases
Acidity refers to the number of hydroxide ions furnished by one molecule of a base:
Chemical Properties of Bases
The chapter acids bases and salts very thoroughly discussed the chemical properties of bases. These include:
Action on Indicators
| Indicator | Effect |
| Red Litmus | Turns blue |
| Methyl Orange | Gives orange color |
| Phenolphthalein | Turns pink |
Action on Metals
Bases react with some metals like Zn, Al, and Pb to liberate hydrogen gas:
Action on Acids
Bases react with acids to form salt and water:
Action on Non-Metal Oxides
Bases react with non-metal oxides to form salt and water:
pH Value
pH means puissance d’ hydrogen i.e. power of hydrogen ion in solution. It was introduced by Prof. Sorenson in 1990.

The pH scale measures the strength of an acid or a base:
- pH = 7: Neutral solution
- pH > 7: Alkaline (basic) solution
- pH < 7: Acidic solution
pH Scale and Common Substances
| Substance | pH Value |
| Concentrated Hydrochloric Acid | 0 |
| Dilute Hydrochloric Acid | 1.0 |
| Gastric Juices | 1.4 |
| Blood | 7.4 |
| Milk | 6.5 |
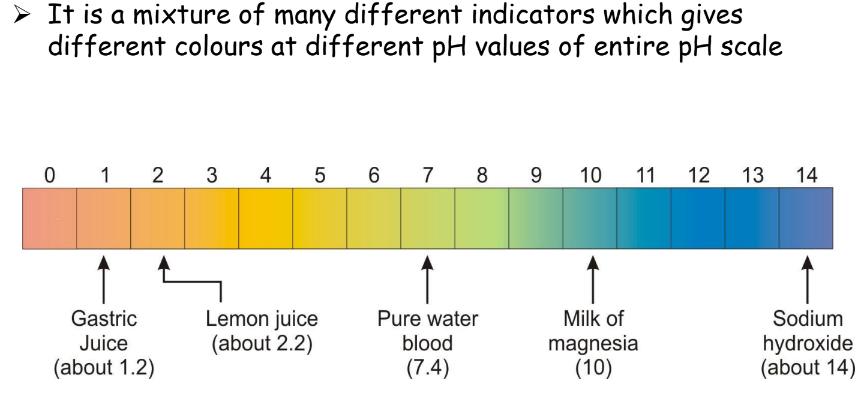
Universal Indicator
A mixture of several indicators that change color at different pH values, providing a comprehensive pH reading.
Applications of pH in our daily lives:
pH in Our Digestive System
- Hydrochloric Acid: Aids digestion and is naturally present in the stomach.
- Antacids: Contain compounds like magnesium hydroxide to neutralize excess stomach acid.
pH and Plants
Plants require a specific pH range for optimal growth. Highly acidic soil is treated with quicklime or slaked lime to lower its acidity.
pH and Nettle Stings
A nettle plant injects methanoic acid into the skin when touched. This can be neutralized by rubbing baking soda on the affected area.
the pH of Salt Solutions
| Type of Salt | pH of Solution |
| Salt of Strong Acid and Strong Base | |
| Salt of Strong Acid and Weak Base | |
| Salt of Weak Acid and Strong Base |
Salts
Salts are ionic compounds formed from the neutralization reaction between an acid and a base. They are electrically neutral and can be categorized into different families based on common radicals.
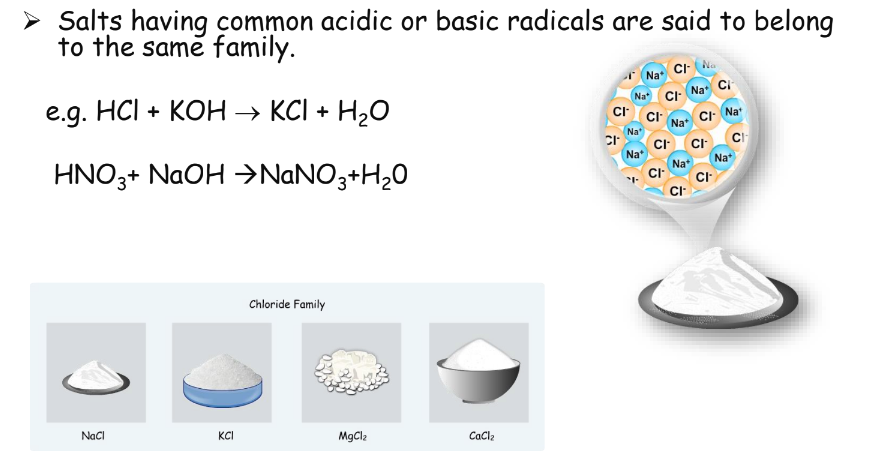
Common Salt (Sodium Chloride)
- Formation: Produced from the reaction between sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid. The pH value of common salt is 7.
