Chemical Reactions and Equations – The Best Guide For Class 10 Science Chapter 1
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, Chemical Reactions and Equations in Science for Class 10th are designed to ensure you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
Chemical reactions are everywhere around us—from the rusting of iron to the digestion of food in our bodies. They form the basis of countless natural and industrial processes that sustain life and drive innovation. CBSE Class 10th Science Chapter 1 – Chemical Reactions and Equations introduces you to the fascinating world of chemical changes, teaching you how substances transform and interact to create new compounds.
This chapter not only helps you understand the mechanics of chemical reactions but also equips you with the skills to write and balance chemical equations, a critical tool for any budding scientist. Ready to unlock the mysteries behind everyday phenomena? Let’s dive into Chemical Reactions and Equations and explore the science behind these remarkable transformations!
What are Chemical Changes?
As stated in the chapter Chemical Reactions and Equations, Chemical changes are processes that involve the transformation of substances into new products. These changes are always accompanied by chemical reactions. In a chemical reaction, substances can decompose, combine with others, or interchange constituents.
Key Observations of Chemical Changes
You can determine whether a chemical reaction has occurred by observing the following changes:
- Change in Physical State: Solid to liquid, liquid to gas, etc.
- Change in Color: For instance, rusting of iron.
- Change in Temperature: Whether it releases or absorbs heat.
- Evolution of Gas: Formation of bubbles or gas.
Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chemical Reactions
As per the chapter Chemical Reactions and Equations, A chemical reaction brings about a permanent change in substances. The basic components of a chemical reaction are:
- Reactants: Substances that undergo the reaction.
- Products: New substances formed as a result of the reaction.
Example:
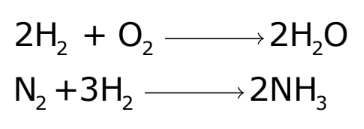
Chemical Equations
A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction. It includes:
- Formulas and Symbols: Representing reactants and products.
- Physical States: Indicating the state of each substance (solid, liquid, gas, aqueous).
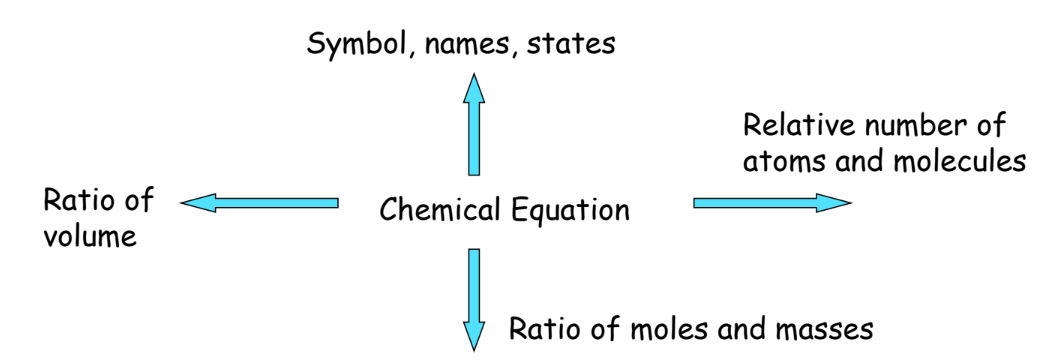
Information Conveyed by Chemical Equations
The chapter Chemical Reactions and Equations mentions that Chemical equations provide several pieces of information:
- Formulas, Symbols, and Physical States: Of reactants and products.
- Relative Number of Atoms and Molecules: Involved in the reaction.
- The ratio of Moles and Masses: Of reactants and products.
- Ratio of Volumes: For gaseous reactants and products.
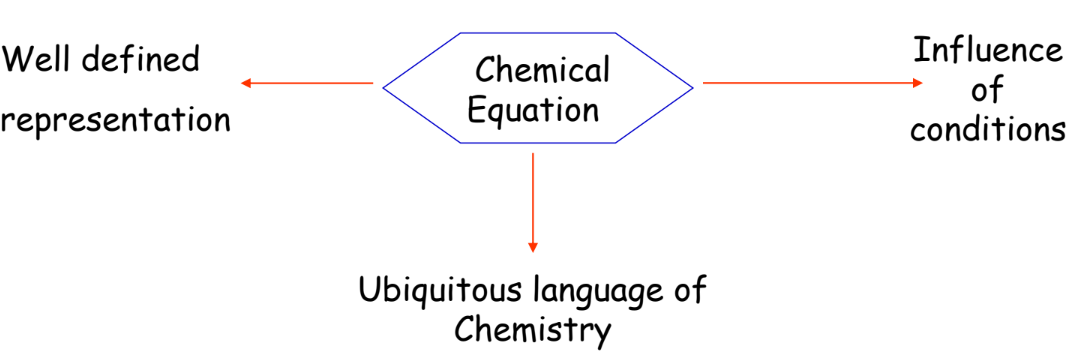
Advantages of Chemical Equations
- Simplified Representation: Makes understanding the reaction easier.
