Shadow Story (Togalu) – Complete Guide For Class 2 Math Chapter 4

Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App. Our learning resources for the chapter, Shadow Story (Togalu) in Mathematics for Class 2nd are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
The chapter “Shadow Story (Togalu)” introduces children to the concept of shadows, focusing on how light interacts with objects to form shadows. Students learn to explore 2D shapes, trace shapes, identify edges and corners, and recognize patterns through playful activities. This chapter emphasizes visual learning by connecting shapes with real-life experiences and encourages children to explore their environment to understand shadows.
What is a Shadow?
According to the chapter Shadow Story, when something blocks the light, a shadow is created. Since light moves in a straight path, obstructions such as hands, books, or toys cause a shadow to appear behind the object.
- Example:
When you stand under the sun, your body blocks the sunlight and creates a shadow on the ground. - Fun Fact:
Shadows are usually black or dark because they block the light. The shape of the shadow depends on the shape of the object and the direction of the light.
Activity:
Place an object (like a pencil or a toy) under a torchlight and observe its shadow on the wall.
- Question: Does the shadow change if the object is moved closer or farther from the light?
Understanding Torchlight and 3D Objects:
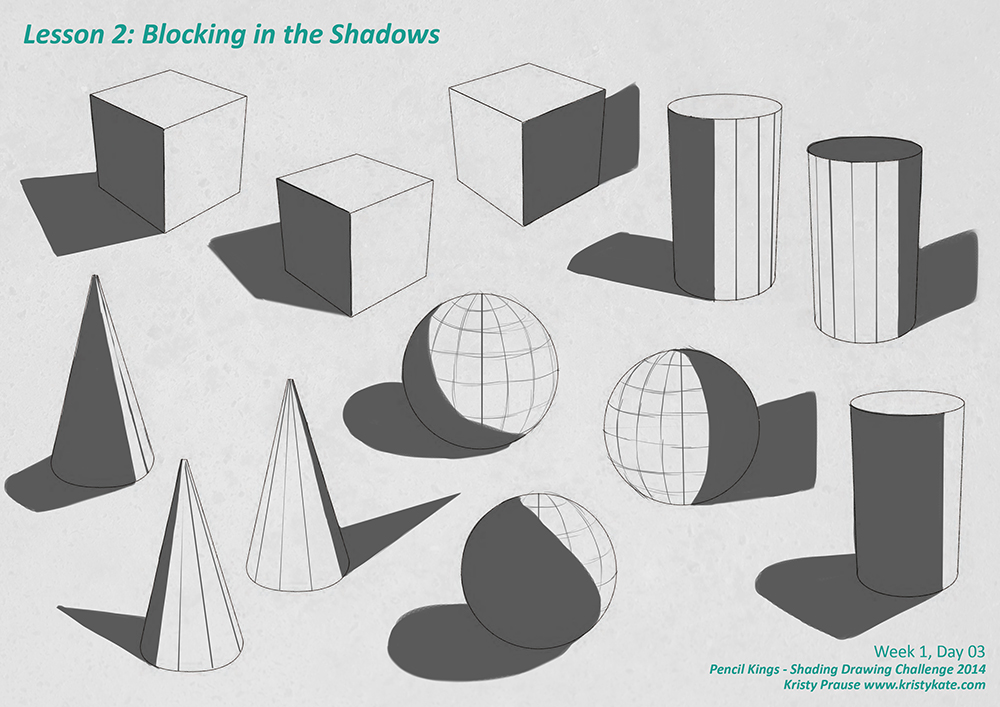
As per the chapter Shadow Story, when a torchlight shines on a 3D object like a sphere, cube, or cylinder, the shape of the shadow it creates depends on:
- The shape of the object.
- The angle and direction of the light.
- The position of the object concerning the light source and a surface.
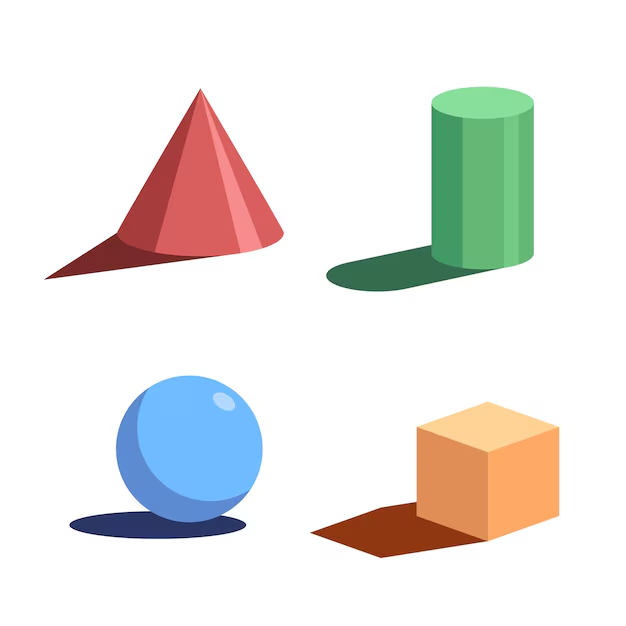

