Heredity – Complete Guide For Class 10 Science Chapter 8
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, Heredity in Science for Class 10th are designed to ensure you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the method through which all higher organisms propagate. It involves:
- Participation of individuals of opposite sexes, who produce gametes.
- Fusion of gametes to form a zygote, which then develops into a new individual.
Reproduction and Variation
MEIOSIS = Chromosome break + Reunion = VARIATION
Variation is a natural outcome of sexual reproduction, and it plays a crucial role in the process of evolution.
Variation in Nature
Variations can be observed in numerous aspects of nature, such as hair color, eye color, and earlobe shapes in humans.
Variation and Speciation
Accumulation of variations within a generation can lead to the emergence of a new species that is entirely different from its ancestors. While variations within a species can be beneficial to some populations, asexual reproduction often results in fewer variations due to the inefficiency of DNA replication.
What is Heredity?
Heredity is a fundamental biological process that governs the transmission of genetic traits from parents to their offspring. This process plays a crucial role in shaping the characteristics and variations observed within a species. At its core, heredity involves the passing of genes—units of heredity that encode information for specific traits—through generations. Understanding heredity is essential not only for grasping how traits are inherited but also for appreciating the complex relationships among living organisms and the diversity of life on Earth. In this chapter, we will delve into the mechanisms of heredity, the pivotal experiments of Gregor Mendel, and the laws that underpin genetic inheritance, providing a solid foundation for your studies in biology.
Heredity and Inherited Traits
Inherited Traits are those that are passed down from the parental generation to their offspring. While offspring inherit basic characteristics from their parents, they are not exact copies. These inheritable traits may have multiple alternate forms, manifesting as variations.
Hair Type, an Inheritable Trait
Human hair types—curly, straight, and wavy—are examples of inheritable traits.
Gregor Johann Mendel: The Father of Genetics
Gregor Johann Mendel, born in 1822 in Austria, is regarded as the Father of Genetics. He discovered the most fundamental laws of genetics by conducting breeding experiments with the common garden pea plant (Pisum sativum). Mendel selected seven pairs of contrasting characters in pea plants to study their inheritance patterns.
Contrasting Characters in Pea Plants
| Characters | Form 1 (Dominant) | Form 2 (Recessive) |
| Height of stem | Tall | Dwarf |
| Position of flower | Axial | Terminal |
| Colour of flower | Violet | White |
| Colour of pod | Green | Yellow |
| Shape of pod | Inflated | Constricted |
| Shape of seed | Round | Wrinkled |
| Colour of seed | Yellow | Green |
Mendel’s Observations
Mendel observed that the seven characters of pea plants showed clear variations in two forms:
- F1 Generation (First-generation progeny): All individuals exhibited only one parental character, with the other character not appearing.
- F2 Generation (Second-generation progeny): After self-pollination in F1 progeny, both parental characters reappeared in the second generation.
Mendel concluded that since individuals possess two copies of each gene from each parent, factors exist in pairs in cells. Therefore, each character is determined by a pair of factors.
Genes and Alleles
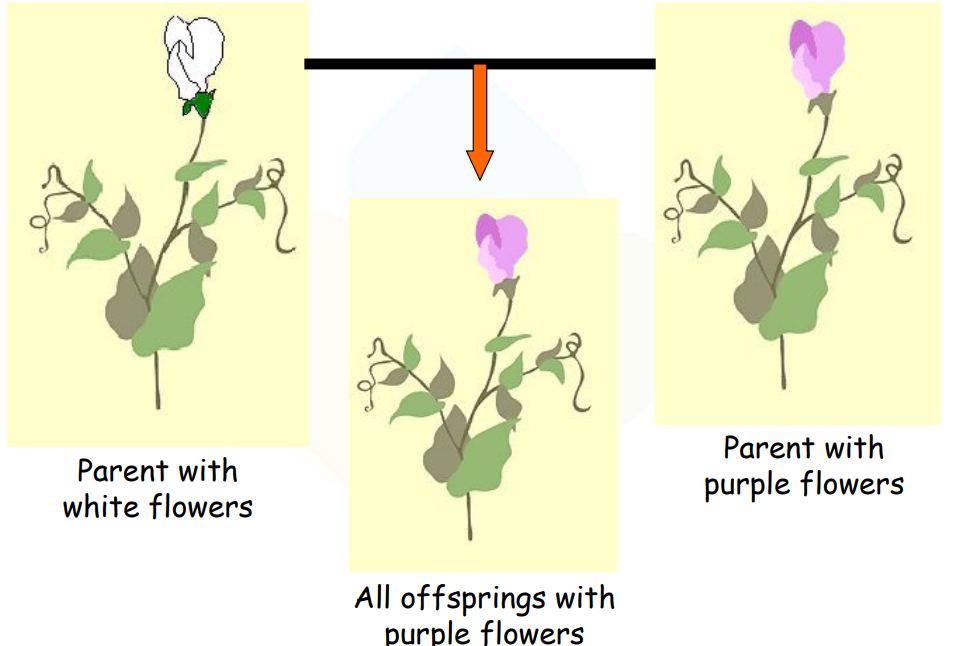
A character controlled by a single gene, or ‘factor,’ can have two alternate forms known as allelomorphs or alleles. These alleles are denoted by alphabets (in capital and small letters).
For example, in a cross between tall and dwarf plants, the first generation of plants was all tall. However, to determine if they were genetically similar to the parental tall plants, Mendel performed a self-pollination test on both parents and progeny tall plants.