- Universal Language: Understood globally by chemists.
- Analysis of Conditions: Helps in studying the effect of temperature, pressure, and concentration.
Writing Chemical Equations
When writing chemical equations, follow these steps:
- Write the Molecular Formulas: Reactants on the left-hand side (LHS) and products on the right-hand side (RHS).
- Use Plus (+) Signs: To separate reactants and products.
- Use an Arrow (→): To indicate the direction of the reaction.
Example:
The reaction of zinc with hydrochloric acid can be represented as:

Balancing Chemical Equations
A balanced chemical equation has the same number of atoms for each element on both sides of the equation.
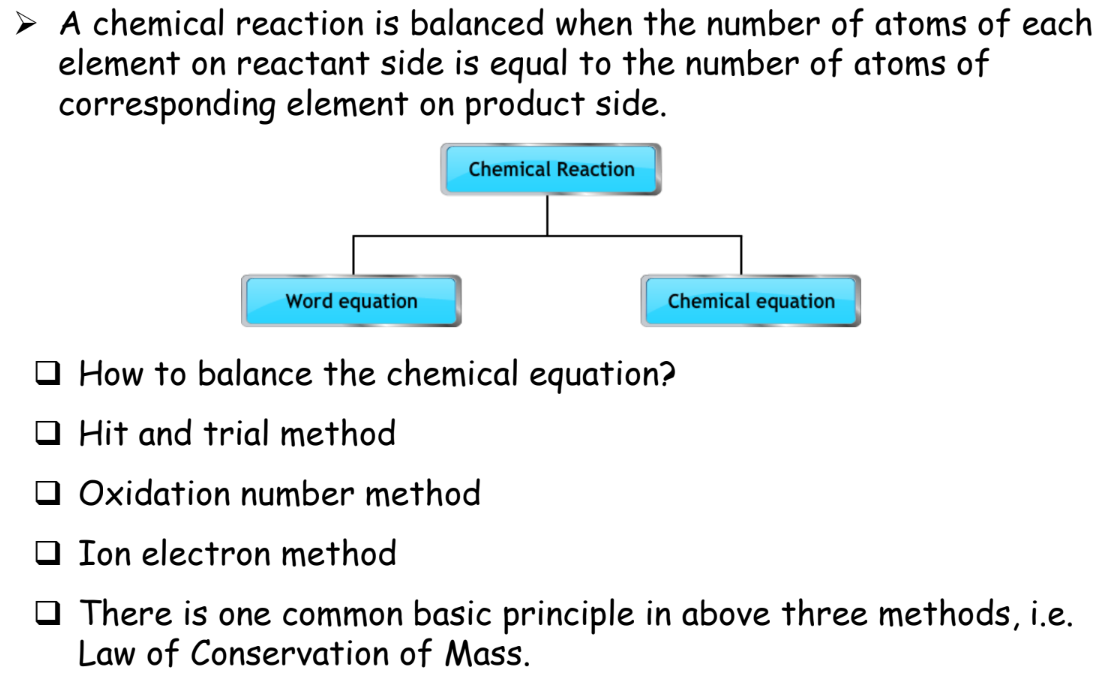
Here’s how to balance an equation:
Steps for Balancing Equations
- Write the Unbalanced Equation:
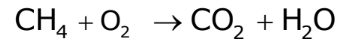
- List Number of Atoms:
| Element | Reactants | Products |
| C | 1 | 1 |
| H | 4 | 2 |
| O | 2 | 3 |
- Balance the Compounds:

4. Recount Atoms: Count on both sides again:
Element
Reactants
Products
C
1
1
H
4
4
O
2
4
Final Balanced Equation:- Include Physical States:
Thus, we can conclude that:

Chemical changes bring out permanent changes in substances through chemical reactions which are represented by chemical equations.
