Our Environment – Awesome Guide For Class 10 Science Chapter 13

Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, Our Environment in Science for Class 10th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best-integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
In today’s world, understanding the environment and our role in protecting it is more important than ever. CBSE Class 10th Science Chapter 13 – Our Environment introduces students to the dynamic interactions between living and non-living components of the ecosystem, energy flow, and the impact of human activities on the natural world. This chapter serves as a foundation for students to grasp essential concepts like food chains, food webs, and environmental issues, all of which are crucial in developing a deeper awareness of the environment and the need for sustainable living. Now let’s begin by addressing the question of the hour-
Our Environment
Our environment is the sum of all living and nonliving things that surround an organism or group of organisms. It encompasses a diverse array of elements, both biotic and abiotic, that interact with each other in various ways.
Let’s talk about two main components of our environment, that is, Living and Non-Living components.
Components of the Environment
Living Components
- Different kinds of plants (such as grasses, trees, and flowering plants)
- Various animals, insects, and birds found in forests
Non-Living Components
- Wind
- Air
- Soil
- Rocks
Types of Environment
The environment can be classified into two main types:
- Natural Environment: Includes natural settings like forests and ponds.
- Artificial Environment: Includes human-made settings like crop fields and aquariums.
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a specific area within the natural environment where physical factors interact with interdependent organisms, such as plants and animals within the same habitat.
Components of an Ecosystem
Abiotic Components
Non-living elements like sunlight, water, air, minerals, and temperature.
Biotic Components
Living elements are classified into:
- Producers: Organisms like green plants that prepare their food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
- Consumers: Organisms that consume food made by producers, classified as:
- Herbivores: Eat plants.
- Carnivores: Eat other animals.
- Omnivores: Eat both plants and animals.
- Decomposers: Organisms that clean the environment of dead and decaying matter, break down complex organic matter into simpler substances, and replenish the soil.
Energy Flow in the Ecosystem
- Energy is essential for living organisms to perform various activities.
- Energy flows through the ecosystem in the form of food.
- The flow of energy is unidirectional, starting from producers to consumers.
Food Chain
A food chain represents the feeding relationships between living organisms, starting with green plants. The ultimate source of energy for these chains is the sun.
Example of a Food Chain:
Sun → Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
Food Web
A food web is a network of interconnected food chains. It explains the complex interrelationships between organisms that eat each other and shows that one organism can have multiple food sources and be eaten by various predators.
Biological Magnification
Biological magnification refers to the accumulation of certain non-biodegradable chemicals, like pesticides, in the bodies of living organisms through the food chain.
Environmental Issues
Human activities have significantly impacted the environment, leading to various problems:
Ozone Depletion
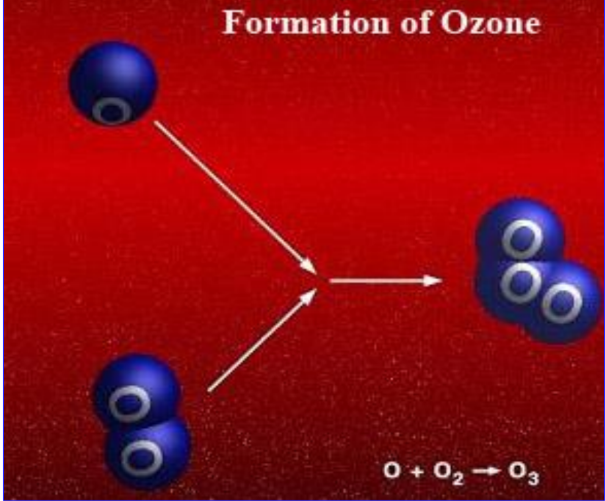
Ozone (O₃) is formed when diatomic oxygen (O₂) is broken down into atomic oxygen, which then combines with O₂. Although ozone is toxic at ground level, it is crucial at higher atmospheric levels as it shields the Earth’s surface from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Garbage Management
Garbage management is a major environmental issue, as large amounts of waste are produced daily in human habitations.
Types of Waste
| Biodegradable | Non-Biodegradable |
| Originates from plant or animal sources and can be broken down by living organisms. | Cannot be broken down naturally. Examples include plastic bags, synthetics, plastic bottles, tin cans, and computer hardware. |
Key Terms on Your Fingertips
- Biomagnification: The gradual increase in the concentration of harmful chemicals in the bodies of higher animals through the food chain or food web.
- Ecosystem: The interaction of living organisms and their physical surroundings within a specific area, such as a forest, garden, or river.
- Food Chain: The feeding relationship between living organisms, starting with producers.
By understanding these key concepts, we can better appreciate the intricate relationships within our environment and the impact of our actions on the natural world.
Let’s Conclude
In conclusion, CBSE Class 10th Science Chapter 13 – Our Environment plays a vital role in helping students understand the delicate balance of living and non-living components within ecosystems. From the energy flow through food chains and food webs to the pressing environmental issues like biological magnification and ozone depletion, this chapter covers crucial topics that highlight the importance of environmental conservation. With iPrep’s engaging resources for Our Environment, you can reinforce your knowledge through animated videos, notes, and practice questions, ensuring a thorough understanding of this essential chapter for your Class 10th Science exams. Keep exploring Our Environment and take the first step towards becoming a more environmentally conscious individual!
Practice questions on Chapter 13 - Our Environment
Get your free Chapter 13 - Our Environment practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








