Origin and Evolution of the Earth – Complete Guide For 11 Geography Chapter 2
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, “Origin and Evolution of the Earth” in Geography for Class 11th are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
This chapter explores the various theories about the origin of the Earth and its subsequent evolution. It delves into early theories and modern scientific explanations, including the formation of the universe, stars, and planets. The chapter also discusses the evolution of the Earth’s lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and the eventual origin of life.
The Earth, our home planet, has a fascinating history. How did it come into existence? What processes shaped its evolution over billions of years? This chapter investigates the early theories and modern scientific explanations for the origin and evolution of the Earth.
Objectives Of Learning The Chapter – Origin And Evolution Of Earth
Now that we have explored the importance of the chapter, let’s outline the objectives of studying it.
- To understand the different theories about the origin of the Earth.
- To explore the process of star formation and planet formation.
- To discuss the evolution of the Earth’s lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere.
- To learn about the origin of life on Earth.
Now let’s explore the various sections of the chapter.
Firstly, in order to understand the early theories related to the Earth’s origin, let’s delve into the “Early Theories“ section of the chapter “Origin and Evolution of the Earth.”
Early Theories
Early theories about the origin of the Earth were often based on mythological or religious beliefs. The key early theory includes:
Origin of the Earth
- The early theories about the Earth’s origin were largely speculative and based on religious and mythological beliefs.
- Philosophers like Immanuel Kant and Pierre-Simon Laplace proposed the Nebular Hypothesis, suggesting that the Earth and other planets formed from a rotating cloud of gas and dust.
- Other early theories included the Tidal Hypothesis and Binary Star Hypothesis, which attempted to explain the Earth’s formation through gravitational interactions.
Now, to gain a better understanding of contemporary theories about the universe’s beginning, let’s explore the “Origin of the Universe” section within the chapter “Origin and Evolution of the Earth.”
Modern Theories
- Modern scientific theories about the origin of the Earth are based on evidence from astronomy, geology, and other fields.
Now, let’s discuss the key points covered under this topic.
Origin of the Universe
- The most widely accepted theory about the origin of the universe is the Big Bang theory. This theory proposes that the universe began as a singularity and then expanded rapidly.
- The modern view of the universe’s origin is based on the Big Bang Theory. According to this theory, the universe began with a massive explosion approximately 13.8 billion years ago.
- This explosion led to the expansion of the universe, cooling down the temperatures and allowing the formation of subatomic particles and simple elements.
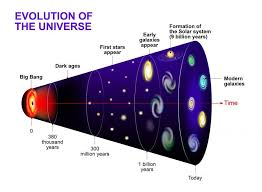
The Star Formation
- Stars are formed from large clouds of gas and dust known as nebulae.
- Gravity pulls the gas and dust together, increasing pressure and temperature, leading to nuclear fusion—a process that powers stars and gives them their light and heat.
Formation of Planets
- Planets are formed from the residual material left after star formation, known as the protoplanetary disk.
- Through a process called accretion, dust and gas particles clump together to form planetesimals, which further collide and combine to form planets.
Now, in order to understand the Earth’s solid structure, let’s explore the “Evolution of Lithosphere” section of the chapter “Origin and Evolution of the Earth.”
Evolution of the Earth
The Earth has undergone a long and complex evolution.
Evolution of Lithosphere
- The Earth’s lithosphere, the outermost layer of the Earth, is composed of tectonic plates.
- These plates move slowly over time, shaping the Earth’s surface through processes such as continental drift and mountain building.
Evolution of Atmosphere and Hydrosphere
- The Earth’s atmosphere and hydrosphere have also evolved over time.
- The atmosphere has changed in composition, becoming richer in oxygen.
- The hydrosphere has formed from the condensation of water vapor in the atmosphere.
Origin of Life
- The origin of life on Earth is believed to have occurred in the primordial soup, a mixture of organic molecules formed in the early Earth’s oceans.
- The first forms of life were simple, single-celled organisms, which gradually evolved into more complex life forms through the process of natural selection.
Finally, as we have gained comprehensive knowledge about the chapter “Origin and Evolution of the Earth”, let’s reflect on the overall learning value of this important lesson.
Overall Learning Value of the Chapter
This chapter has provided a comprehensive overview of the origin and evolution of the Earth. It has explored early theories and modern scientific explanations, including the formation of the universe, stars, and planets. The chapter has also discussed the evolution of the Earth’s lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and the eventual origin of life. By understanding the Earth’s history, we can gain a deeper appreciation for our planet and its place in the universe.
Practice questions on Chapter 2 - Origin And Evolution Of The Earth
Get your free Chapter 2 - Origin And Evolution Of The Earth practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