- Uses:
- Enhances food taste.
- Hydrogen gas is used as fuel, margarine, in making ammonia for fertilizers, etc.
- Chlorine gas is used in water treatment, manufacturing of PVC, disinfectants, and CFC pesticides. It is also used in the manufacturing of bleaching powder and hydrochloric acid.
- Sodium hydroxide: De-greasing of metals, manufacturing of paper, soap, detergents, artificial fibers, bleach, etc.
Preparation and Uses of Sodium Hydroxide
Preparation
.
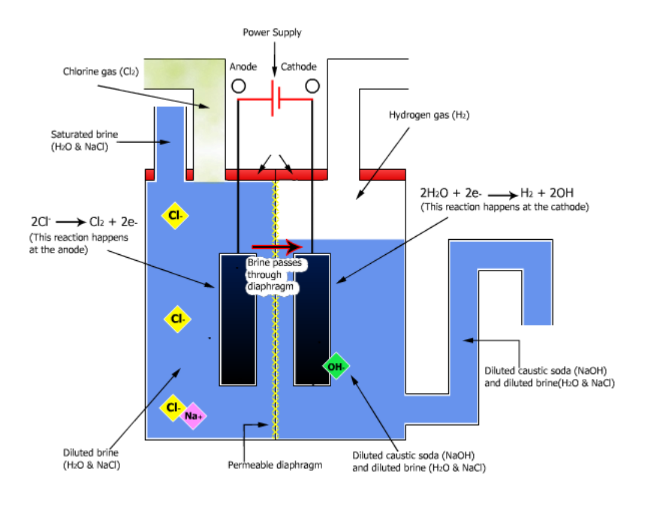
Uses
- Manufacturing soap, paper, rayon, and other chemicals.
- Refining petroleum and vegetable oils.
- Purifying bauxite for aluminum extraction.
- As a cleansing agent and laboratory reagent.
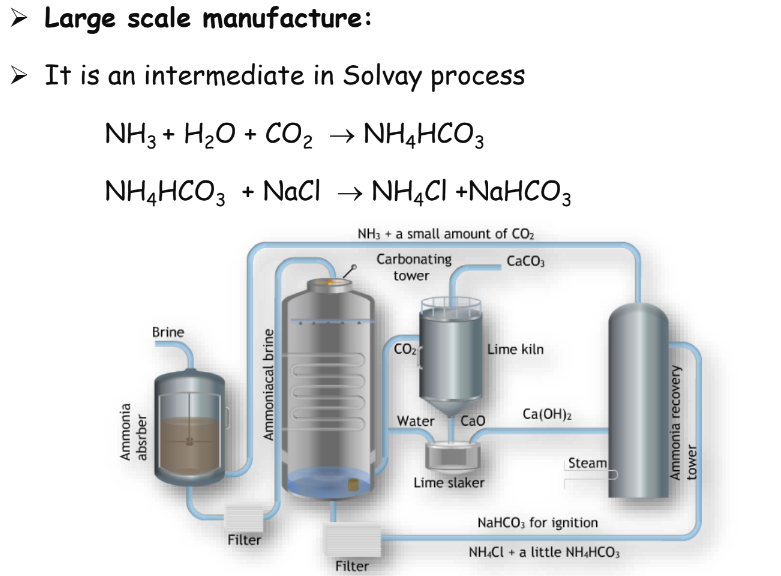
Preparation and Uses of Sodium Carbonate (Washing Soda)
Preparation
- Name: Washing soda
- Chemical Formula:
Uses
- Soap making, paper industry, removing permanent hardness of water, medicine manufacture, and domestic cleaning.
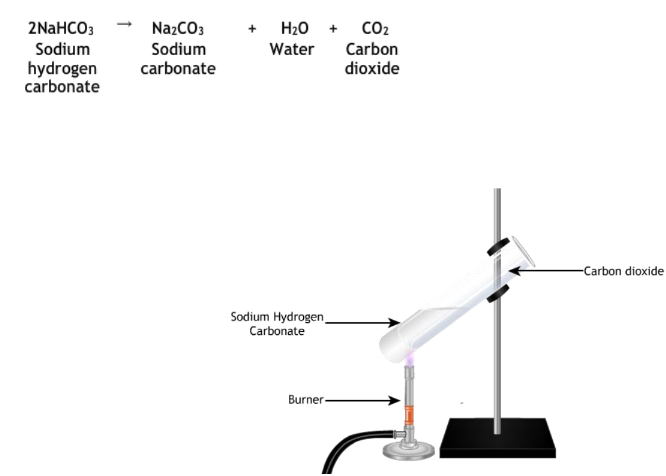
Preparation and Uses of Baking Soda
Preparation
- Common Name: Baking soda
- Chemical Formula:
- Laboratory Preparation:
Uses
- Fire extinguishing, neutralizing stomach acidity, aerated water, mild antiseptic.
