Coal And Petroleum – Complete Guide For Class 8 Science Chapter 3
Welcome to iPrep, your Learning Super App! Our learning resources for the chapter, Coal and Petroleum in Science Class 8th chapter 3 are designed to ensure that you grasp this concept with clarity and perfection. Whether you’re studying for an upcoming exam or strengthening your concepts, our engaging animated videos, practice questions and notes offer you the best of integrated learning with interesting explanations and examples.
The concept of Coal and Petroleum in Class 8 Science introduces students to a comprehensive understanding of Coal and Petroleum as an integral part of our energy landscape. This topic explores Coal and Petroleum as non-renewable fossil fuels, they are formed from ancient organic matter, providing over 85% of our energy needs. However, their extraction and use pose significant environmental challenges.
Fuels
A fuel is any material burned or altered to obtain energy. Fuels release energy through chemical reactions or nuclear processes. Examples include wood, coal, and petroleum.

Natural Resources of Fuel
Natural resources are substances found in nature that are valuable in their natural form. They are categorized into:
- Inexhaustible Natural Resources: These are abundant and not depleted by use, such as sunlight and wind.

- Exhaustible Natural Resources: These are limited and can be exhausted by human activities, like coal, petroleum, and forests.
Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are energy-rich compounds formed from decomposed biomass buried under the Earth over millions of years. Key fossil fuels include coal, petroleum, and natural gas.
Coal
Coal is a black mineral formed from plant matter over about 300 million years through carbonization—a process involving high pressure, temperature, and anaerobic bacteria.
Uses of Coal
Coal is used for:
- Generating electricity
- Making coke
- Manufacturing natural gas
- Various industrial processes
Products of Coal
- Coke: A black, porous substance used as a fuel and in steel production.
- Coal Tar: A thick liquid used to manufacture synthetic dyes, drugs, explosives, and more.

- Coal Gas: A flammable gas used for heating and lighting.
Petroleum
Petroleum is a dark, viscous liquid formed from the remains of sea organisms. It is extracted through drilling and processed through refining.
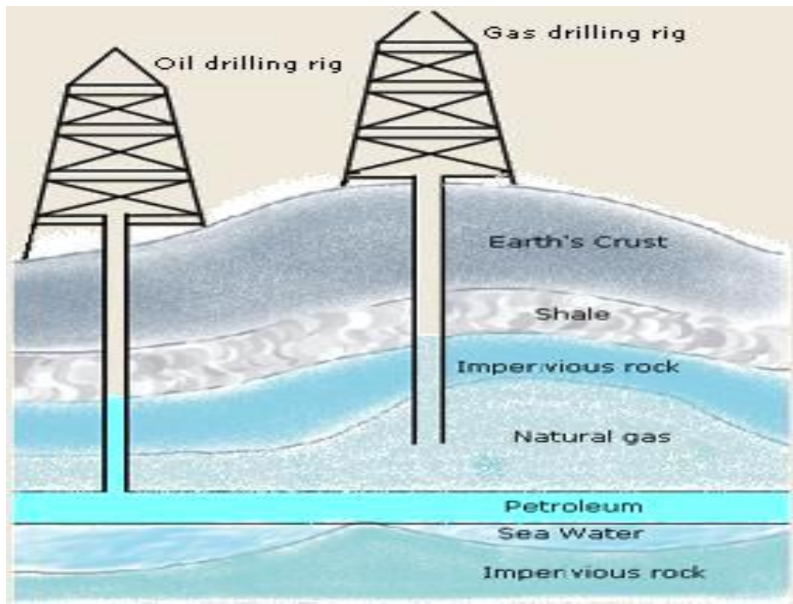
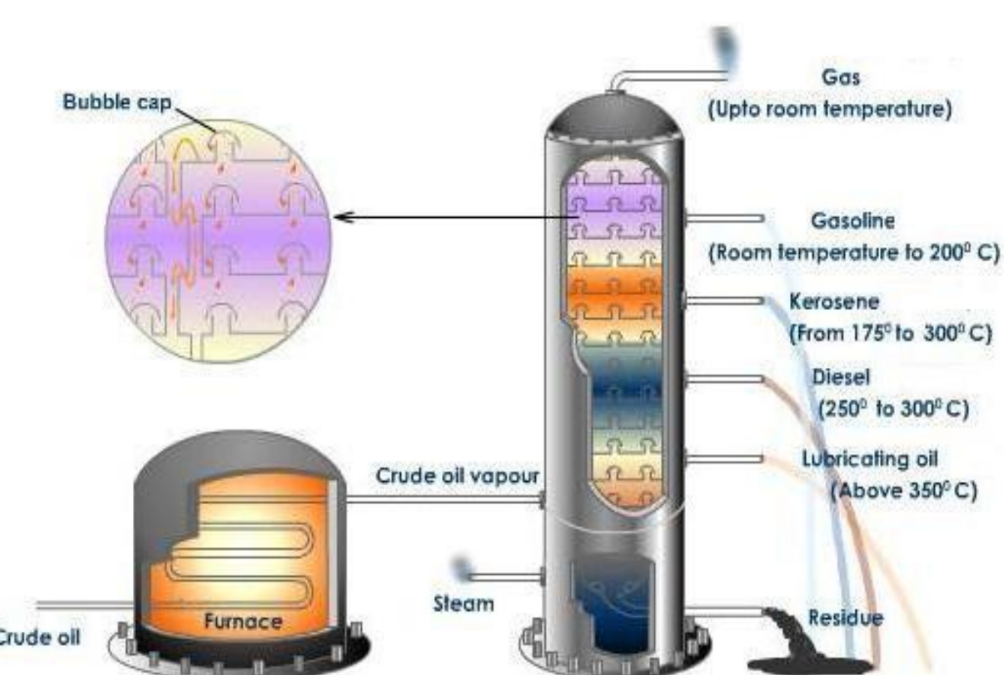
Refining of Petroleum
Petroleum refining involves heating crude oil to produce vapors, which are then separated into different fractions in a fractionating column based on boiling points.
Natural Gas
Natural gas primarily consists of methane and is used for power generation, hydrogen production, and as a cleaner fuel for transport. It is stored as compressed natural gas (CNG) for easy transportation.
Uses of Natural Gas
- Electricity generation
- Hydrogen production
- Cleaner transport fuel
- Cooking and home heating
- Manufacturing various products
Fossil Fuels are Limited
Coal and petroleum are finite resources, formed over millions of years and will last for only a few hundred more years. Their burning contributes to air pollution and global warming.
How to Save Petrol and Diesel
- Drive at a steady, moderate speed.
- Switch off engines during long waits.
- Maintain proper tire pressure.
- Regular vehicle maintenance.
This comprehensive guide on coal and petroleum highlights their significance, uses, and the environmental issues associated with fossil fuels. Understanding these aspects is crucial for managing our energy resources and mitigating environmental impacts.
Practice questions on Chapter 3 - Coal And Petroleum
Get your free Chapter 3 - Coal And Petroleum practice quiz of 20+ questions & detailed solutions
Practice Now