Types of Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions can be classified into several types based on their nature:
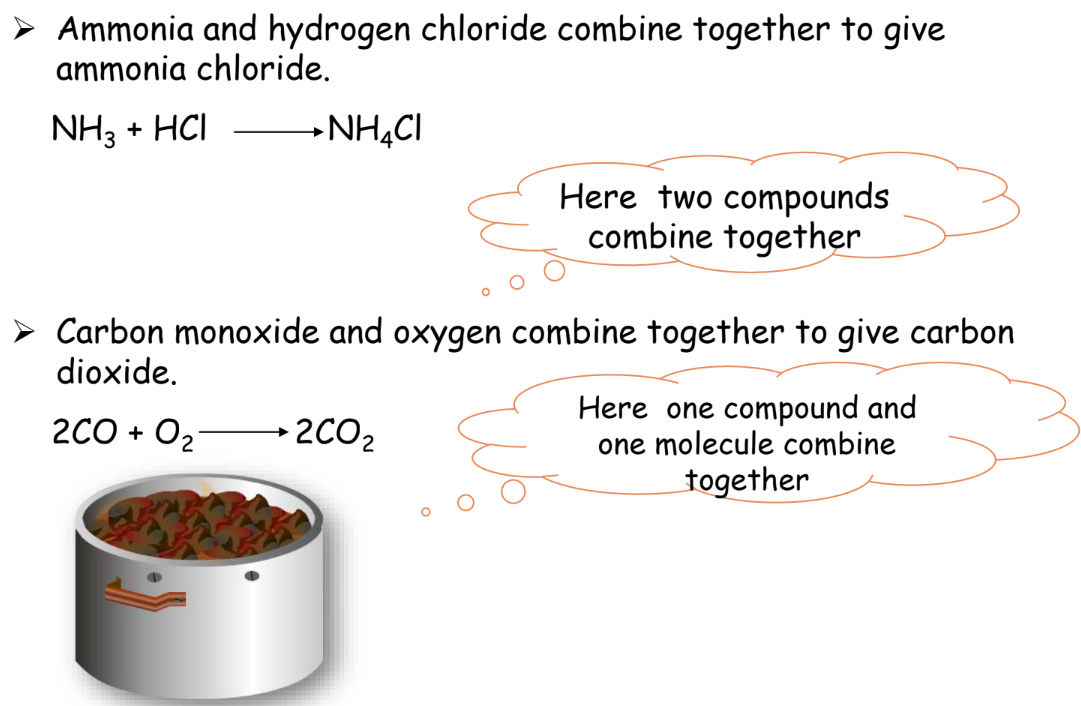
Combination Reaction
Two or more substances combine to form a single product.
Example:
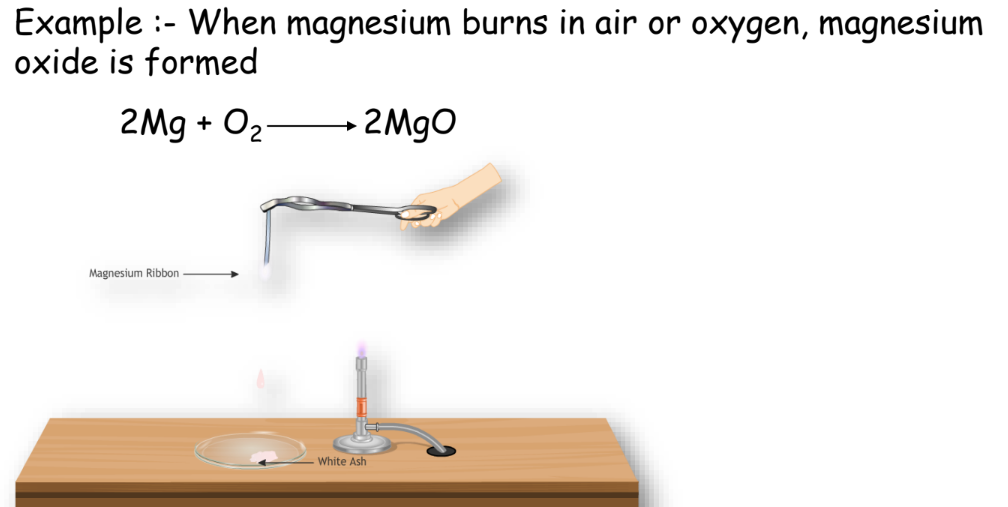
Decomposition Reaction
A single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
Example:

Displacement Reaction
An atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group.