Key Concepts with Torchlight and 3D Objects:
There are various key concepts with Torchlight and 3D objects discussed in the chapter Shadow Story. These include-
- Projection of shadows:
- A torchlight shining on a sphere will create a circular shadow.
- If a torchlight shines on a cylinder, it can create either a rectangle or a circle depending on the direction of the light.
- A cube may create square or rectangular shadows based on the angle of the light.
- Real-life examples:
- Flashlights create shadows of everyday objects on walls.
- Sundials use the position of the sun and the shadow of an object to tell time.
- Applications in learning:
- Learning how 2D shapes (like circles, squares, or rectangles) appear as shadows of 3D objects.
- Understanding how shadows change in size and shape when the angle of the light changes.
Activity:
- Use cut-outs of different 2D shapes (circle, triangle, square, and rectangle).
- Shine a torchlight on the cut-out and ask students to guess which shape’s shadow they see.
Tracing 2D Shapes: Drawing with Shadows
Tracing shadows is an enjoyable method of investigating shapes. Drawing along the shadowed borders of an object is called tracing. Through observation, students can learn about the characteristics and structure of 2D shapes with this practice.
- How to Trace:
Place a flat object (like a square cardboard) on a piece of paper. Shine a torchlight on it so it casts a shadow. Now, trace the outline of the shadow with a pencil. - Activity:
Provide simple objects like bottle caps, paper cups, and toy blocks. Trace the shadow of each object and name the shapes.

Exploring Edges and Corners of 2D Shapes
Each 2D shape has a unique structure, and as stated in the chapter Shadow Story, each 2D shape is defined by its edges (sides) and corners (vertices). Identifying these parts helps students understand the differences between shapes.
- Circle: No edges, no corners.
- Square: 4 equal edges, 4 corners.
- Rectangle: 4 edges (2 long, 2 short), 4 corners.
- Triangle: 3 edges, 3 corners.
Activity:
Provide students with paper cut-outs of different shapes. Ask them to count the edges and corners for each shape and fill in a table.
Shape Edges Corners Circle 0 0 Square 4 4 Rectangle 4 4 Triangle 3 3
Patterns in Shapes: Recognizing Sequences and Repetitions
As stated in the chapter Shadow Story, Patterns are arrangements that repeat predictably. Patterns with shapes help students develop logical thinking and visual memory.
Types of Shape Patterns:
Various types of shape patterns are discussed in the chapter Shadow Story. These involve-
- Repeating Patterns:
Example: Circle, Square, Circle, Square… What comes next? (Answer: Circle) - Growing Patterns:
In this type of pattern, the number of shapes increases.
Example: One triangle, Two triangles, Three triangles… What comes next? (Answer: Four triangles) - Alternating Patterns:
Two or more shapes alternate repeatedly.
Example: Circle, Square, Circle, Triangle, Circle, Square…
Activity:
- Provide students with a sequence of shapes and ask them to complete the pattern.
- Example: Circle, Triangle, Circle, Triangle, __, __.
Connecting Shapes and Shadows to Real Life
Recognizing shadows and shapes in the real world helps children relate math to their environment. As mentioned in the chapter Shadow Story, They can observe shadows at home, school, or playground.
Real-Life Examples:
- Circle Shadows: Clock, plate, or wheel shadows.
- Rectangle Shadows: Door, book, or mobile phone shadows.
- Triangle Shadows: Party hat or cone-shaped object shadows.
Encourage children to observe shadows throughout the day and notice how they change based on the position of the light.
Conclusion: Exploring the World with Shadows and Shapes
The chapter “Shadow Story (Togalu)” in CBSE Class 2nd Math offers young learners an exciting journey into the world of light, shadows, and shapes. Through hands-on activities like tracing shadows, recognizing patterns, and identifying edges and corners, students build a strong foundation in visual learning. This chapter provides a fun and engaging way to understand key concepts that are both practical and enjoyable.
By observing how shadows form and change, students in CBSE Class 2nd Math gain an appreciation for how math connects to their everyday experiences. From shadow experiments to identifying 2D shapes, the chapter helps them discover that math is present all around us—in the objects we use, the patterns we see, and the shadows we cast.
“Shadow Story (Togalu)” not only introduces critical math concepts but also sparks curiosity and creativity in learners. Whether it’s at home or in the playground, children will now be able to identify shadows and shapes and apply these skills in a real-world context. With this knowledge, students in CBSE Class 2nd Math are well-prepared for future lessons in geometry.
Let’s continue to explore the fascinating world of shadows and shapes in CBSE Class 2nd Math, and make learning both fun and meaningful!
Practice questions on Chapter 4 - Shadow Story (Togalu)
Get your free Chapter 4 - Shadow Story (Togalu) practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now