Preparation and Uses of Bleaching Powder
Preparation
Bleaching powder is made by reacting chlorine with dry-slaked lime:
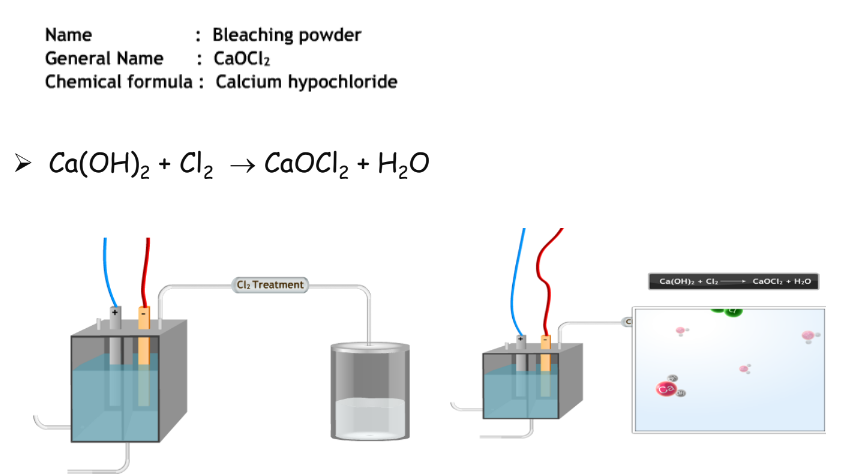
Uses
- Bleaching textiles and paper, disinfecting drinking water, and as an oxidizing agent in many chemical industries.
Preparation and Uses of Plaster of Paris
Preparation
Plaster of Paris is prepared by heating gypsum at 390 K.
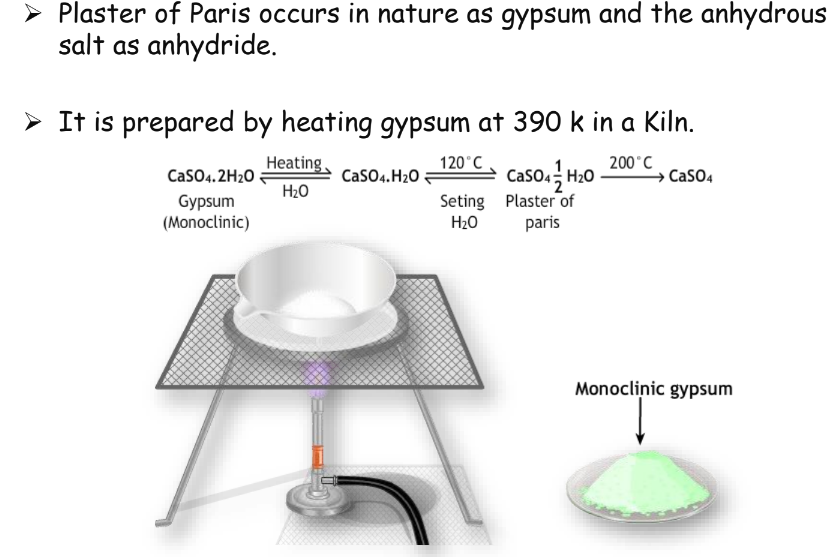
Uses
- Used in construction, mold making, ceramics, statues, and medical casts.
Let’s Conclude
In conclusion, understanding the concepts covered in Acids Bases and Salts is essential for mastering CBSE Class 10th Science. This chapter delves into the characteristics and chemical properties of acids, bases, and salts, helping students comprehend their everyday applications. At iPrep, we strive to make learning Acids Bases and Salts engaging and insightful through our interactive videos, comprehensive notes, and practice questions. Whether you’re preparing for exams or seeking to strengthen your understanding of Acids Bases and Salts, iPrep provides the tools you need for success.
Practice questions on Chapter 2 - Acids Bases and Salts
Get your free Chapter 2 - Acids Bases and Salts practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