Example:
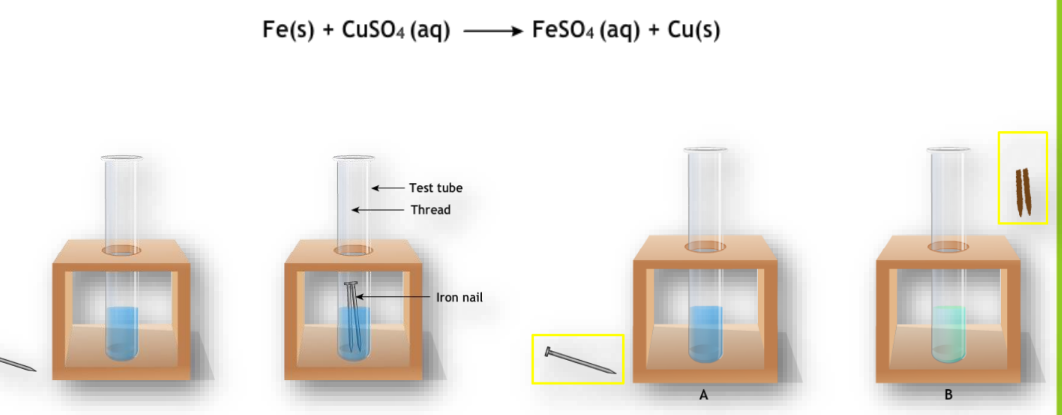
Double Displacement Reaction
Two compounds exchange ions to form two new compounds.
Example:
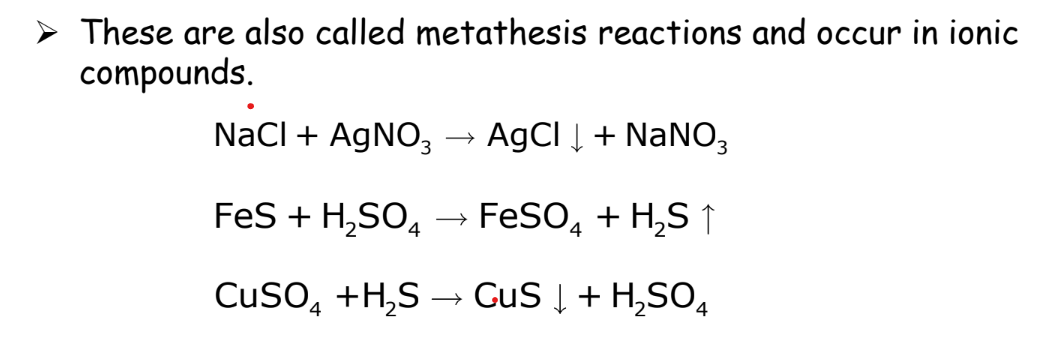
Redox Reaction
Involves both oxidation (loss of electrons) and reduction (gain of electrons).
Classical Concept of Redox Reaction
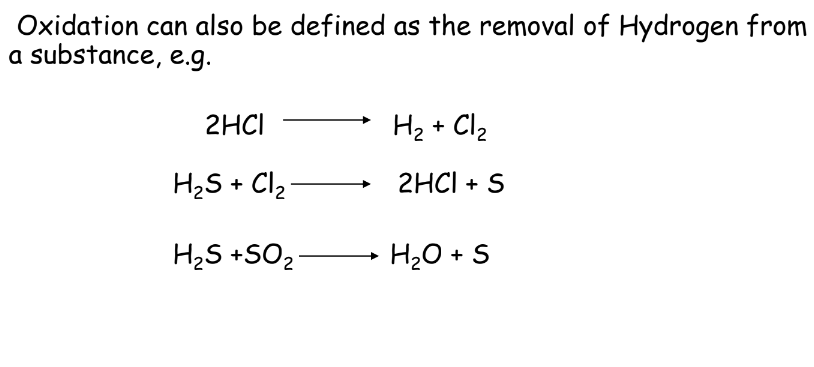
Reduction reaction means the removal of oxygen or the addition of hydrogen.
Oxidation Reaction means adding oxygen or removing hydrogen from a substance.