Inheritance of Two Characters
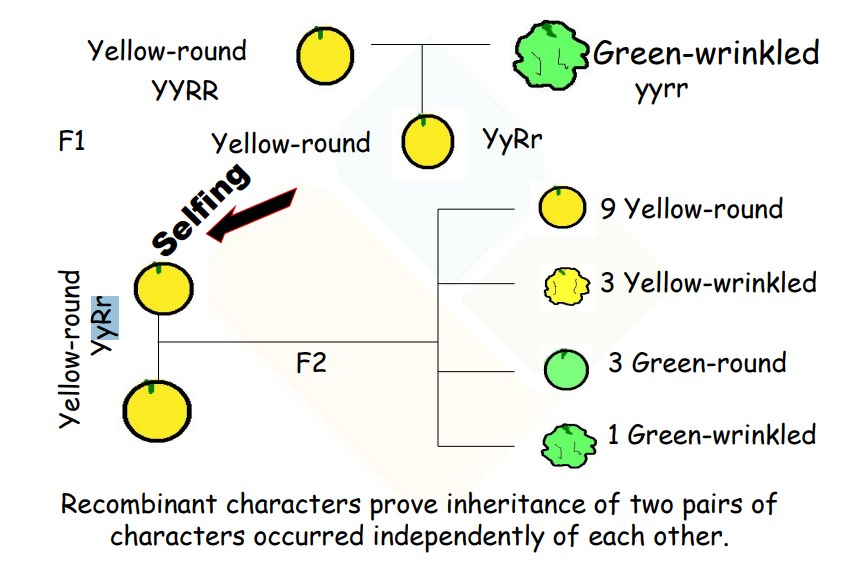
Mendel also conducted crosses between individuals varying in two pairs of characters (dihybrid crosses), such as seed shape and seed color. In a cross between plants with round-yellow seeds and plants with green-wrinkled seeds, all F1 plants had round-yellow seeds. Upon selfing F1 plants, the F2 generation exhibited all possible combinations of characters in a 9:3:3:1 ratio.
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance
Based on his observations, Mendel proposed three laws of inheritance:
- Law of Dominance: Among two alleles, one is dominant over the other. When present together in a diploid cell, the dominant one expresses itself, while the recessive one is masked.
- Law of Segregation: During gamete formation, alleles segregate and reunite during fertilization to restore the diploid condition.
- Law of Independent Assortment: When more than one pair of characters are present, each pair is inherited independently of the other.
How Do Genes Work?
Genes function by producing proteins, which in turn influence the functioning of cells and the organism as a whole. For instance, plant growth is influenced by hormones, and the synthesis of these hormones depends on the accuracy of enzymes coded by genes. If a gene is modified, the corresponding enzymes may not be produced, thereby affecting hormone synthesis.

Sex Determination
Sex determination is the phenomenon by which the sex (male or female) of an individual is defined. In most multicellular eukaryotic organisms, there are two well-defined sexes. However, in some cases, organisms may be hermaphrodites. Male and female organisms might differ in their genetic composition, allelic composition, chromosomal morphology, and even chromosome number. In many other organisms, sex is also determined by environmental influence. Like, temperature can influence the sex of fertilized eggs.
Sex Determination in Human Beings
Humans exhibit the XX/XY method of sex determination. This system is prevalent not only in humans but also in almost all other mammals and is also observed in Drosophila.
In humans:
- Males have autosomes plus a pair of X and Y chromosomes as sex chromosomes, producing two types of gametes—one with an X chromosome and the other with a Y chromosome.
- Females have autosomes plus a pair of X chromosomes as sex chromosomes, producing only one type of gamete, i.e., autosomes and X chromosomes.

Chromosomal Basis of Variation
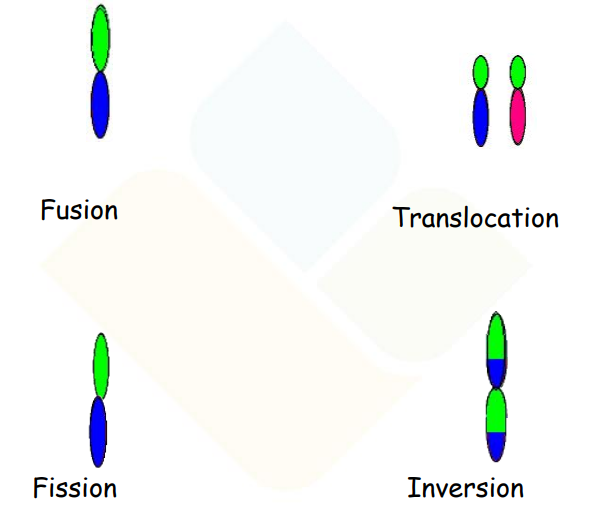
Variations can arise due to various chromosomal events such as fusion, fission, translocation, and inversion.
This chapter provides a detailed understanding of heredity and the factors influencing the development of new species. Understanding these processes is essential to comprehend the diversity of life on Earth and the intricate relationships among various species.
Let’s Conclude
In conclusion, CBSE Class 10th Science Chapter 8 – Heredity provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamental concepts related to genetic inheritance and variation. By exploring key topics such as sexual reproduction, the role of Gregor Mendel in genetics, and the laws of inheritance, students gain valuable insights into how traits are passed from one generation to the next. The chapter emphasizes the significance of heredity in understanding biological diversity and the evolution of species, making it essential for students to grasp these concepts for their academic success.
We hope that with iPrep’s engaging resources for Heredity, you feel more confident in your understanding of this critical topic. Remember, the principles of Heredity not only form the foundation for further studies in biology but also enrich your appreciation of the natural world around you. Keep exploring, practicing, and asking questions to deepen your knowledge of Heredity!
Practice questions on Chapter 8 - Heredity
Get your free Chapter 8 - Heredity practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