Example:
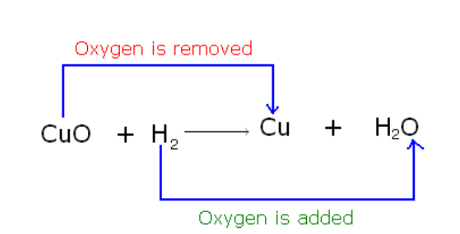
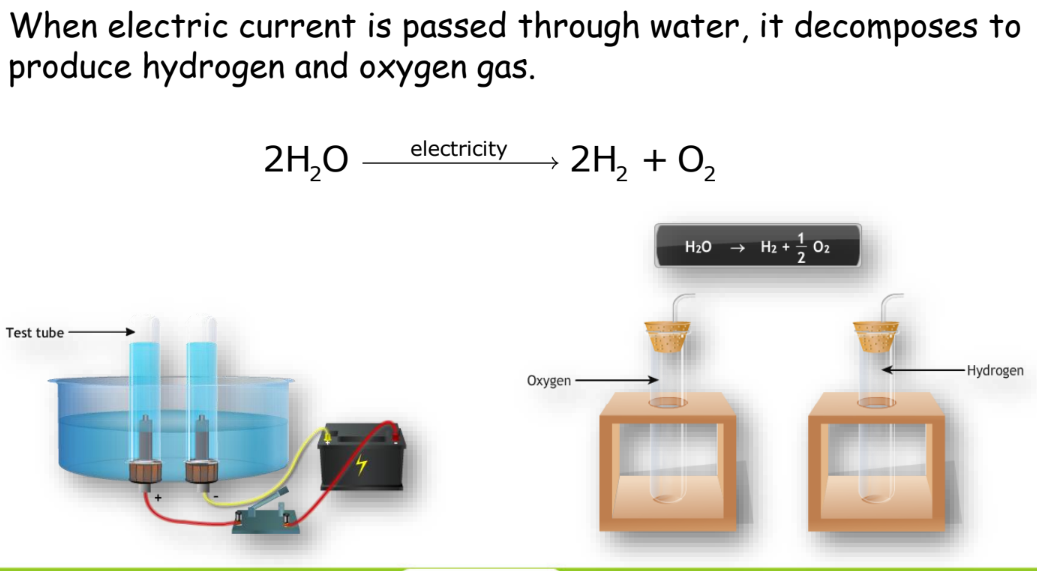
Special Types of Reactions
Electrolytic Decomposition
Decomposition through electricity.
Example:
Photochemical Decomposition
Decomposition in the presence of light.
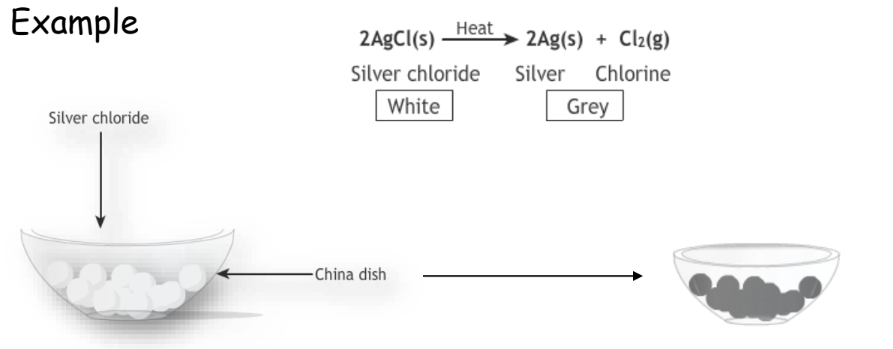
Example:
Used in various applications like metal extraction and photography.
Redox Reactions and Oxidation-Reduction
Oxidation and Reduction
- Oxidation: Loss of electrons or addition of oxygen.
- Reduction: Gain of electrons or removal of oxygen.
Example:
- Oxidation:


- Reduction:
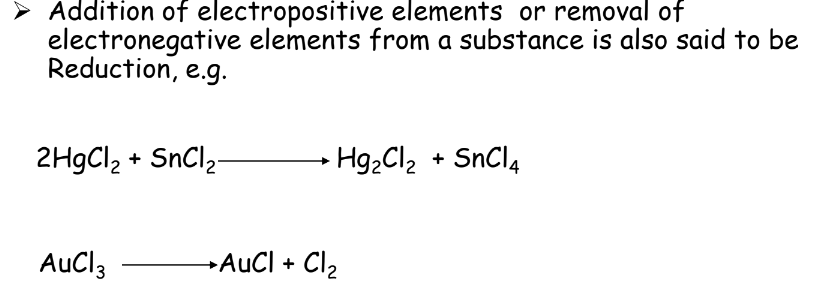

Oxidizing and Reducing Agents
- Oxidizing Agent: Causes oxidation, itself gets reduced.
- Reducing Agent: Causes reduction, itself gets oxidized.
Example:
- Oxidizing Agent:
- Reducing Agent:
Now, let’s move towards the different applications of chemical reactions in our daily lives.
Applications of Chemical Reactions
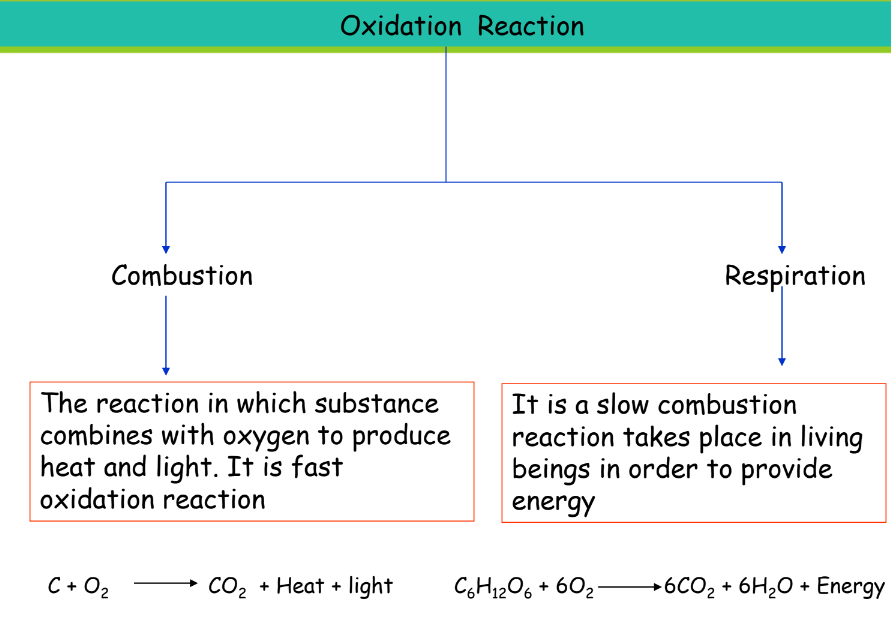
Combustion
- Definition: Fast oxidation produces heat and light.
- Example: Burning of wood or gasoline.
Conditions for Combustion
- Presence of Combustible Substances
- Presence of Oxygen
- Ignition Temperature: Minimum temperature required for a substance to start burning.
Respiration
- Definition: Slow combustion in living beings to produce energy.
Effects of Redox Reactions
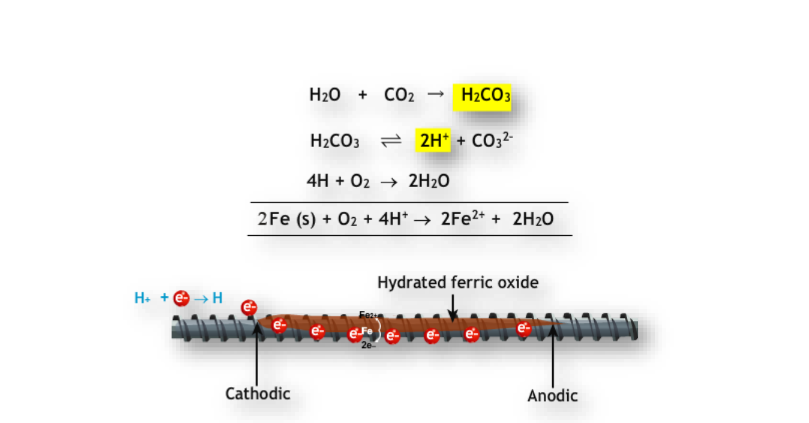
Corrosion
- Definition: Slow conversion of metal into compounds due to atmospheric conditions.
- Example: Rusting of iron.
Rancidity
- Definition: Deterioration of fatty and oily foods due to oxidation.
- Prevention: Using antioxidants, airtight packaging, and nitrogen gas in containers.
If you liked this summary and want to read a similar post on Class 10 Science Chapter 13 – Our Environment, click here.
Let’s Conclude
In conclusion, mastering CBSE Class 10th Science Chapter 1 – Chemical Reactions and Equations is crucial for a deeper understanding of chemical changes and their real-life applications. From recognizing chemical reactions through changes in physical state, color, and temperature, to balancing complex chemical equations, this chapter lays a strong foundation in chemistry.
The diverse types of reactions such as combination, decomposition, and redox reactions are pivotal in understanding how substances interact and transform. As you continue your learning journey with iPrep, you can be confident that the Chapter – Chemical Reactions and Equations is well within your grasp with our comprehensive resources. Dive into this chapter, practice regularly, and watch your confidence grow as you master the intricacies of Chemical Reactions and Equations.
Practice questions on Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations
Get your free Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








